
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.1, Problem 14.9P
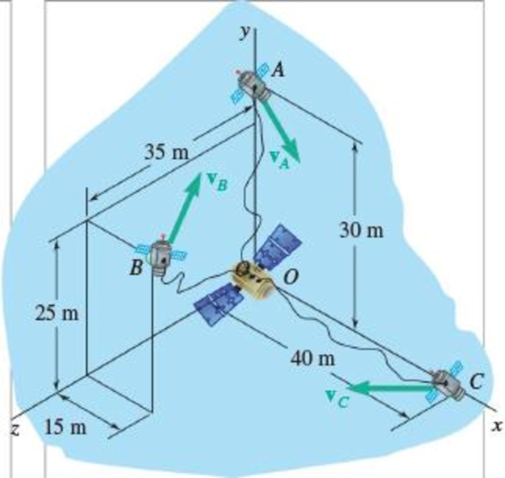
A 20-kg base satellite deploys three sub-satellites, each of which has its own thrust capabilities, to perform research on tether propulsion. The masses of sub-satellites A, B, and C are 4 kg, 6 kg, and 8 kg, respectively, and their velocities expressed in m/s are given by vA = 4i − 2j + 2k, vB = i + 4j, vC = 2i + 2j + 4k. At the instant shown, what is the angular momentum HO of the system about the base satellite?
Fig. P14.9 and P14.10
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How can you define impulsive force in terms of momentum.
The resistance to motion is
given by
R, = (0.011 + 0.000 06 V) Mg
+ 0.028 AV²
%3D
where M is the mass in kg, V is the velocity in
km/h and A is the frontal area in m².
A jeep of 1400 kg mass and 2.4-m² frontal
area is used to pull a trailor with a gross mass of
800 kg at 50 km/h in top gear on level road. If the
jeep is capable of developing 40 kW of power for
propulsion, find whether it is adequate for the
job. The transmission efficiency may be taken as
92%. Also, find the pull on the coupling at this
speed.
If all the power is used by the loading trailor,
determine the pull in the coupling at 50 km/h
and the load put on the trailor.
7. Two carts with masses of 4.0 kg and 3.3 kg move toward each other on a frictionless
track with speeds of 5.9 m/s and 4.6 m/s, respectively. The carts stick together after
colliding head-on. Find their final speed.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.3PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.4PCh. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9, assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.19PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.20PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.21PCh. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.23PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.24PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.25PCh. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation HO=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.28PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA, where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.32PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.33PCh. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.35PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.36PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14.2 - 14.38 Two hemispheres arc held together by a cord...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14.2 - 14.41 and 14.42 In a game of pool, ball A is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.49PCh. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, and C, each of mass m,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.51PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.55PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.56PCh. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of = 1000 kg/m3...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.59PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.60PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.61PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.62PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.64PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.67PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.69PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.70PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.71PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.73PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.74PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.78PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.79PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.80PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.81PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.82PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.83PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.84PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.85PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.86PCh. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.88PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.89PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.90PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.91PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.92PCh. 14.3 - A rocket sled burns fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.94PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.95PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.96PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.97PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.98PCh. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb, including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.102PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.103PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.106RPCh. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.108RPCh. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.110RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.111RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.112RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.113RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.114RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.115RPCh. 14 - A chain of length l and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The 3.55 kg collar shown below is attached to a spring and released from rest at A. The collar then travels downward a distance of y = 2.10 m. The spring has a spring constant of k = 23.5 N/m. The distance a is given as 1.20 m. The datum for gravitational potential energy is set at the horizontal line through A and B.( Figure 1) Figure A TIarrow_forward1. A block with a mass of 1kg is initially at rest while held in contact with a compressed spring. The spring has a stiffness constant of 1000 N/m and is initially compressed by a length of 0.3 meters. Once the mass leaves the spring it will slide 1 meter across the surface of a table where u, = 0.2 is the coefficient of kinetic friction. There are no frictional losses while the mass is in contact with the spring, and there are no losses due to air resistance. Only losses are due to the interaction with the table during the 1-meter slide. The surface of the table is 2 meters above the floor. What is the speed of the mass just before it hits the floor? mass leaves spring 1 meterarrow_forwardA5.2 kg object, initially at rest, is acted on by a net external force in a straight line described by F = Fo - (1-e-0.2 ) where F = 16 N and t is in %D seconds. What is the magnitude of the momentum of the object after 9.2 s has elapsed fromt= 0? Number Units What is the work of the net external force over the same duration? Number Unitsarrow_forward
- A 0.515-oz model rocket is launched vertically from rest at time t = 0 with a constant thrust of 0.9 lb for 0.3 s and no thrust for t > 0.3 s. Neglect air resistance and the decrease in mass of the rocket. Determine the time required to reach this maximum height. The time required to reach this maximum height is ____s.arrow_forwardA system consists of three identical 19.32-lb particles A, B, and C. The velocities of the particles are, respectively, VA = VAI, VB=vgi, and vC= vck, and the magnitude of the linear momentum L of the system is 10 lb-s. VC B H 2 ft A 2 ft 1 ft VB The velocities of the particles are: VA= ft/s) j VB= ft/s) i VC= ft/s) k 3 ft 4 ft Knowing that HG=Ho, where HG is the angular momentum of the system about its mass center G and Ho is the angular momentum of the system about O, determine the velocities of the particles. (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.)arrow_forward5 8 ✓ 11 ✓ Q4. As shown in the image below, a 112-kg crate starts sliding down the inclined plane from rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the inclined plane is = 0.22. Take g = 9.81 m/s². k = 2 kN/m 10 m 45° (1) Apply the principle of work and energy to determine the speed (in the unit of m/s) of the crate when it has slid down 10 m, just before it reaches the spring. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point.arrow_forward
- A 60kg woman holds a 9kg package as she stands within an elevator that briefly accelerates upward at a rate of 1/4 of the acceleration due to gravity. The elevator starts from rest. a. If the elevator cables ruptured and the elevator starts to freely fall, determine the force exerted by the elevator on the woman. b. Determine the work done by the elevator on the woman carrying a package in 3 seconds. c. Determine the power supplied by the elevator on the woman carrying a package at t = 3 seconds. d. Determine the work done by gravity on the woman carrying a package in 3 seconds.arrow_forwardA 1-lb stone is dropped down the “bottomless pit” at Carlsbad Caverns and strikes the ground with a speed of 108 ft/s. Neglecting air resistance, determine the kinetic energy of the stone as it strikes the ground and the height h from which it was dropped. The kinetic energy of the stone is ____ft·lb. The height from which the stone was dropped is ___ft.arrow_forwardQ2: Sphere A collides with B as shown. If the coefficient of restitution is e = 0.5, determine the velocities of the two balls after impact if the velocities and masses of sphere A&B before impact are (ma= 10 kg, ms = 1 kg, vA= 2 m/sec, Us= 10 m/sec) respectively. "g- m/s kg /30 m2 mi kg A m/sarrow_forward
- A 2.50-kg textbook is forced against a horizontal spring of negligible mass and force constant 250 N/m, compressing the spring a distance of 0.250 m. When released, the textbook slides on a horizontal tabletop with coefficient of kinetic friction μk=0.30\mu k = 0.30μk=0.30. Use the work–energy theorem to find how far the text-book moves from its initial position before it comes to rest.arrow_forward6. For a satellite cruising in a circular orbit at an altitude of 500 km, determine the period of revolution, the flight speed, and the energy expended to bring a unit mass into this orbit. Answers: 1.58 hr, 7613 m/sec, 33.5 MJ/kg.arrow_forwardA small fixed‐wing RC UAV with a mass of 3kg is equipped with a pack of Li─Po (Lithium Polymer) batteries for its electric motor. If the energy of batteries is just con- sumed in a loiter mission (for electric motor), for a maximum endurance of 40min- utes, determine the mass of batteries pack. Assume that the electric motor is creating 6 N of thrust, with a prop efficiency of 0.77, and the UAV is flying at a speed of 40 m/s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY