
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 64P
GO In Fig. 14-49, water flows through a horizontal pipe and then out into the atmosphere at a speed v1 = 15 m/s. The diameters of the left and right sections of the pipe are 5.0 cm and 5.0 cm. (a) What volume of water flows into the atmosphere during a 10 min period? In the left section of the pipe, what are (b) the speed v2 and (c) the gauge pressure?
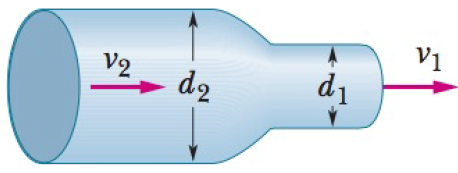
Figure 14-49 Problem 64.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
Consider the situation in the figure below; a neutral conducting ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating string, and a charged insulating rod is going to be placed nearby.
A. First, if the rod was not there, what statement best describes the charge distribution of the ball?
1) Since it is a conductor, all the charges are on the outside of the ball. 2) The ball is neutral, so it has no positive or negative charges anywhere. 3) The positive and negative charges are separated from each other, but we don't know what direction the ball is polarized. 4) The positive and negative charges are evenly distributed everywhere in the ball.
B. Now, when the rod is moved close to the ball, what happens to the charges on the ball?
1) There is a separation of charges in the ball; the side closer to the rod becomes positively charged, and the opposite side becomes negatively charged. 2) Negative charge is drawn from the ground (via the string), so the ball acquires a net negative charge. 3)…
answer question 5-9
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 14 - We fully submerge an irregular 3 kg lump of...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-21 shows four situations in which a red...Ch. 14 - A boat with an anchor on board floats in a...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-22 shows a tank filled with water. Five...Ch. 14 - The teapot effect. Water poured slowly from a...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-24 shows three identical open-top...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-25 shows four arrangements of pipes...Ch. 14 - A rectangular block is pushed face-down into three...Ch. 14 - Water flows smoothly in a horizontal pipe. Figure...Ch. 14 - We have three containers with different Liquids....
Ch. 14 - ILW A fish maintains its depth in fresh water by...Ch. 14 - A partially evacuated airtight container has a...Ch. 14 - SSM Find the pressure increase in the fluid in a...Ch. 14 - Three liquids that will not mix are poured into a...Ch. 14 - SSM An office window has dimensions 3.4 m by 2.1...Ch. 14 - Prob. 6PCh. 14 - In 1654 Otto von Guericke, inventor of the air...Ch. 14 - The bends during flight. Anyone who scuba dives is...Ch. 14 - Blood pressure in Argentinosaurus. a If this...Ch. 14 - The plastic tube in Fig. 14-30 has a...Ch. 14 - Giraffe bending to drink. In a giraffe with its...Ch. 14 - The maximum depth dmax that a diver can snorkel is...Ch. 14 - At a depth of 10.5 km, the Challenger Deep in the...Ch. 14 - Calculate the hydrostatic difference in blood...Ch. 14 - What gauge pressure must a machine produce in...Ch. 14 - Snorkeling by humans and elephants. When a person...Ch. 14 - SSM Crew members attempt to escape from a damaged...Ch. 14 - In Fig. 14-32, an open tube of length L = 1.8 m...Ch. 14 - GO A large aquarium of height 5.00 m is filled...Ch. 14 - The L-shaped fish tank shown in Fig. 14-33 is...Ch. 14 - SSM Two identical cylindrical vessels with their...Ch. 14 - Prob. 22PCh. 14 - GO In analyzing certain geological features, it is...Ch. 14 - GO In Fig. 14-35, water stands at depth D = 35.0 m...Ch. 14 - In one observation, the column in a mercury...Ch. 14 - To suck lemonade of density 1000 kg/m3 up a straw...Ch. 14 - SSM What would be the height of the atmosphere if...Ch. 14 - A piston of cross-sectional area a is used in a...Ch. 14 - In Fig 14-37, a spring of spring constant 3.00 ...Ch. 14 - A 5.00 kg object is released from rest while fully...Ch. 14 - SSM A block of wood floats in fresh water with...Ch. 14 - In Fig. 14-38, a cube of edge length L = 0.600 m...Ch. 14 - SSM An iron anchor of density 7870kg/m3 appears...Ch. 14 - A boat floating in fresh water displaces water...Ch. 14 - Three children, each of weight 356 N, make a log...Ch. 14 - GO In Fig. 14-39a, a rectangular block is...Ch. 14 - ILW A hollow spherical iron shell floats almost...Ch. 14 - GO A small solid ball is released from rest while...Ch. 14 - SSM WWW A hollow sphere of inner radius 8.0 cm and...Ch. 14 - Lurking alligators. An alligator waits for prey by...Ch. 14 - What fraction of the volume of an iceberg density...Ch. 14 - A Flotation device is in the shape of a right...Ch. 14 - When researchers find a reasonably complete fossil...Ch. 14 - A wood block mass 3.67 kg, density 600 kg/m3 is...Ch. 14 - GO An iron casting containing a number of cavities...Ch. 14 - GO Suppose that you release a small ball from rest...Ch. 14 - The volume of air space in the passenger...Ch. 14 - GO Figure 14-44 shows an iron ball suspended by...Ch. 14 - Canal effect. Figure 14-45 shows an anchored barge...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-46 shows two sections of an old pipe...Ch. 14 - SSM A garden hose with an internal diameter of 1.9...Ch. 14 - Two streams merge to form a river. One stream has...Ch. 14 - SSM Water is pumped steadily out of a flooded...Ch. 14 - GO The water flowing through a 1.9 cm inside...Ch. 14 - How much work is done by pressure in forcing 1.4...Ch. 14 - Suppose that two tanks, 1 and 2, each with a large...Ch. 14 - SSM A cylindrical tank with a large diameter is...Ch. 14 - The intake in Fig. 14-47 has cross-sectional area...Ch. 14 - SSM Water is moving with a speed of 5.0 m/s...Ch. 14 - Models of torpedoes are sometimes tested in a...Ch. 14 - ILW A water pipe having a 2.5 cm inside diameter...Ch. 14 - A pitot tube Fig. 14-48 is used to determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 63PCh. 14 - GO In Fig. 14-49, water flows through a horizontal...Ch. 14 - SSM WWW A venturi meter is used to measure the...Ch. 14 - Consider the venturi tube of Problem 65 and Fig....Ch. 14 - ILW In Fig. 14-51, the fresh water behind a...Ch. 14 - GO Fresh water flows horizontally from pipe...Ch. 14 - A liquid of density 900 kg/m3 flows through a...Ch. 14 - GO In Fig. 14-53, water flows steadily from the...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-54 shows a stream of water flowing...Ch. 14 - GO A very simplified schematic of the rain...Ch. 14 - About one-third of the body of a person floating...Ch. 14 - A simple open U-tube contains mercury. When 11.2...Ch. 14 - If a bubble in sparkling water accelerates upward...Ch. 14 - Suppose that your body has a uniform density of...Ch. 14 - Prob. 77PCh. 14 - Caught in an avalanche, a skier is fully submerged...Ch. 14 - An object hangs from a spring balance. The balance...Ch. 14 - In an experiment, a rectangular block with height...Ch. 14 - SSM Figure 14-30 shows a modified U-tube: the...Ch. 14 - What is the acceleration of a rising hot-air...Ch. 14 - Figure 14-56 shows a siphon, which is a device for...Ch. 14 - When you cough, you expel air at high speed...Ch. 14 - A tin can has a total volume of 1200 cm3 and a...Ch. 14 - The tension in a string holding a solid block...Ch. 14 - What is the minimum area in square meters of the...Ch. 14 - A 8.60 kg sphere of radius 6.22 cm is at a depth...Ch. 14 - a For seawater of density 1.03 g/cm3, find the...Ch. 14 - The sewage outlet of a house constructed on a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What is the significance of interphase?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
The number of named species is about ________, but the actual number of species on Earth is estimated to be abo...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS The gene that causes sickle-cell disease is present in a higher percentage of residents of su...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
21. What is the thinnest film of MgF2 (n = 1.38) on glass that produces a strong reflection for orange light wi...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- AMPS VOLTS OHMS 5) 50 A 110 V 6) .08 A 39 V 7) 0.5 A 60 8) 2.5 A 110 Varrow_forwardThe drawing shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m², while surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m². The electric field in the drawing is uniform and has a magnitude of 215 N/C. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (1 and 2 combined) if the angle 8 made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0°. Solve in Nm²/C 1 Ө Surface 2 Surface 1arrow_forwardPROBLEM 5 What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force acting on the connection support shown here? F₁ = 700 lbs F2 = 250 lbs 70° 60° F3 = 700 lbs 45° F4 = 300 lbs 40° Fs = 800 lbs 18° Free Body Diagram F₁ = 700 lbs 70° 250 lbs 60° F3= = 700 lbs 45° F₁ = 300 lbs 40° = Fs 800 lbs 18°arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 3 Cables A and B are Supporting a 185-lb wooden crate. What is the magnitude of the tension force in each cable? A 20° 35° 185 lbsarrow_forwardThe determined Wile E. Coyote is out once more to try to capture the elusive Road Runner of Loony Tunes fame. The coyote is strapped to a rocket, which provide a constant horizontal acceleration of 15.0 m/s2. The coyote starts off at rest 79.2 m from the edge of a cliff at the instant the roadrunner zips by in the direction of the cliff. If the roadrunner moves with constant speed, find the minimum velocity the roadrunner must have to reach the cliff before the coyote. (proper sig fig in answer)arrow_forwardPROBLEM 4 What is the resultant of the force system acting on the connection shown? 25 F₁ = 80 lbs IK 65° F2 = 60 lbsarrow_forward
- Three point-like charges in the attached image are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 38.0 cm, and the point (C) is located half way between q1 and q3 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (C). Let q1 = −2.80 µC, q2 = −3.40 µC, and q3 = −4.50 µC. Thank you.arrow_forwardSTRUCTURES I Homework #1: Force Systems Name: TA: PROBLEM 1 Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force in the cable shown. PROBLEM 2 The horizontal component of force F is 30 lb. What is the magnitude of force F? 6 10 4 4 F = 600lbs F = ?arrow_forwardThe determined Wile E. Coyote is out once more to try to capture the elusive Road Runner of Loony Tunes fame. The coyote is strapped to a rocket, which provide a constant horizontal acceleration of 15.0 m/s2. The coyote starts off at rest 79.2 m from the edge of a cliff at the instant the roadrunner zips by in the direction of the cliff. If the roadrunner moves with constant speed, find the minimum velocity the roadrunner must have to reach the cliff before the coyote. (proper sig fig)arrow_forward
- Hello, I need some help with calculations for a lab, it is Kinematics: Finding Acceleration Due to Gravity. Equations: s=s0+v0t+1/2at2 and a=gsinθ. The hypotenuse,r, is 100cm (given) and a height, y, is 3.5 cm (given). How do I find the Angle θ1? And, for distance traveled, s, would all be 100cm? For my first observations I recorded four trials in seconds: 1 - 2.13s, 2 - 2.60s, 3 - 2.08s, & 4 - 1.95s. This would all go in the coloumn for time right? How do I solve for the experimental approximation of the acceleration? Help with trial 1 would be great so I can use that as a model for the other trials. Thanks!arrow_forwardAfter the countdown at the beginning of a Mario Kart race, Bowser slams on the gas, taking off from rest. Bowser get up to a full speed of 25.5 m/s due to an acceleration of 10.4 m/s2. A)How much time does it take to reach full speed? B) How far does Bowser travel while accelerating?arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. I believe side 1 is 60 degrees but could be wrong. Thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How to Calculate Density of Liquids - With Examples; Author: cleanairfilms;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DVQMWihs3wQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY