
Concept explainers
A test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb simulated foot attached to the end of a 6-ft long pendulum arm of negligible mass. Knowing that the arm is released from the horizontal position and that the coefficient of restitution between the foot and the 1-lb ball is 0.8, determine the exit velocity of the ball (a) if the ball is stationary, (b) if the ball is struck when it is rolling toward the foot with a velocity of 10 ft/s.
Fig. P13.184
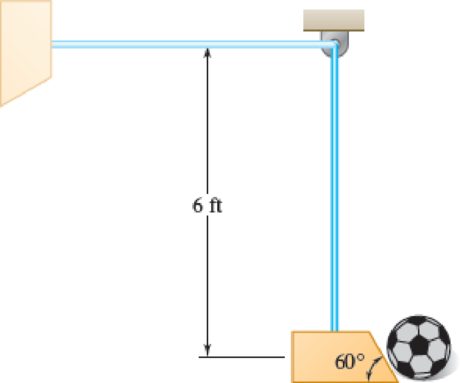
(a)
Find the exit velocity of the ball
Answer to Problem 13.184P
The exit velocity of the ball
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the stimulated foot
The weight of the ball
The length of the pendulum arm (l) is
The coefficient of restitution between the foot (e) is 0.8.
The angle
The acceleration of gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Calculate the mass of the stimulated foot
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the ball
Substitute
Calculate the speed of the foot
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Substitute
Show the impulse momentum diagram for the ball and foot as Figure (1).
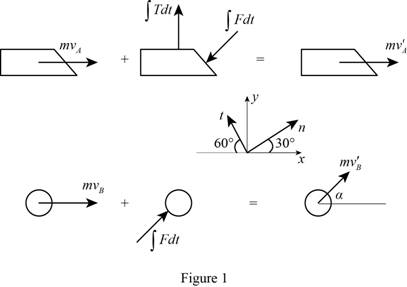
The expression for the velocity of the ball
The expression for the conservation of momentum of the ball in tangent t direction as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
The expression for the speed of the ball
The expression for the conservation of momentum of the system in x direction as follows:
Substitute
The expression for the velocity of foot
The expression for the velocity of foot
The expression for the velocity of ball
The expression for the coefficient of restitution for both ball and foot in normal direction as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Solve the equations (2) and (3).
Calculate the magnitude of the exit velocity of the ball
Substitute
The velocity of the ball
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the direction of the velocity of the ball
Substitute
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the exit velocity of the ball
(b)
Find the exit velocity of the ball
Answer to Problem 13.184P
The exit velocity of the ball
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the stimulated foot
The weight of the ball
The length of the pendulum arm (l) is
The coefficient of restitution between the foot (e) is 0.8.
The angle
The velocity
Calculation:
Calculate the magnitude of the exit velocity of the ball
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the direction of the velocity of the ball
Substitute
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the exit velocity of the ball
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS W/CON >B
- 1. Two discs sliding on a frictionless horizontal plane with opposite speeds of the same magnitude Vo collide with each other head-on. Disk A is known to have a mass of 3 kg and its velocity is observed to be zero after impact. Determine a) the mass of disk B if the coefficient of restitution between the two disks is known to be 0.5, b) the range of possible values of the mass of disk B if the coefficient of restitution between the two disks is unknown.arrow_forwardA 4-lb collar which can slide on a frictionless vertical rod is acted upon by a force P which varies in magnitude as shown. Knowing that the collar is initially at rest, draw the impulse-momentum diagram that can be used to determine its velocity at t= 3 s.arrow_forward4. A 750 kg hammer is used to drive a 2500 kg pile into some loosely packed sand. The hammer is released from a height of 2.5 m above the top of the pile and is seen to rebound to a maximum height of 0.15 m above the point of impact. Determine: (a) the velocity of the pile immediately after impact, (b) the coefficient of restitution, and (c) the average force exerted by the hammer on the pile if the impact takes place over 0.08 s. 2.5 m P Ans. vp, = -2.62 m/s, e = 0.62, Favg = 81.9 kN %3Darrow_forward
- A 750 kg hammer is used to drive a 2500 kg pile into some loosely packed sand. The hammer is released from a height of 2.5 m above the top of the pile and is seen to rebound to a maximum height of 0.15 m above the point of impact. Determine:(a) the velocity of the pile immediately after impact,(b) the coefficient of restitution, and(c) the average force exerted by the hammer on the pile if the impact takes place over 0.08 s.arrow_forwardAfter having been pushed by an airline employee, an empty 40-kg luggage carrier A hits with a velocity of 5 m/s an identical carrier B containing a 15-kg suitcase equipped with rollers. The impact causes the suitcase to roll into the left wall of carrier B. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution between the two carriers is 0.80 and that the coefficient of restitution between the suitcase and the wall of carrier B is 0.30, determine (a) the velocity of carrier B after the suitcase hits its wall for the first time, (b) the total energy lost in that impact.arrow_forwardA 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity of 450 m/s and becomes embedded in block B , which has a mass of 3 kg. After the impact, block B slides on 30-kg carrier C until it impacts the end of the carrier. Knowing the impact between B and C is perfectly plastic and the coefficient of kinetic friction between B and C is 0.2, determine (a) the velocity of the bullet and B after the first impact, (b) the final velocity of the carrier.arrow_forward
- A 10-kg package drops from a chute into a 25-kg cart with a velocity of 3 m/s. The cart is initially at rest and can roll freely. Determine (a) the final velocity of the cart, (b) the impulse exerted by the cart on the package, (c) the fraction of the initial energy lost in the impact.arrow_forwardA ball of mass 5 kg dropped from a five meter height on a smooth floor. If the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor is 0.6. The following is required;Using Newton’s equations of motion for constant acceleration determine the velocity of the ball on hitting the floorUsing conservation of mechanical energy determine the rebound velocity, The maximum height it rises after it bounces off the floor, The impulse exerted by the floor on the ball, The dissipated energy. If the time of impact is 10-5 seconds, determine the magnitude of the impulsive force exerted on the ball by the floor during impact.arrow_forwardMember ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to a pin support at B. A 0.8-kg sphere D strikes the end of member ABC with a vertical velocity v1=3 m/s. Knowing that L=0.75 m and that the coefficient of restitution between the sphere and member ABC is 0.5, answer the following: A D B 1. Which of the following has impulse/s that is/are NOT considered negligible during the impact of the sphere to member AB? I. Weight of Member ABC II. Weight of Sphere D III. Impact force between Sphere D and Member ABC IV. The reactions at pin B III only IV only I and II only III and IVonly →arrow_forward
- q3b please answer before 1 pmarrow_forwardAn 8000 kg truck was travelling at a speed of 10 m/s when it collided with a 2000 kg automobile that was parked at a stoplight. The coefficient of restitution observed during the collision was 0.75. If the impact occurred over a time duration of 0.4 s, calculate the magnitude of the average force between the two vehicles during the collision.arrow_forwardA 35,000 Mg ocean liner has an initial velocity of 4 km/h. Neglecting the frictional resistance of the water, determine the time required to bring the liner to rest by using a single tugboat which exerts a constant force of 150 kN.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





