
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with
Answer to Problem 15.9P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
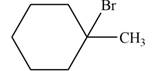
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
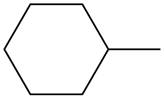
Figure 1
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
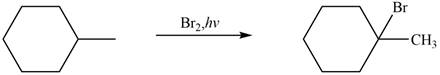
Figure 2
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(b)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.9P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
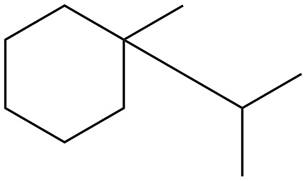
Figure 3
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
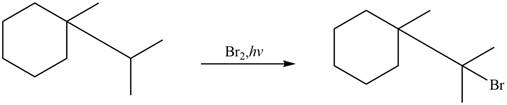
Figure 4
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(c)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.9P
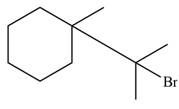
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
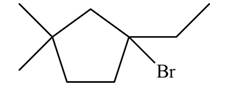
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
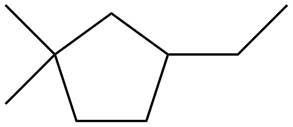
Figure 5
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
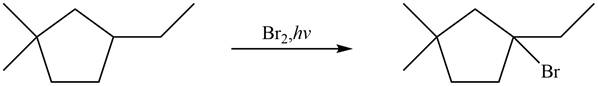
Figure 6
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(c)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.9P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
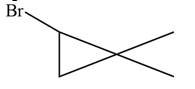
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
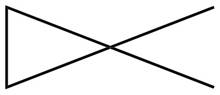
Figure 7
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
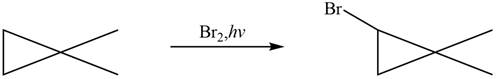
Figure 8
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the mechanism to make the alcohol 2-hexanol. Draw the Mechanism to make the alcohol 1-hexanol.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with 1-pentanal in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardIdentify each chiral carbon as either R or S. Identify the overall carbohydrates as L or Darrow_forward
- Ethers can be formed via acid-catalyzed acetal formation. Draw the mechanism for the molecule below and ethanol.arrow_forwardHOCH, H HO CH-OH OH H OH 11 CH₂OH F II OH H H 0 + H OHarrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
