
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
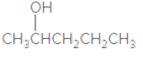
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as
Answer to Problem 14.41P
2-pentanol.
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
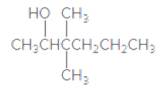
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 14.41P
3,3-dimethyl-2-hexanol.
Explanation of Solution
(
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
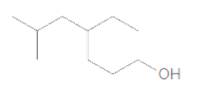
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 14.41P
4-ethyl-6-methylheptanol.
Explanation of Solution
(
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
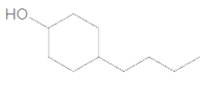
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 14.41P
4-butylcyclohexanol.
Explanation of Solution
(
Hence; IUPAC name of the (
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 14.41P
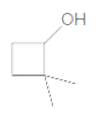
2,2-dimethylcyclobutanol.
Explanation of Solution
(
Hence; IUPAC name of the (
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are the organic molecules which have OH group bonded to a tetrahedral carbon atom.
Longest carbon chain containing the carbon bonded to the OH group is named as an alkane and -e of the alkane replaced by the suffix -ol.
Numbering of main carbon chain is done in such a way so that OH group gets the lowest number.
When OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group and the 1 is normally omitted from the name. The ring is numbered in clockwise or anticlockwise by giving the lowest number to the next substitute.
Compounds which contains two OH groups are named as diols and when in nomenclature, -diol suffix is added to the end of the parent alcohol and position of the OH groups are used as prefix to indicate the location of the two OH groups.
Answer to Problem 14.41P
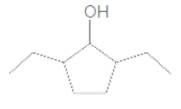
2,5-diethylcyclopentanol.
Explanation of Solution
(
Hence; IUPAC name of the (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- (a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
