
Concept explainers
A small object is attached to the end of a string to form a simple pendulum. The period of its harmonic motion is measured for small
(a)
The period of motion for each length of simple pendulum.
Answer to Problem 15.44P
The period of motion for the length
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The lengths of the simple pendulum are
For the
Here,
Thus, the period for the
For the
Here,
Thus, the period for the
For the
Here,
Thus, the period for the
Conclusion:
Therefore, the period of motion for the length
(b)
The mean value of
Answer to Problem 15.44P
The mean value of
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The lengths of the simple pendulum are
The period of the oscillation of the pendulum is,
Here,
Take square on the both sides and calculate the
Substitute
Thus, the mean value of
Substitute
Thus, the mean value of
Substitute
Thus, the mean value of
Conclusion:
Therefore, the mean value of
(c)
To draw: The graph of
Answer to Problem 15.44P
The graph of
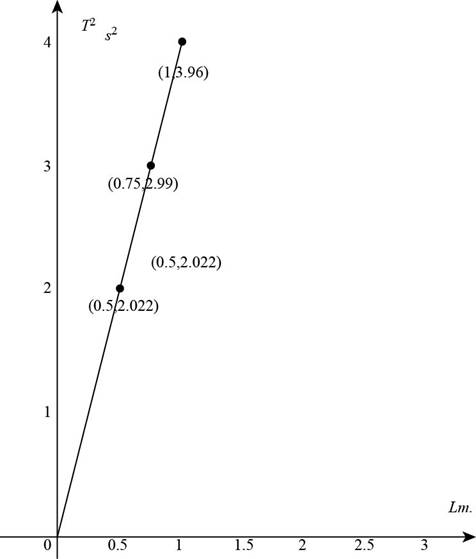
Figure (1)
The value of the
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The lengths of the simple pendulum are
In the part (a), the periods of different given length of pendulum are calculated. Make a table of square of periods
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The above table gives ordered pairs.
Take the ordered pairs from above given table and join them by a straight line and plot the graph of

Figure (1)
The Figure (1) shows the graph of
From the above graph, the slope of the line is,
Here,
Substitute
From the equation of the period of the pendulum,
The slope of
So,
(d)
The comparison of values of
Answer to Problem 15.44P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The lengths of the simple pendulum are
From part (c) the value of
Both values of
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- Can someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardIdentical rays of light enter three transparent blocks composed of different materials. Light slows down upon entering the blocks.arrow_forwardFor single-slit diffraction, calculate the first three values of (the total phase difference between rays from each edge of the slit) that produce subsidiary maxima by a) using the phasor model, b) setting dr = 0, where I is given by, I = Io (sin (10) ². 2arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





