
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.143EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is methylthioethane and common name is ethyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
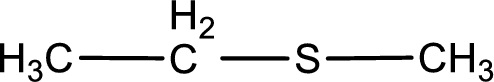
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a two carbon chain. Hence, the base name is ethane.
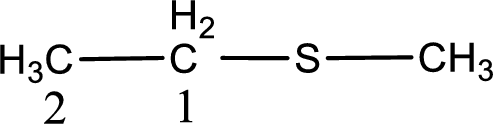
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom.
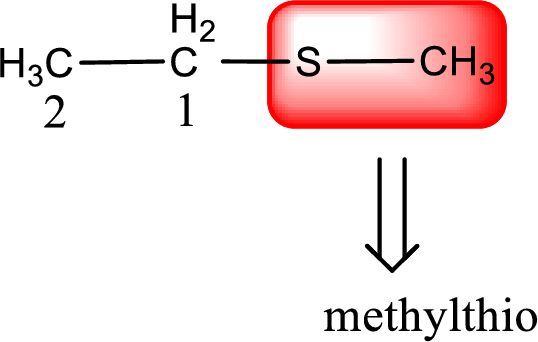
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as methylthioethane.
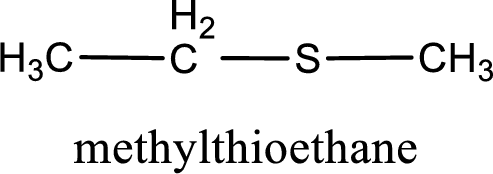
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is methylthioethane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and an ethyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is ethyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.143EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-methylthiopropane and common name is isopropyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
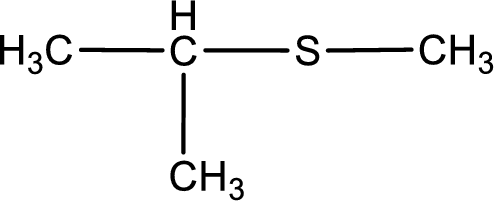
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain. Hence, the base name is propane.
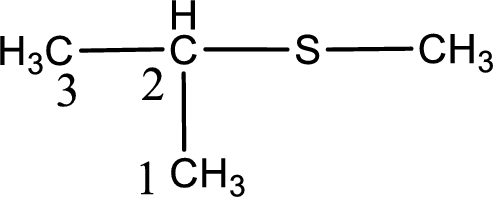
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom. The point of attachment in the propane for methylthio group is in the second carbon atom.
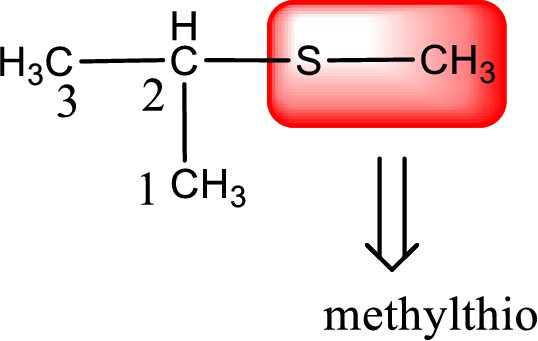
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 2-methylthiopropane.
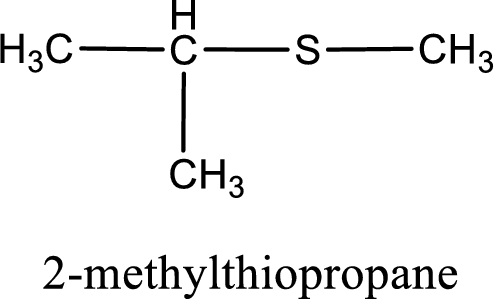
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 2-methylthiopropane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and an isopropyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is isopropyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.143EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is methylthiocyclohexane and common name is cyclohexyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
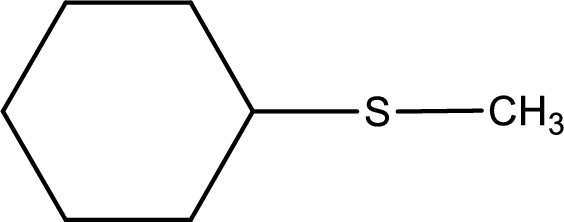
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a six carbon cyclic chain that is saturated. Hence, the base name is cyclohexane.
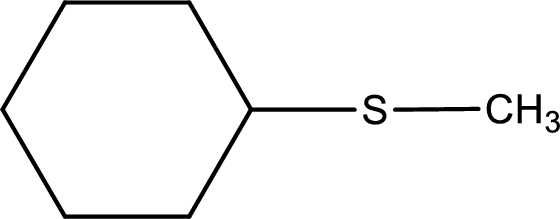
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom.
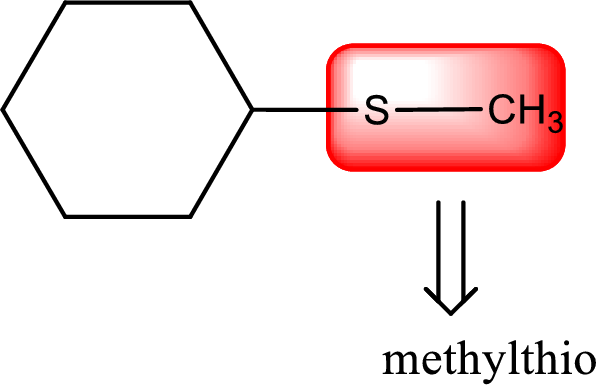
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as methylthiocyclohexane.
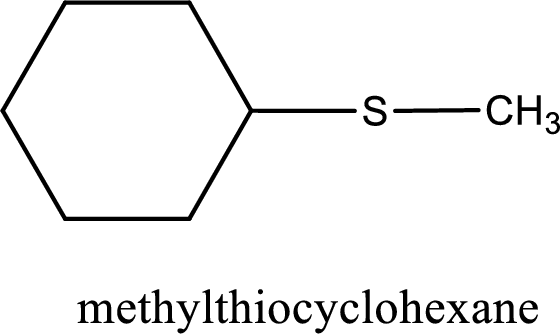
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is methylthiocyclohexane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and a cyclohexyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is cyclohexyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.143EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 3-(methylthio)-1-propene and common name is allyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
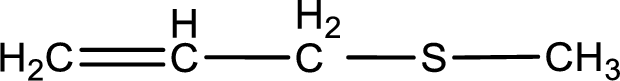
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain with a double bond. Hence, the base name is propene.
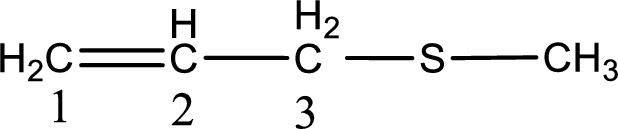
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom.
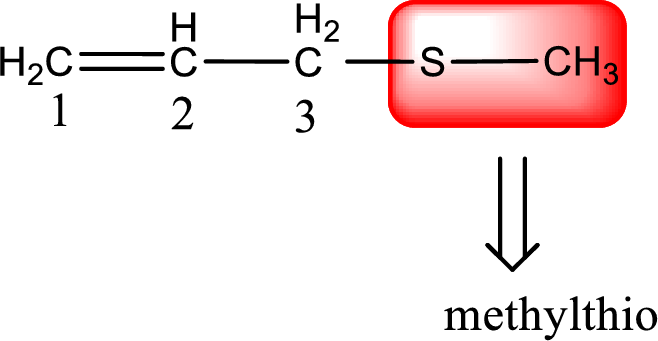
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 3-(methylthio)-1-propene.
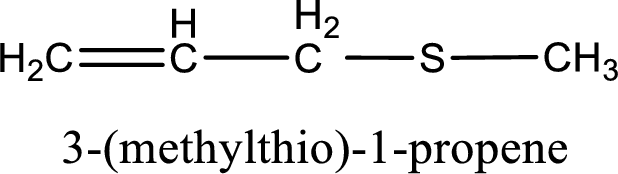
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 3-(methylthio)-1-propene.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and an allyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is allyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





