
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.2, Problem 14.5P
Using bolts of the same material and cross-sectional area, two possible attachments for a cylinder head are shown. Compare the strain energy developed in each case, and then explain which design is better for resisting an axial shock or impact load.
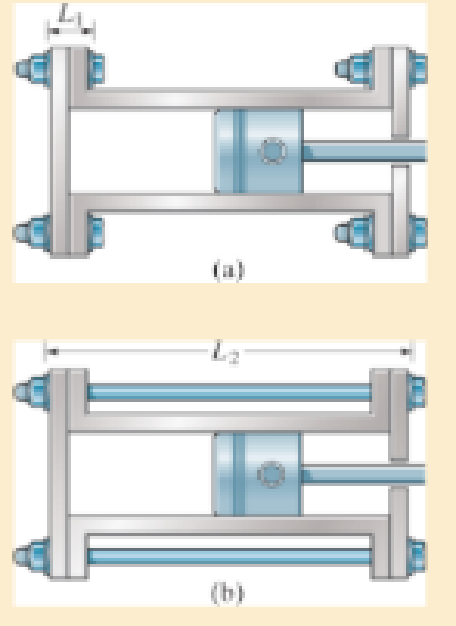
Prob. 14–5
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I really don't know how to approach this problem i've tried approaching it with some of the torsional stress equations I know but i'm comming up with awnsers that don't make any sence can you please help me with this?
I tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?
Q3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel
at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products
of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW.
Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 14.2 - A material is subjected to a general state of...Ch. 14.2 - The strain-energy density for plane stress must be...Ch. 14.2 - The A-36 steel bar consists of two segments, one...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the torsional strain energy in the A992...Ch. 14.2 - Using bolts of the same material and...Ch. 14.2 - If P = 60 kN, determine the total strain energy...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the maximum force P and the...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the torsional strain energy in the A992...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the torsional strain energy in the A-36...Ch. 14.2 - The shaft assembly is fixed at C. The hollow...
Ch. 14.2 - Determine the total axial and bending strain...Ch. 14.2 - If P = 10 kip, determine the total strain energy...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the maximum force P and the...Ch. 14.2 - Consider the thin-walled tube of Fig.5-26 . Use...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the A992...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the beam....Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.17PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.18PCh. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the 2-in...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the total strain energy in the steel...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the beam....Ch. 14.2 - The bolt has a diameter of 10 mm, and the arm AB...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the bending strain energy in the simply...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint D. AE...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint C....Ch. 14.3 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint A....Ch. 14.3 - AE is constant. Prob. 1428Ch. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of point C of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of end B of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of point S on...Ch. 14.3 - EI is constant. Prob. 1432Ch. 14.3 - The A992 steel bars are pin connected at C and D....Ch. 14.3 - The A992 steel bars are pin connected at C. If...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the slope of the beam at the pin support...Ch. 14.3 - The cantilevered beam has a rectangular...Ch. 14.3 - The rod has a circular cross section with a moment...Ch. 14.3 - The rod has a circular cross section with a moment...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of point B on...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.40PCh. 14.3 - Determine the vertical displacement of end B of...Ch. 14.4 - A bar is 4 m long and has a diameter of 30 mm....Ch. 14.4 - Determine the diameter of a red brass C83400 bar...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 14.44PCh. 14.4 - The collar has a weight of 50 lb and falls down...Ch. 14.4 - The collar has a weight of 50 lb and falls down...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 14.47PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 14.48PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 14.49PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 14.50PCh. 14.4 - The A-36 steel bolt is required to absorb the...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.4 - The composite aluminum 2014T6 bar is made from two...Ch. 14.4 - The composite aluminum 2014-T6 bar is made from...Ch. 14.4 - When the 100-lb block is at h = 3 ft above the...Ch. 14.4 - If the bar has a diameter of 20 mm, determine the...Ch. 14.4 - The collar has a mass of 5 kg and falls dawn the...Ch. 14.4 - The tugboat has a weight of 120 000 lb and is...Ch. 14.4 - The W10 12 beam is made from A-36 steel and is...Ch. 14.4 - The weight of 175 lb is dropped from a height of 4...Ch. 14.4 - The weight of 175 lb, is dropped from a height of...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the maximum height h from which an 80-lb...Ch. 14.4 - The 80-lb weight is dropped from rest at a height...Ch. 14.4 - The 75-lb block has a downward velocity of 2 ft/s...Ch. 14.4 - The 75-lb block has a downward velocity of 2 ft/s...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.4 - The overhang beam is made of 2014T6 aluminum....Ch. 14.4 - If the beam is a W1015, determine the maximum...Ch. 14.4 - If the maximum allowable bending stress for the...Ch. 14.4 - A 40-lb weight is dropped from a height of h = 2...Ch. 14.4 - The car bumper is made of...Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint A....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint B....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint B....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint B....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint E....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint B....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint B....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint B...Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint C of...Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint C....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint D....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the vertical displacement of joint A....Ch. 14.6 - The truss is made from A992 steel rods having a...Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint D....Ch. 14.6 - Determine the horizontal displacement of joint E....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at point C. El is...Ch. 14.7 - The beam is made of southern pine for which Ep =...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at point C. El is...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at point C. El is constant....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at point A. El is constant....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement of point C of the beam...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at B of the beam made from...Ch. 14.7 - The beam is made of Douglas fir. Determine the...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at pulley B. The A992...Ch. 14.7 - The A992 steel beam has a moment of inertia of I =...Ch. 14.7 - The A992 steel beam has a moment of inertia of I =...Ch. 14.7 - The A992 structural steel beam has a moment of...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at point C of the...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at A of the shaft. El is...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope of end C of the overhang beam....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement of point D of the...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at A of the 2014T6 aluminum...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 14.105PCh. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at point C of the W14 ...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at A of the W14 26 beam made...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at A. El is constant. Prob....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope at C of the overhang white...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the displacement at point D of the...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the maximum deflection of the beam...Ch. 14.7 - The beam is made of oak, for which Eo = 11 GPa....Ch. 14.7 - Determine the slope of the shaft at the bearing...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 14.7 - Beam AB has a square cross section of 100 mm by...Ch. 14.7 - Beam AB has a square cross section of 100 mm by...Ch. 14.7 - Bar ABC has a rectangular cross section of 300 mm...Ch. 14.7 - Bar ABC has a rectangular cross section of 300 mm...Ch. 14.7 - The L-shaped frame is made from two segments, each...Ch. 14.7 - The L-shaped frame is made from two segments, each...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the vertical displacement of the ring at...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the horizontal displacement at the...Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1473 using Castiglianos theorem. 1473....Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1474 using Castiglianos theorem. 1474....Ch. 14.9 - Prob. 14.125PCh. 14.9 - Prob. 14.126PCh. 14.9 - Prob. 14.127PCh. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1478 using Castiglianos theorem. 1478....Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1481 using Castiglianos theorem. 1481....Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1482 using Castiglianos theorem. 1482....Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1485 using Castiglianos theorem. 1485....Ch. 14.9 - Solve Prob. 1486 using Castiglianos theorem. 1486....Ch. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 1490 using Castiglianos theorem. 1490....Ch. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 1491 using Castiglianos theorem. 1491....Ch. 14.10 - Prob. 14.135PCh. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 1493 using Castiglianos theorem. 1493....Ch. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 1495 using Castiglianos theorem. 1495....Ch. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 1496 using Castiglianos theorem. 1496....Ch. 14.10 - Prob. 14.139PCh. 14.10 - Prob. 14.140PCh. 14.10 - Prob. 14.141PCh. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 14119 using Castiglianos theorem....Ch. 14.10 - Prob. 14.143PCh. 14.10 - Solve Prob. 14105 using Castiglianos theorem....Ch. 14 - A = 2300 mm2, I = 9.5(106) mm4. R141Ch. 14 - If the spring at B has a stiffness k = 200 kN/m....Ch. 14 - The spring at B has a stiffness k = 200 kN/m....Ch. 14 - If they each have a diameter of 30 mm, determine...Ch. 14 - and a length of 10 in. It is struck by a hammer...Ch. 14 - Determine the total axial and bending strain...Ch. 14 - The truss is made from A992 steel rods each having...Ch. 14 - The truss is made from A992 steel rods each having...Ch. 14 - El is constant. Use the method of virtual work....Ch. 14 - using Castiglianos theorem. R149. The cantilevered...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What are the design issues for character string types?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward(Read Question)arrow_forwardIn figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward
- (Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forward
- Problem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forward
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Material Properties 101; Author: Real Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHZALtqAjeM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY