
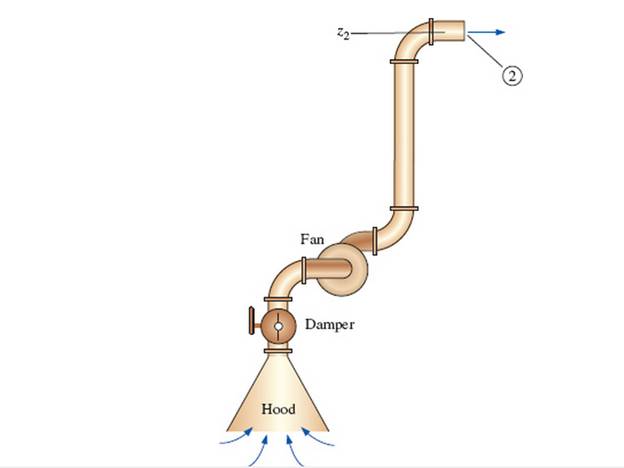
A local ventilation system (a hood and duct system) is used to remove air and contaminants produced by a welding operation (Fig. P 14-55E). The inner diameter (ID) of the duct is D = 9.06 in, its average roughness is 0.0059 in, and its total length is L = 34.0 ft. There are three elbows along the duct, each with a minor loss coefficient of 0.21. Literature from the hood manufacturer lists the hood entry loss coefficient as 4.6 based on duct velocity. When the damper is fully open, its loss coefficient is 1.8. A squirrel cage centrifugal fan with a 9.0-in inlet is available. Its performance data fit a parabolic curve of the form

The volume flow rate.
Answer to Problem 55EP
The volume flow rate is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The inner diameter of the duct is
Expression for steady energy equation from point 1 in the stagnant air region to point 2 at the duct outlet
Here, the required head for the fan is
Expression for the total head loss
Here, the velocity of the air is
Expression for Reynold's number
Here, the kinematic viscosity is
Expression for relative roughness
Here, the roughness of the pipe is
Expression for the friction factor
Expression for the volume flow rate
Here, the area of the pipe is
Expression for the area of the pipe
Substitute
Expression to convert the shutoff head from inches of water column to inches of air column
Here, the density of the water is
Expression to convert
Calculation:
Refer to the Table-A-9E, "Properties of air at 1 atm pressure" to obtain the density of the air as
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Since at the operating point the available head and the required head are equal, therefore equate equation (XII) and (XIII).
Solve Equation (XII) and Equation (XIV) to obtain the value of velocity as
Substitute
Conclusion:
The volume flow rate is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS+APPS
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardA gear has a gear wheel with 16 teeth. The gear should be dimensioned for the highest and lowest gear ratio. Looking for output power, torque, speed?nin= 2000 rpmmin = 30Nmn=0,9a max= 450 mmModule 4Gear limitsz1 z213 13-1614 14-2615 15-4516 16-10117 17-131418 18-…..I have calculate but I can’t get the right answers…..√16 =459x60/56x57=1.1 lowest59x60/13x13=20,94 highestnut=2000/1.1= 1818rpmnut=2000/20.94=95.5 rpmMut=1.1x30=33 NmMut=20.94x30=628,2 Nm(Right answer)LowestZ=13, M=24,4Nm, n=2462 rpmHighestZ=92, M=172,5Nm, n=347,8 rpmP=5655W on botharrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
