
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The possible structures of the starting materials of the given Diels-Alder product are to be given.
Concept introduction:
In order to find the starting materials of the given compounds follows the rules are given below.
First, label the double bond carbons as
In order to complete the diene structure, eliminate the double bonds between
In order to complete the dienophile structure, add the double bonds between its carbons.
Also, dienophile is substituted with electron withdrawing groups.
Answer to Problem 15.20P
The possible structures of starting materials of given compound can be as follows.
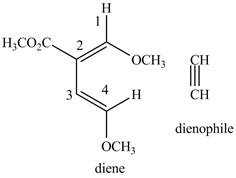
Explanation of Solution
First designate the double bond carbon atoms as
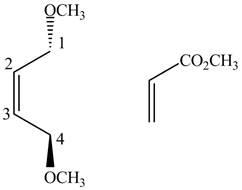
Figure 1
In order to complete the structure of diene, remove the double bonds present between carbons
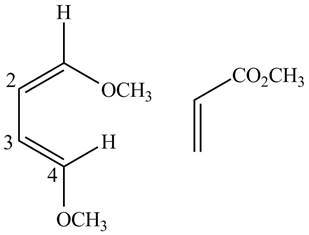
Figure 2
Finally, complete the dienophile structure by adding the double bonds between carbons.
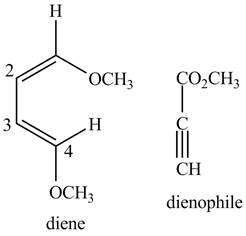
Figure 3
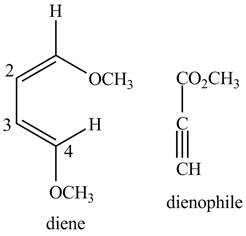
Similarly, second possibility on the basis of above mentioned steps will be as follows.
First designate the double bond carbons as
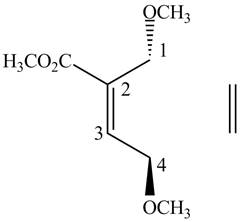
Figure 4
In order to complete the structure of diene, remove the double bonds present between carbons
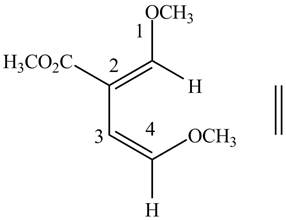
Figure 5
Finally, complete the dienophile structure by adding the double bonds between carbons
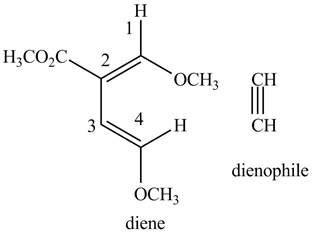
Figure 6
The possible starting materials of the given compound are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
The possible structures of the starting materials of the given Diels-Alder product are to be given.
Concept introduction:
First, label the double bond carbons as
In order to complete the diene structure, eliminate the double bonds between
In order to complete the dienophile structure, add the double bonds between its carbons.
Also, dienophile is substituted with electron withdrawing groups.
Answer to Problem 15.20P
The possible structures of starting materials of given compound are shown below.
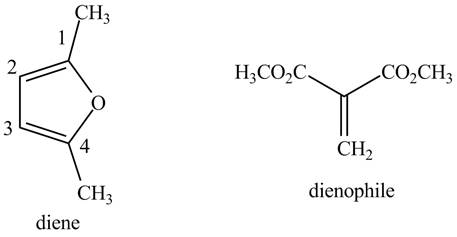
Explanation of Solution
First designate the double bond carbons as
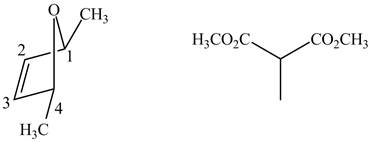
Figure 7
In order to complete the structure of diene, remove the double bonds present between carbons
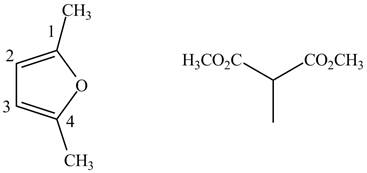
Figure 8
Finally, complete the dienophile structure by adding the double bonds between carbon atoms.
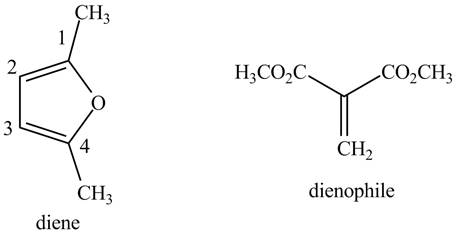
Figure 9
The possible starting materials of given compound are shown in Figure 9.
(c)
Interpretation:
The possible structures of the starting materials of the given Diels-Alder product are to be given.
Concept introduction:
First, label the double bond carbons as
In order to complete the diene structure, eliminate the double bonds between
In order to complete the dienophile structure, add the double bonds between its carbons.
Also, dienophile is substituted with electron withdrawing groups.
Answer to Problem 15.20P
The possible structures of starting materials of given compound are as follows.
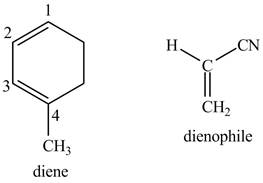
Explanation of Solution
First designate the double bond carbons as
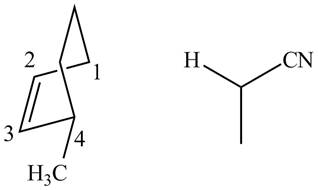
Figure 10
In order to complete the structure of diene, remove the double bonds present between carbons
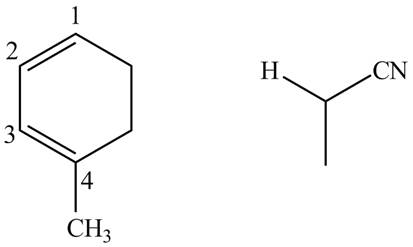
Figure 11
Finally, complete the dienophile structure by adding the double bonds between carbons.
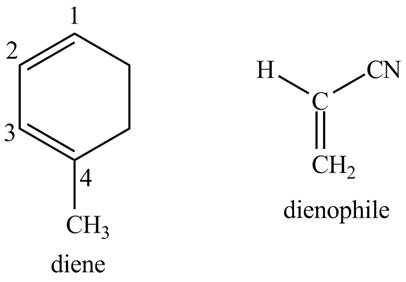
Figure 12
The possible starting materials of given compound are shown in Figure 12.
(d)
Interpretation:
The possible structures of the starting materials of the given Diels-Alder product are to be given.
Concept introduction:
First, label the double bond carbons as
In order to complete the diene structure, eliminate the double bonds between
In order to complete the dienophile structure, add the double bonds between its carbons.
Also, dienophile is substituted with electron withdrawing groups.
Answer to Problem 15.20P
The possible structures of starting materials of given compound are as follows.
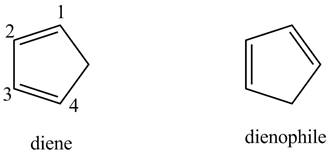
Explanation of Solution
First designate the double bond carbons as
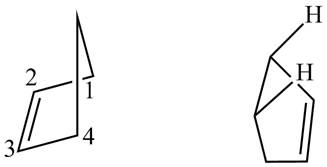
Figure 13
In order to complete the structure of diene, remove the double bonds present between carbons

Figure 14
Finally, complete the dienophile structure by adding the double bonds between carbons.
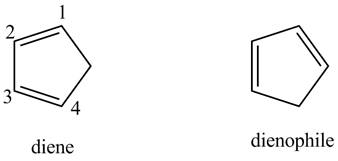
Figure 15
The possible starting materials of given compound are shown in 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE AND S
- - Consider the data in the Table below to answer the following questions: Acidities of Substituted Benzoic and Acetic Acids pk,s at 25C Y-CH COOH Y Y - CH₂COOH meta para H 4.75 4.19 4.19 2.47 3.64 3.55 3.57 4.09 4.46 CN OCH 3 A. Draw the structure of the strongest acid in the table above. B. Explain why cyanoacetic acid and methoxyacetic acid are more acidic than their correspondingly substituted benzoic acid counterparts.arrow_forwardDraw the curved arrow mechanism for this reaction starting with 2-propanol in sulfuric acid. Show all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonded electrons in each step. Species not involved in a particular step do not need to be included in that step, and resonance forms do not need to be shown. Note that the alcohol is in much higher concentration than H₂O in this reaction. Harrow_forwardProvide reactions showing the following conversions: * see imagearrow_forward
- . Draw structures corresponding to each of the following names or Provide IUPAC names for each of the ollowing structures [for 4 ONLY]. A. 2-propylpentanoic acid. B. m-chlorobenzoic acid. D. C. O O HOC(CH2)3COH glutaricadd OH OH H3C CH3 C=C H COOH salicylicadd tiglicadd CH₂C=N Joe Marrow_forward. Provide structure(s) for the starting material(s), reagent(s) or the major organic product(s) of each of the ollowing reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [five only] A. O B. OET CH3 1. LIAIH, ether 2 H₂O O (CH3)2CH-C-CI + 0 0 ether (CH3)2CH-C-O-C-CH3 CH3 C. 0 OH HO CH3 ° Clarrow_forwardHow would you prepare each of the following compounds using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or a alonic ester synthesis? Show all intermediate structures and all reagents.[Three only] A. B. COOH OH C. D. 0 H2C CHCH2CH2CCH3arrow_forward
- Fats and greases have mostly aliphatic regions which are hydrophobic. Provide a schematic of howsoaps/detergents remove fats and grease from the soiled material. * see imagearrow_forwardWhat chemical has the common name "lye"? Pick one of the 3 esters and show the hydrolysis mechanism to make a carboxylic acid. The organic “R” should be used to limit the redrawing time of the entire molecule. * see imagearrow_forwardProvide the products for each reaction. There are two and they are not related. *see imagearrow_forward
- d. a phenylal Give the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all levant stereochemistry. [three only] 0 A. B. CH3 Bra CH3COOH OH 1. Br₂, PBrz 2 H₂O 12arrow_forward2arrow_forwardShow how the following conversions might be accomplished. Show all reagents and all intermediate ructures. More than one step may be required [2 ONLY]: A. B. ° C. OH 0 OH 0arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





