
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The target molecule transformation should be draw and identified given the starting molecule of
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation Reaction: Generally alcohol can be oxidizing to aldehyde or
Reduction Reaction: This process in which any substance atoms, ion or molecule gains one or more electrons it is called reduction.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.20UKC
The hydride added to the carbonyl carbon, the polar (C=O) carbon has a partial positive charge, then the reduction process has
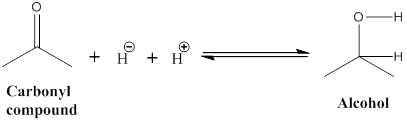
Explanation of Solution
Reduction reaction: The given carbonyl molecule is converted into alcohol (b) in this undergoes for reduction process was occurred. The hydride ion added to the carbonyl carbon, because carbonyl carbon is polar it as partial positive charges in carbon atom.
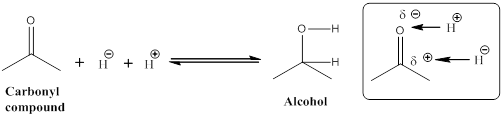
(b)
To determine give the reactions indicate which direction represents reduction and which represents oxidation.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl group: This group presence of a
Oxidation Reaction: Generally alcohol can be oxidizing to aldehyde or ketone and aldehyde can be further oxidized to carboxylic acids.
Reduction Reaction: This process in which any substance atoms, ion or molecule gains one or more electrons it is called reduction.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.20UKC
Given the arrow to the right represents reduction and the arrow to the left represents oxidation.
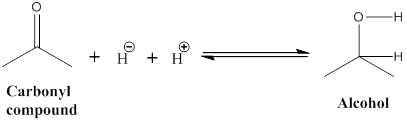
Explanation of Solution
Let us consider given reaction,
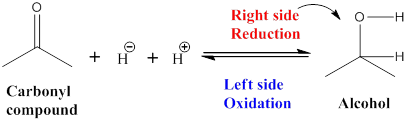
Given the arrow to the right represents reduction and the arrow to the left represents oxidation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack ... and Biological Chemistry (4th Edition)
- Which features of the curves in Figure 30-2 indicates that the enzyme is not consumed in the overall reaction? ES is lower in energy that E + S and EP is lower in energy than E + P. What does this tell you about the stability of ES versus E + S and EP versus E + P.arrow_forwardLooking at the figure 30-5 what intermolecular forces are present between the substrate and the enzyme and the substrate and cofactors.arrow_forwardprovide short answers to the followings Urgent!arrow_forward
- Pyruvate is accepted into the TCA cycle by a “feeder” reaction using the pyruvatedehydrogenase complex, resulting in acetyl-CoA and CO2. Provide a full mechanismfor this reaction utilizing the TPP cofactor. Include the roles of all cofactors.arrow_forwardB- Vitamins are converted readily into important metabolic cofactors. Deficiency inany one of them has serious side effects. a. The disease beriberi results from a vitamin B 1 (Thiamine) deficiency and ischaracterized by cardiac and neurological symptoms. One key diagnostic forthis disease is an increased level of pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate in thebloodstream. How does this vitamin deficiency lead to increased serumlevels of these factors? b. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 5 deficiency? c. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 2 /B 3 deficiency?arrow_forwardDraw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle - (Draw the Mechanism). How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forward
- Sodium fluoroacetate (FCH 2CO2Na) is a very toxic molecule that is used as rodentpoison. It is converted enzymatically to fluoroacetyl-CoA and is utilized by citratesynthase to generate (2R,3S)-fluorocitrate. The release of this product is a potentinhibitor of the next enzyme in the TCA cycle. Show the mechanism for theproduction of fluorocitrate and explain how this molecule acts as a competitiveinhibitor. Predict the effect on the concentrations of TCA intermediates.arrow_forwardIndicate for the reactions below which type of enzyme and cofactor(s) (if any) wouldbe required to catalyze each reaction shown. 1) Fru-6-P + Ery-4-P <--> GAP + Sed-7-P2) Fru-6-P + Pi <--> Fru-1,6-BP + H2O3) GTP + ADP <--> GDP + ATP4) Sed-7-P + GAP <--> Rib-5-P + Xyl-5-P5) Oxaloacetate + GTP ---> PEP + GDP + CO 26) DHAP + Ery-4-P <--> Sed-1,7-BP + H 2O7) Pyruvate + ATP + HCO3- ---> Oxaloacetate + ADP + Piarrow_forwardTPP is also utilized in transketolase reactions in the PPP. Give a mechanism for theTPP-dependent reaction between Xylulose-5-phosphate and Ribose-5-Phosphate toyield Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and Sedoheptulose-7-Phosphate.arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning





