
Biological Science (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134678320
Author: Scott Freeman, Kim Quillin, Lizabeth Allison, Michael Black, Greg Podgorski, Emily Taylor, Jeff Carmichael
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 14, Problem 23PIAT
Summary Introduction
To analyze:
The probability of the first child of the couple to have ALD (adrenoleukodystrophy).
Introduction:
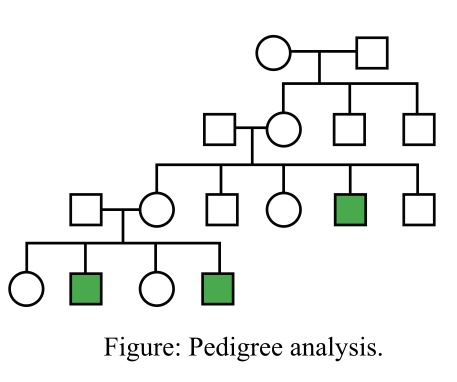
Adrenoleukodystrophy is a type of X-linked disorder. It occurs as a result of mutation in the ABCD1 gene, which is present on the Xq28 chromosome. Furthermore, the nonfunctioning of these enzymes damages the myelin sheath present on the axon, which further causes degeneration of the neuron. In the given pedigree, the first daughter in the last generation is married to a man with no history of ALD in his family. Being a genetic counselor, advise the couple about chances of their first child having ALD. The pedigree is shown below:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Based on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?
help tutor please
Q8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant
women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their
pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants:
One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo
medication. In this study what are:
Independent variable:
Dependent variable:
Control variable:
Experimental group: "
Control group:
If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills.
This study is
It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months.
The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study?
If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this
research work?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Biological Science (7th Edition)
Ch. 14 - 1. The genes for the trails that Mendel worked...Ch. 14 - Example Problem Two black female mice are crossed...Ch. 14 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 6TYPSSCh. 14 - Prob. 7TYPSSCh. 14 - 11. In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant...Ch. 14 - Prob. 9TYPSSCh. 14 - The smooth feathers on the back of the neck in...Ch. 14 - SOCIETY As a genetic counselor, you advise couples...Ch. 14 - 15. Suppose you are heterozygous for two genes...
Ch. 14 - Suppose a woman with blood type O married a man...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14TYPSSCh. 14 - Society Two mothers give birth to sons at the same...Ch. 14 - Prob. 16TYPSSCh. 14 - QUANTITATIVE Recall that hemophilia is an X-linked...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18PIATCh. 14 - Given the pedigree, what is the most likely mode...Ch. 14 - Prob. 20PIATCh. 14 - QUANTITATIVE If the son with ALD in the third...Ch. 14 - Prob. 22PIATCh. 14 - Prob. 23PIAT
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to the Human Genome | HMX Genetics; Author: Harvard University;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jEJp7B6u_dY;License: Standard Youtube License