
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The oxidized product of the following alcohol when oxidized with
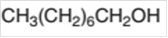
Concept Introduction:
A
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant whereas the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
The oxidation reaction is the reaction that involves the addition of O atom in the presence of certain oxidizing agents such as
Answer to Problem 14.69P
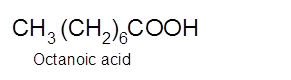
Explanation of Solution
To get the oxidized product of any alcohol, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the C atom in the parent chain that is bonded with −OH group.
- Convert that C atom to carbonyl C atom or
carboxylic acid as it is overall removal of H atoms. - Primary alcohols are oxidized to
aldehyde which further oxidized to a carboxylic acid. - Secondary alcohols are oxidized to a
ketone (R2CO). - Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized as they do not have H atom on the C with the −OH group.
Hence, the oxidization of 1-octanol will form octanoic acid molecule as 1-octanol is a primary alcohol.
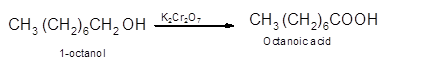
(b)
Interpretation:
The oxidized product of the following alcohol when oxidized with
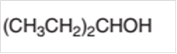
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant whereas the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
The oxidation reaction is the reaction that involves the addition of O atom in the presence of certain oxidizing agents such as
Answer to Problem 14.69P
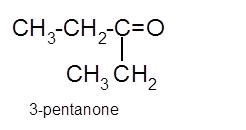
Explanation of Solution
To get the oxidized product of any alcohol, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the C atom in the parent chain that is bonded with −OH group.
- Convert that C atom to carbonyl C atom or carboxylic acid as it is overall removal of H atoms.
- Primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehyde which further oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
- Secondary alcohols are oxidized to a ketone (R2CO).
- Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized as they do not have H atom on the C with the −OH group.
Hence the oxidization of 3-pentanol will form 3-pentanone molecule as 3-pentanol is a secondary alcohol.
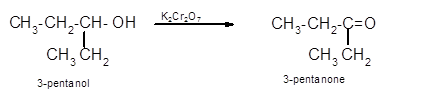
(c)
Interpretation:
The oxidized product of the following alcohol when oxidized with
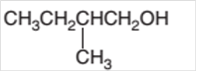
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant whereas the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Oxidation reaction is the reaction that involves the addition of O atom in the presence of certain oxidizing agents such as
Answer to Problem 14.69P
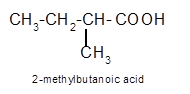
Explanation of Solution
To get the oxidized product of any alcohol, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the C atom in the parent chain that is bonded with −OH group.
- Convert that C atom to carbonyl C atom or carboxylic acid as it is overall removal of H atoms.
- Primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehyde which further oxidized to carboxylic acid.
- Secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketone (R2CO).
- Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized as they do not have H atom on the C with the −OH group.
Hence the oxidization of 3-pentanol will form 3-pentanone molecule as 3-pentanol is a secondary alcohol.
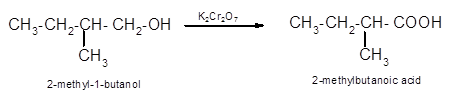
(d)
Interpretation:
The oxidized product of following alcohol when oxidized with
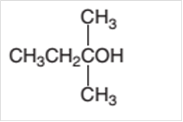
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction; the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant whereas the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactant and products must be separated by an arrow.
Oxidation reaction is the reaction that involves the addition of O atom in the presence of certain oxidizing agents such as
Answer to Problem 14.69P
2-ethyl-2-propanol cannot oxidize as it is a tertiary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
To get the oxidized product of any alcohol, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the C atom in the parent chain that is bonded with −OH group.
- Convert that C atom to carbonyl C atom or carboxylic acid as it is the overall removal of H atoms.
- Primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehyde which further oxidized to the carboxylic acid.
- Secondary alcohol is oxidized to ketone (R2CO).
- Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized as they do not have H atom on the C with the −OH group.
Hence 2-ethyl-2-propanol cannot oxidize as it is a tertiary alcohol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- (a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




