
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
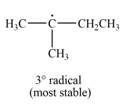
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
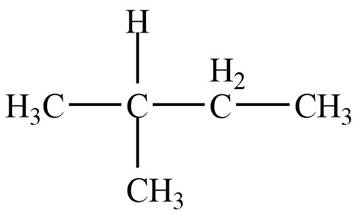
Figure 1
Three types of radicals can be formed by the cleavage of
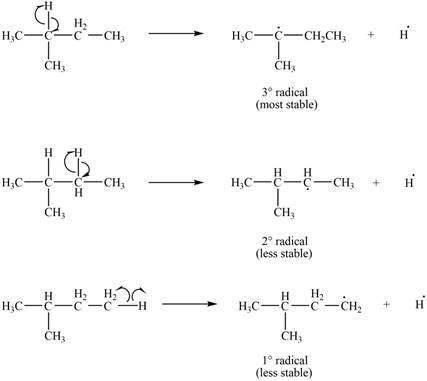
Figure 2
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(b)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
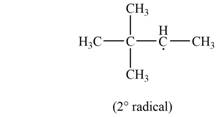
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
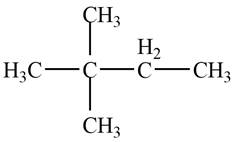
Figure 3
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
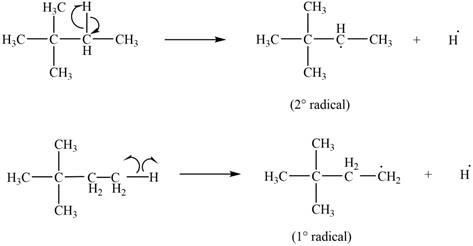
Figure 4
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(c)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can results from the cleavage of
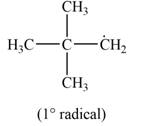
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
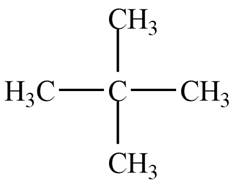
Figure 5
Only
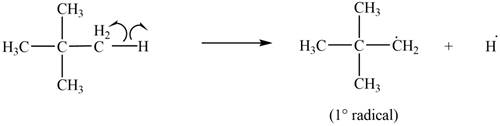
Figure 6
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
(d)
Interpretation: The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Concept introduction: A free radical is an atom or ion with unpaired electrons. They are reactive intermediates formed by the homolysis of covalent bond. Free radicals are classified as
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
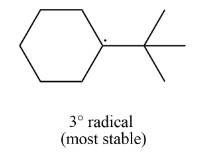
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
Figure 7
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
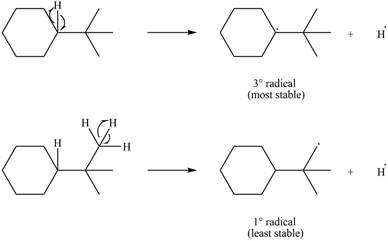
Figure 8
The number of alkyl substitutents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
The most stable radical that can result from cleavage of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Provide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forward
- If I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
