
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.52SP
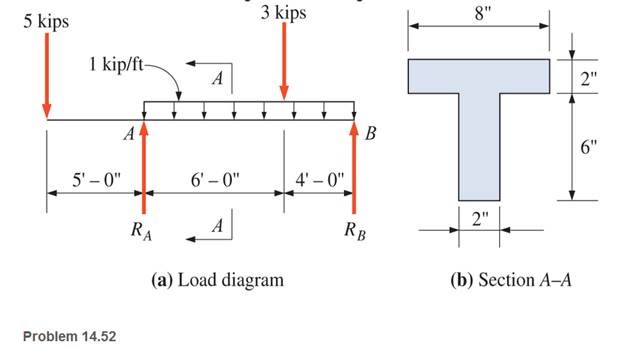
For the beam shown, calculate the maximum tensile and compressive bending stresses and the maximum shear stresses. Neglect the beam weight.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule15:02
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help. This problem involves bending moments and moments of inertia. I just need the moment of inertia. Thank you.
The cantilever beam in Fig. (a) carries a triangular load, the intensity of which varies from zero at the left end to 360 lb/ft at the right end. In addition, a 1000-lb upward vertical load acts at the free end of the beam. (1) Derive the shear force and bending moment equations, and (2) draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. Neglect the weight of the beam
A circular shaft is subjected to combined loads of bending M and torque T. With the help
of Mohr's circle diagram, represent the stresses on an element of the shaft surface. From this
diagram or by calculation, find the maximum shear stress due to the combined effect of these
gradually applied loads of M and T.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 14 - Calculate the section modulus for: (a) a 6 -in-by-...Ch. 14 - Calculate the section modulus (with respect to the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.3PCh. 14 - Rework Problem 14.3 changing the orientation of...Ch. 14 - Assume that the timber member (a) of Problem 14.2...Ch. 14 - The structural steel built-up member (b) of...Ch. 14 - A round steel rod, 25 mm in diameter, is subjected...Ch. 14 - A square steel bar, 38 mm on each side, is used as...Ch. 14 - Calculate the moment strength for a W36302...Ch. 14 - Calculate the allowable bending moment for a solid...
Ch. 14 - The beams of cross sections shown are subjected to...Ch. 14 - A solid rectangular simply supported timber beam 6...Ch. 14 - A W1430 supports the loads shown. Calculate the...Ch. 14 - If the allowable shear stress is 100 MPa,...Ch. 14 - A steel pin 112 in diameter is subjected to a...Ch. 14 - A timber power-line pole is 10 in. in diameter at...Ch. 14 - Calculate the value of S and Z and the shape...Ch. 14 - For beams that have cross sections as shown for...Ch. 14 - Calculate the maximum load P that the beam shown...Ch. 14 - A 412 (S4S) hem-fir timber beam carries a...Ch. 14 - A simply supported W1636 A992 steel beam carries a...Ch. 14 - A W250115 steel wide-flange section supports a...Ch. 14 - Assume that the floor joist dimensions of Example...Ch. 14 - Calculate the allowable superimposed uniformly...Ch. 14 - A 3 -in.-by- 12 -in. (S4S) scaffold timber plank...Ch. 14 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 14 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 14 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 14 - Calculate the section modulus with respect to the...Ch. 14 - The timber box section (a) of Problem 14.29 is...Ch. 14 - A timber beam is subjected to a maximum bending...Ch. 14 - Rework Problem 14.31 assuming that the beam is...Ch. 14 - A 12 -in.-diameter steel rod projects 2 ft...Ch. 14 - Calculate the maximum bending stress in a W530101...Ch. 14 - A cantilever cast-iron beam is 6 ft long and has a...Ch. 14 - 14.36 Calculate the moment strength for a...Ch. 14 - A W813 steel wide-flange beam on a 20 -ft span is...Ch. 14 - A simply supported beam with a cruciform cross...Ch. 14 - A rectangular beam 100 mm in width and 250 mm in...Ch. 14 - The timber box section (a) of Problem 14.29 is...Ch. 14 - For the I-shaped timber beam shown, calculate the...Ch. 14 - 14.42 A steel wide-flange beam is oriented so that...Ch. 14 - A W1045steel wide-flange beam supports a uniformly...Ch. 14 - 14.44 A steel wide-flange section is subjected to...Ch. 14 - A W30108 steel wide-flange beam is simply...Ch. 14 - A W612 is strengthened with a 34 -in.-by- 34 -in....Ch. 14 - Four wood boards 1 in. by 6 in. in cross section...Ch. 14 - A lintel consists of two 8 -in.-by- 12 in. steel...Ch. 14 - A 50 -mm-by- 300 -mm scaffold timber plank, placed...Ch. 14 - A laminated wood beam is built up by gluing...Ch. 14 - A rectangular hollow shape carries loads as shown....Ch. 14 - For the beam shown, calculate the maximum tensile...Ch. 14 - 14.53 A box beam is built up of four -in.-by--in....Ch. 14 - 14.54 Find the value of the loads P that can be...Ch. 14 - 14.55 Solve Problem 14.54 assuming that the timber...Ch. 14 - Calculate the values of S and Z and the shape...Ch. 14 - 14.57 A is supported on simple supports on a -ft...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
The two identical boards are bolted together to form the beam. Determine the maximum spacing s of the bolts to ...
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
The impulses created by a falling weight onto a sample of URETHANE foam and CONFOR foam.
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Replace this loading by an equivalent resultant force and specify its location, measured from point O.
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
11. If a pump moves water at 70 gallons per minute [gal/min or gpm], what is the volumetric flow rate in units ...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the ring and the load applied. Calculate the normal stresses at point A and B. Hint: Normal stresses are due to both the normal force and the bending moment calculated for curved beams.arrow_forwardFor the beam shown, derive the expressions for V and M, and draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. Calculate the shear force V and bending moment M at a cross section located 0.5 m from the fixed support. Neglect the weight of the beam. (Show complete calculation and step by step process. Show free body diagram)arrow_forwardA cantilever beammade up of a material with the density of 2000kg/m3 has a circular cross section with a diameter of 150mm. In addition to the self weight, the beam is subjected concentrated point load of 88 kN at its midspan. Find out the flexural and shear stresses at top, bottom and neutral axis of the cross section produced due to the maximum bending moment if the span length of the beam is 4m. Consider the self weight of the beam in solving the question.arrow_forward
- a 80 mm wide and 300 mm high simply supported bean has a length of 7.4 m and supports a concentrated load of 7.2 kN acting at the midspan. Find the maximum shear stress and maximum bending stress.arrow_forwardCalculate the modulus of section of rectangle beam of breadth 120 mm and height 200 mm.arrow_forward(d) Show the stress distribution of a l-section subjected to major axis bending and shear force. Highlight where will you get the maximum shear and bending stress within the section.arrow_forward
- A simply supported beam, 50mm wide by 100mm high and 300 mm long is subjected to a concentrated load of 3000 N at a point 100 mm from one of the supports. Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam.arrow_forwardstrenght of materials problemsarrow_forwardFor the simply supported beam subjected to the loading shown, derive equations for the shear force Vand the bending moment M for any location in the beam. (Place the origin at point A.) Let a=2.50 m, b=4.25 m, PB = 45kN, and Pc = 90kN. Construct the shear- force and bending-moment diagrams on paper and use the results to answer the questions in the subsequent parts of this GO exercise. Answers: Ay = Dy= Mi i B Calculate the reaction forces Ay and Dy acting on the beam. Positive values for the reactions are indicated by the directions of the red arrows shown on the free-body diagram below. (Note: Since Ax = 0, it has been omitted from the free-body diagram.) PB a PB B a Pc a Pc C kN b KN b D X D₂ Xarrow_forward
- For the simply supported beam subjected to the loading shown, derive equations for the shear force Vand the bending moment M for any location in the beam. (Place the origin at point A.) Let a=2.75 m, b=5.00 m, PB = 60KN, and Pc = 80kN. Construct the shear- force and bending-moment diagrams on paper and use the results to answer the questions in the subsequent parts of this GO exercise. Answers: Ay = Dy= tel tel a i B a Calculate the reaction forces Ay and Dy acting on the beam. Positive values for the reactions are indicated by the directions of the red arrows shown on the free-body diagram below. (Note: Since Ax = 0, it has been omitted from the free-body diagram.) PB B a PB Pc a C Pc C KN b KN D b D X D₂ Xarrow_forwardDetermine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses developed in the overhanging beam that is loaded and has the cross- sectional properties as shown. 1600 lb 4000 lb 2 in N.A. 6 in 6 ft R I- 90 in 6 ft tensile stress = 3, 840 psi and compressive stress = 7, 680 psi tensile stress = 1, 280 psi and compressive stress = 2,560 psi tensile stress = 7, 680 psi and compressive stress = 3, 840 psi tensile stress = 7, 680 psi and compressive stress = 2, 560 psiarrow_forwardLet a=4 ft, b=6 ft, c=4 ft and w-7.5 kips/ft. Construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams on paper and use the results to answer the questions a B b W C- C D -X Calculate the reaction forces Ay acting on the beam. (Note: Since Ax = 0, it has been omitted from the free-body diagram.) Final answer in kips rounded-off to 1 decimal placearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Types of Manufacturing Process | Manufacturing Processes; Author: Magic Marks;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=koULXptaBTs;License: Standard Youtube License