
Find the factors of safety with respect to overturning, sliding, and bearing capacity failure.
Answer to Problem 15.4P
The factor of safety with respect to overturning is
The factor of safety with respect to sliding is
The factor of safety with respect to bearing capacity failure is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The cohesion
The unit weight
The friction angle
The unit weight
The cohesion
The unit weight of soil
The friction angle
The backfill angle
Calculation:
Check stability with respect to overturning.
Consider point C as the left end of the toe base as named as C.
Divide the retaining wall into section as in Figure 1.
Sketch the section of the retaining wall as shown in Figure 1.
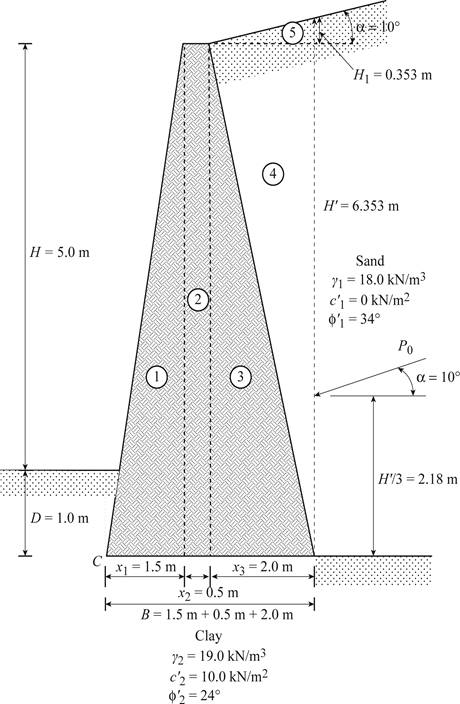
Here,
Refer Table 14.2, “Values of
Take the value of active earth pressure coefficient
Refer Figure 1.
Find the height of the inclined portion of backfill
Substitute 2 m for
Find the total height of the inclined backfill
Here, H is the height of retaining wall and D is the depth to the bottom of the base slab.
Substitute 5.0 m for H, 1.0 m for D, and 0.353 m
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the vertical component of the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the horizontal component of the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the weight of section 1
Here,
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 2
Here,
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 3
Here,
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 4
Here,
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute 108 kN/m for
Find the weight of section 5
Substitute 2 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the total moment about the point C
Substitute
Find the total vertical load
Substitute
Summarize the values of weight, moment arm from C, and moment about C as shown in Table 1.
| Section | weight | moment arm from C | moment about C |
| 1 | 108 | 1 | 108 |
| 2 | 72 | 1.75 | 126 |
| 3 | 144 | 2.67 | 384.5 |
| 4 | 108 | 3.33 | 359.6 |
| 5 | 6.35 | 3.33 | 21.15 |
| 4 | 75.56 | ||
Find the overturning moment
Substitute
Find the factor of safety
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to overturning is
Check the stability with respect to sliding.
Find the coefficient of passive earth pressure
Substitute
Find the passive earth pressure
Here,
Substitute 1 m for D,
Find the angle of friction
Substitute
Find the factor of safety against sliding
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to sliding is
Check the stability with bearing capacity failure.
Find the eccentricity (e) using the equation:
Substitute 4 m for B,
Check for eccentricity.
Substitute 0.22 m for e and 4 m for B.
The eccentricity is within the limit. Therefore, there is no tensile stress produced at the end of the steel section.
Find the maximum pressure
Substitute
Find the effective breadth
Substitute 4 m for B and 0.22 m for e.
Refer Table 16.2, “Bearing Capacity Factors” in the textbook.
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Find the depth factor
Substitute 1 m for D and 4 m for B.
Find the load (q) due the soil in front of heel using the equation:
Substitute
Find the inclination angle of vertical load
Substitute
Find the inclination factor
Substitute
Find the depth factor
Here,
Substitute
The depth factor
Find the inclination factor
Substitute
Find the ultimate bearing capacity of the shallow foundation
Substitute
Find the factor of safety against bearing capacity failure
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to bearing capacity failure is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- A silty sand sample failed during a consolidated-undrained triaxial test at F1=280 kPa andF3=170 kPa. With the assumption that c=0 and A=0.65, determine the consolidated-undrainedfriction angle Ncu and a drained friction angle N. If a consolidated-undrained test on such a soil isconducted at a confining pressure F3 =340 kPa, what will be major total and effective stresses andthe pore water pressure at failure? What will be the maximum shear stress J during a "slow" directshear test, if the vertical stress Fv=160 kPa?arrow_forwardCheck the adequacy of a 15ft long A992 W12x65 beam-column shown in figure (1). The axial loads and end moments have been obtained from 2nd order analysis of the gravity loads. The frame and loading are symmetric. Assume that (Cb) is 1.06. PD-85k, PL-220k MD-15k-ft, ML-45k-ft Le-8.6ft MD-18k-ft, ML-52kfarrow_forwardecos y dyarrow_forward
- حل ستركجرarrow_forwardSome of them are answered corretly I just need help with the ones in red thank you.arrow_forward*13-12. The control linkage for a machine consists of two L2 steel rods BE and FG, each with a diameter of 1 in. If a device at G causes the end G to freeze up and become pin connected, determine the maximum horizontal force P that could be applied to the handle without causing either of the two rods to buckle. The members are pin connected at A, B, D, E, and F. P 12 in. C G F B 2 in. E 4 in. 4 in. A D + -15 in.- + -20 in.-arrow_forward
- 13-31. The steel bar AB has a rectangular cross section. If it is pin connected at its ends, determine the maximum allowable intensity w of the distributed load that can be applied to BC without causing bar AB to buckle. Use a factor of safety with respect to buckling of 1.5. Est = 200 GPa, σy 360 MPa. = B W 5 m 3 m -20 mm 30 mm x x A 20 mm y Carrow_forwardProblem 1: A man-made 30 ft tall, 1.5:1 slope is to be build as shown in the figure. The soil is homogeneous with shear strength parameters c = 400 psf and φ = 290 . The moist unit weight of the soil is 119 pcf above the groundwater table and the saturated unit weight is 123 pcf below. Using the ordinary method of slices, compute the Factor of Safety (FS) along the trial failure surface shown. (Hint: Please note the unit weight is changing within the same slice.) Note 1: Use the same number of slices and dimensions as provided. Document ALL the calculations of weight (W) for each slice. Note 2: Document your solutions by following the same approach illustrated in the class, including a summary table showing all the variables and calculations involved in assessing FS.arrow_forwardhow to manually plotting by coordinatesarrow_forward
- mapping surveys/mappingarrow_forwardQuestion 3 (15pt) A traffic signal control is being designed for a four-leg intersection on a divided highway with the characteristics show in the table below. Determine an appropriate length of the yellow interval for each approach. (assuming the average vehicle length is 20ft, and the perception-reaction time is 1.0 sec, and deceleration rate of 11.2ft/sec²) Median width (ft) Number of 12ft lanes on each approach Design speed (mph) Grade North South approaches East West Approaches 18 3 45 0 10 2 35 3.5 SPEED LIMIT 45 18ft SPEED LIMIT 45 5arrow_forwardHi! Can you help me compute the concrete and masonry works for this structure based on the attached elevation drawing?The image shows the side view of a small building with labeled sections, wall openings (windows), and dimensions in centimeters. Specifically, I need help computing the following: For Concrete Works: Volume of concrete for footings, columns, and slab (if applicable) For Masonry Works (CHB Walls): Total wall area (excluding window openings) Number of CHBs required (based on 0.4 m x 0.2 m CHB) Cement and sand for block laying Cement, sand, and gravel for core filling (if reinforced) Cement and fine sand for plastering (both sides) Rebars needed for CHB reinforcement (if any) Please base it on the drawing dimensions. Let me know if additional assumptions or standards are needed (e.g., CHB size, mix ratio, thickness of plaster). Thank you!arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



