
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 3-methyl-3-pentanol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as
Answer to Problem 40P
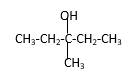
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the 3-methyl-3-pentanol contains five carbon length main carbon chain which connects to an alcohol group in the 3rd carbon of the main carbon chain. Furthermore, methyl group also connects to the 3rd position of the main carbon chain. And according to the structure it should be a tertiary alcohol.
According to the name, structure of the compound is as below;
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 4-methyl-2-pentanol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 40P
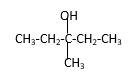
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the 4-methyl-2-pentanol consist one main C chain which contains five C atoms, and alcohol group is connected to the 2nd position of the main C ring. Methyl group is connects to the 4th position of the main C chain. And as per the name it should be a secondary alcohol.
Structure of the compound is as below;
(c)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 2,4-dimethyl-2-hexanol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 40P
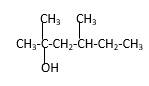
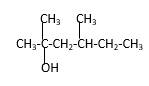
Explanation of Solution
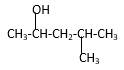
Structure of the 2, 4-dimethyl-2-hexanol consist one main C chain which contains six C atoms, and alcohol group is connected to the 2nd position of the main C ring. Two methyl groups are connected to the 4th position and 2nd position of the main C chain. And as per the name it should be a tertiary alcohol.
Structure of the compound is as below;
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 1,3-propanediol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
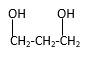
Answer to Problem 40P
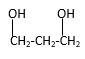
Explanation of Solution
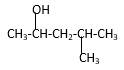
Structure of the 4-methyl-2-pentanol consist one main C chain which contains five C atoms, and alcohol group is connected to the 2nd position of the main C ring. Methyl group is connects to the 4th position of the main C chain. And as per the name it should be a secondary alcohol.
Structure of the compound is as below;
(e)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 3,5-dimethylcyclohexanol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 40P
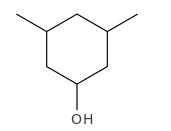
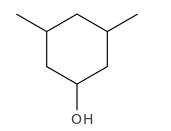
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the 3,5-dimethylcyclohexanol consist one main C ring which contains six C atoms, and alcohol group is connected to the 1st position of the main C ring. Two methyl groups are connected to the 3rd and 5th position of the main C ring. And as per the name it should be a secondary alcohol.
Structure of the compound is as below;
(f)
Interpretation:
Structure of the 4-methyl-2-pentanol should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 40P
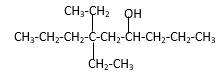
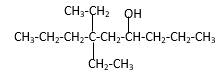
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the 4-methyl-2-pentanol consist one main C chain which contains five C atoms, and alcohol group is connected to the 2nd position of the main C ring. Methyl group is connects to the 4th position of the main C chain. And as per the name it should be a secondary alcohol.
Structure of the compound is as below;
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forward
- Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forwardFormulate the reaction: Naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºCarrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





