
Concept explainers
Single-rate method, budgeted versus actual costs and quantities. Chocolat Inc. is a producer of premium chocolate based in Palo Alto. The company has a separate division for each of its two products: dark chocolate and milk chocolate. Chocolat purchases ingredients from Wisconsin for its dark chocolate division and from Louisiana for its milk chocolate division. Both locations are the same distance from Chocolat’s Palo Alto plant.
Chocolat Inc. operates a fleet of trucks as a cost center that charges the divisions for variable costs (drivers and fuel) and fixed costs (vehicle depreciation, insurance, and registration fees) of operating the fleet. Each division is evaluated on the basis of its operating income. For 2017, the trucking fleet had a practical capacity of 50 round-trips between the Palo Alto plant and the two suppliers. It recorded the following information:
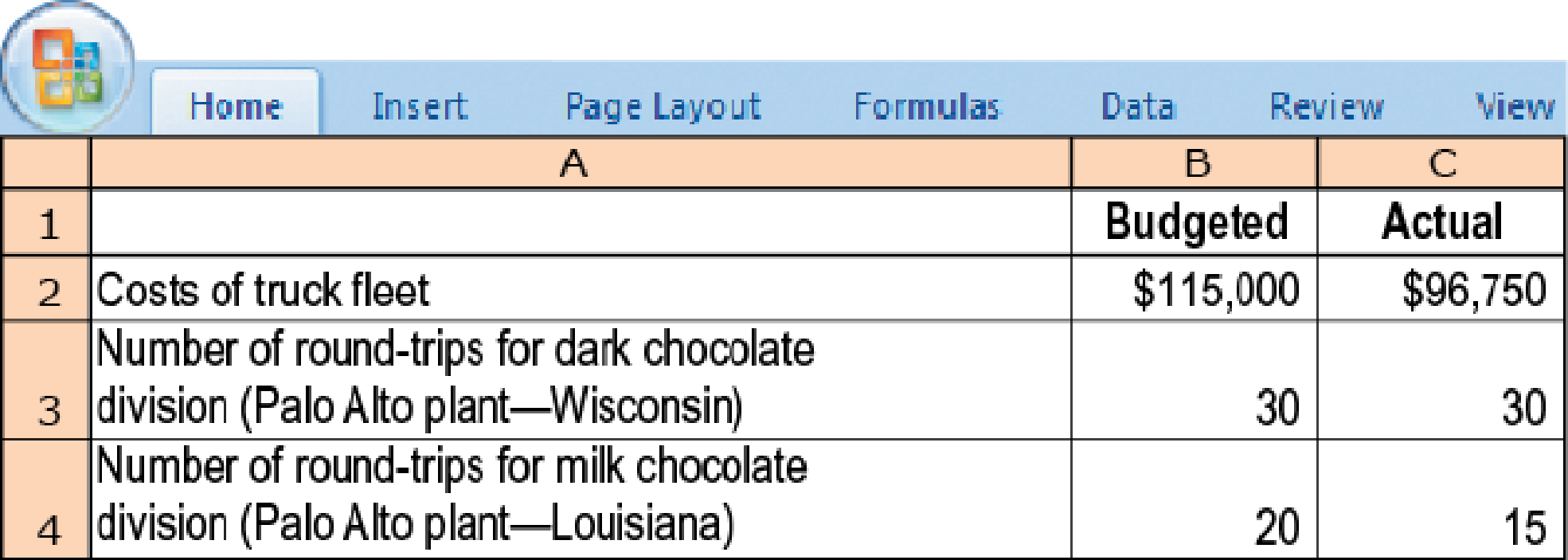
- 1. Using the single-rate method, allocate costs to the dark chocolate division and the milk chocolate division in these three ways.
- a. Calculate the budgeted rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on round-trips budgeted for each division.
- b. Calculate the budgeted rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on actual round-trips used by each division.
- c. Calculate the actual rate per round-trip and allocate costs based on actual round-trips used by each division.
- 2. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using each of the three methods in requirement 1. Would you encourage Chocolat Inc. to use one of these methods? Explain and indicate any assumptions you made.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING
- Accountingarrow_forwardExpress Delivery Company (EDC) is considering outsourcing its Payroll Department to a payroll processing company for an annual fee of $220,800. An internally prepared report summarizes the Payroll Department’s annual operating costs as follows: Supplies $ 30,800 Payroll clerks’ salaries 120,800 Payroll supervisor’s salary 58,800 Payroll employee training expenses 10,800 Depreciation of equipment 20,800 Allocated share of common building operating costs 15,800 Allocated share of common administrative overhead 28,800 Total annual operating cost $ 286,600 EDC currently rents overflow office space for $36,800 per year. If the company closes its Payroll Department, the employees occupying the rented office space could be brought in-house and the lease agreement on the rented space could be terminated with no penalty. If the Payroll Department is outsourced the payroll clerks will not be retained; however, the supervisor would be transferred to the company’s Human…arrow_forwardThalassines Kataskeves, S.A., of Greece makes marine equipment. The company has been experiencing losses on its bilge pump product line for several years. The most recent quarterly contribution format income statement for the bilge pump follows: Thalassines Kataskeves, S.A. Income Statement—Bilge Pump For the Quarter Ended March 31 Sales $ 410,000 Variable expenses: Variable manufacturing expenses $ 123,000 Sales commissions 50,000 Shipping 21,000 Total variable expenses 194,000 Contribution margin 216,000 Fixed expenses: Advertising (for the bilge pump product line) 27,000 Depreciation of equipment (no resale value) 120,000 General factory overhead 38,000* Salary of product-line manager 113,000 Insurance on inventories 5,000 Purchasing department 49,000† Total fixed expenses 352,000 Net operating loss $ (136,000) *Common costs allocated on the basis of machine-hours. †Common costs allocated on the basis of…arrow_forward
- Carichem Company produces sanitation products after processing specialized chemicals. The following relates to its activities: 1 Kilogram of chemicals purchased for $4000 and with an additional $2000 is processed into 400 grams of Crystals and 80 litres of a Cleaning agent. At split-off, a gram of Crystal can be sold for $2 and the Cleaning agent can be sold for $8 per litre. At an additional cost of $800, Carichem can process the 400 grams of Crystal into 500 grams of Detergent that can be sold for $4 per gram. The 80 litres of Cleaning agent is packaged at an additional cost of $600 and made into 200 packs of Softener that can be sold for $4 per pack. Required: 1. Allocate the joint cost to the Detergent and the Softener using the following: a. Sales value at split-off method b. NRV method 2. Should Carichem have processed each of the products further? What effect does the allocation method have on this decision?arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardKindly help me with accounting questionsarrow_forward
- Don't use ai given answer accounting questionsarrow_forwardPlease provide correct solution this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardAllocate the two support departments’ costs to the two operating departments using the following methods: a. Direct method b. Step-down method (allocate HR first) c. Step-down method (allocate IS first) d. The Algebraic method.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
