
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
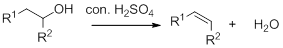
Alcohol on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
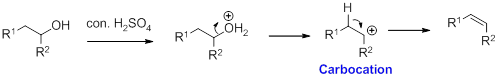
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
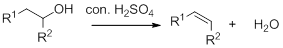
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
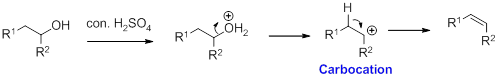
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
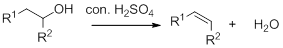
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
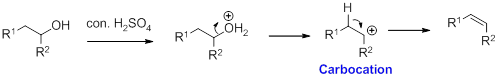
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Pearson eText Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- You have isolated a protein and determined that the native molecular weight of the holoenzyme is 160 kD using size exclusion chromatography. Analysis of this protein using SDS-PAGE revealed 2 bands, one at 100 kD and one at 30 kD. Describe the architecture of the polypeptide component of this enzyme.arrow_forwardIn a cell free preparation of beta-lactamase, penicillin is hydrolyzed in a D2O enriched assay. After one round of catalysis, where would you anticipate finding Deuterium? please help thank youarrow_forwardTo map the active site of -lactamase, the enzyme was hydrolyzed with trypsin to yield a hexapeptide (P1) with the following amino acids. Glu, Lys, Leu, Phe, Met, and Ser. Treatment of P1 with phenyl isothiocyanate yielded a PTH derivative of phenylalanine and a peptide (P2). Treatment of P1 with cyanogenbromide gave an acidic tetrapeptide (P3) and a dipeptide (P4).Treatment of P2 with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, followed by complete hydrolysis, yields N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-Glu. P1, P2, and P3 contain the active site serine. question: the b-lactamase hydrolyzes the lactam-ring in antibiotics like penicillin. Describe the mechanism, of hydrolysis, insuring to include the involvement of S, D, and K in the reaction sequence. Please help!arrow_forward
- Three of these amino acids participate in the proteolytic hydrolysis of polypeptides. Show the charge-relay network generated by the serine proteases and identify the nucleophilic species that initiates the hydrolysis. please help!arrow_forwardYou have isolated a protein and determined that the native molecular weight of the holoenzyme is 160 kD using size exclusion chromatography. Analysis of this protein using SDS-PAGE revealed 2 bands, one at 100 kD and one at 30 kD. 1. Describe the architecture of the polypeptide component of this enzyme. 2. The enzyme was found to be 0.829% NAD (by weight). What further can be said regarding the architecture? can you please help me with question number 2arrow_forwardTo map the active site of -lactamase, the enzyme was hydrolyzed with trypsin to yield a hexapeptide (P1) with the following amino acids. Glu, Lys, Leu, Phe, Met, and Ser. Treatment of P1 with phenyl isothiocyanate yielded a PTH derivative of phenylalanine and a peptide (P2). Treatment of P1 with cyanogenbromide gave an acidic tetrapeptide (P3) and a dipeptide (P4).Treatment of P2 with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, followed by complete hydrolysis, yields N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-Glu. P1, P2, and P3 contain the active site serine. Question: although S, K, and D are involved in the catalysis, the E in this hexapeptide does not participate in the hydrolysis of the b-lactam ring. Why is that?arrow_forward
- To map the active site of beta-lactamase, the enzyme was hydrolyzed with trypsin to yield a hexapeptide (P1) with the following amino acids. Glu, Lys, Leu, Phe, Met, and Ser. a) Using the experimental results described below deduce the primary sequence of the active site hexapeptide. Treatment of P1 with phenyl isothiocyanate yielded a PTH derivative of phenylalanine and a peptide (P2). Treatment of P1 with cyanogenbromide gave an acidic tetrapeptide (P3) and a dipeptide (P4).Treatment of P2 with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, followed by complete hydrolysis, yields N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-Glu. P1, P2, and P3 contain the active site serine. please help!arrow_forwardThe beta-lactamase hydrolyzes the lactam-ring in penicillin. Describe the mechanism of hydrolysis, insuring to include the involvement of S, D, & K in the reaction sequence. Please helparrow_forwardTo map the active site of beta-lactamase, the enzyme was hydrolyzed with trypsin to yield a hexapeptide (P1) with the following amino acids. Glu, Lys, Leu, Phe, Met, and Ser. Treatment of P1 with phenyl isothiocyanate yielded a PTH derivative of phenylalanine and a peptide (P2). Treatment of P1 with cyanogenbromide gave an acidic tetrapeptide (P3) and a dipeptide (P4).Treatment of P2 with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, followed by complete hydrolysis, yields N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-Glu. P1, P2, and P3 contain the active site serine. Why doesn't D in this hexapeptide not participate in the hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring even though S, K, and D are involved in the catalyst?arrow_forward
- To map the active site of -lactamase, the enzyme was hydrolyzed with trypsin to yield a hexapeptide (P1) with the following amino acids. Glu, Lys, Leu, Phe, Met, and Ser. Treatment of P1 with phenyl isothiocyanate yielded a PTH derivative of phenylalanine and a peptide (P2). Treatment of P1 with cyanogenbromide gave an acidic tetrapeptide (P3) and a dipeptide (P4).Treatment of P2 with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, followed by complete hydrolysis, yields N-2,4-dinitrophenyl-Glu. P1, P2, and P3 contain the active site serine. Using the experimental results described above derive the primary sequence of the active site hexapeptide. Please help!arrow_forwardWhich type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward+NH+ CO₂ +P H₂N + ATP H₂N NH₂ +ADParrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax CollegeEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax CollegeEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage





