
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260265453
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.2, Problem 13.98P
Using the principles of conservation of energy and conservation of angular momentum, solve part a of Sample Prob. 12.14.
Sample Problem 12.14
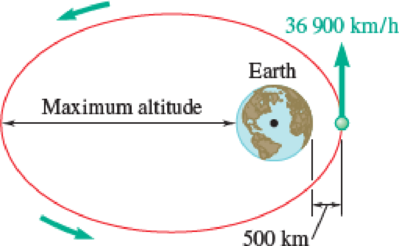
A satellite is launched in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface with a velocity of 36 900 km/h from an altitude of 500 km. Determine (a) the maximum altitude reached by the satellite, (b) the periodic time of the satellite.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?
This is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but how
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 13.1 - Block A is traveling with a speed v0 on a smooth...Ch. 13.1 - A 400-kg satellite is placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 13.1 - A 0.5-lb stone is dropped down the bottomless pit...Ch. 13.1 - A baseball player hits a 5.1-oz baseball with an...Ch. 13.1 - A 500-kg communications satellite is in a circular...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.5PCh. 13.1 - In an ore-mixing operation, a bucket full of ore...Ch. 13.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 13.1 - A 2000-kg automobile starts from rest at point A...Ch. 13.1 - An athlete is holding 30 lb of weights at a height...
Ch. 13.1 - A 1.4-kg model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 13.1 - Packages are thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - A package is thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - A 1200-kg trailer is hitched to a 1400-kg car. The...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.16PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.17PCh. 13.1 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 13.1 - The system shown is at rest when a constant 30-lb...Ch. 13.1 - Car B is towing car A at a constant speed of 10...Ch. 13.1 - The motor applies a constant downward force F =...Ch. 13.1 - The motor applies a constant downward force F to...Ch. 13.1 - Two blocks A and B, of mass 4 kg and 5 kg,...Ch. 13.1 - Four 15-kg packages are placed as shown on a...Ch. 13.1 - A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block...Ch. 13.1 - Solve Prob. 13.26, assuming that the 2-kg block is...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.28PCh. 13.1 - A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the...Ch. 13.1 - A 10-kg block is attached to spring A and...Ch. 13.1 - A 5-kg collar A is at rest on top of, but not...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.32PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.33PCh. 13.1 - Two types of energy-absorbing fenders designed to...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.35PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.36PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.37PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.38PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.39PCh. 13.1 - The sphere at A is given a downward velocity v0...Ch. 13.1 - A bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A...Ch. 13.1 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.1 - In Prob. 13.42, determine the range of values of h...Ch. 13.1 - A small block slides at a speed v on a horizontal...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.45PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.46PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.47PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.48PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.49PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.50PCh. 13.1 - A 1400-kg automobile starts from rest and travels...Ch. 13.1 - The frictional resistance of a ship is known to...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.53PCh. 13.1 - The elevator E has a weight of 6600 lb when fully...Ch. 13.2 - Two small balls A and B with masses 2m and m,...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3CQCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.55PCh. 13.2 - A loaded railroad car of mass m is rolling at a...Ch. 13.2 - A 750-g collar can slide along the horizontal rod...Ch. 13.2 - A 2-lb collar C may slide without friction along a...Ch. 13.2 - Solve Prob. 13.58 assuming the spring CD has been...Ch. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction on the...Ch. 13.2 - For the adapted shuffleboard device in Prob 13.28,...Ch. 13.2 - An elastic cable is to be designed for bungee...Ch. 13.2 - It is shown in mechanics of materials that the...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.2-kg collar can slide along the rod shown. It...Ch. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction along...Ch. 13.2 - A thin circular rod is supported in a vertical...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.67PCh. 13.2 - A spring is used to stop a 50-kg package that is...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.69PCh. 13.2 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.2 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.2 - A 1-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - A 10-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.74PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.75PCh. 13.2 - A small package of weight W is projected into a...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.77PCh. 13.2 - The pendulum shown is given an initial speed v0 at...Ch. 13.2 - Prove that a force F(x, y, z) is conservative if,...Ch. 13.2 - The force F = (yzi + zxj + xyk)/xyz acts on the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.81PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.82PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.83PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.84PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.85PCh. 13.2 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit of minimum...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit 200 mi above the...Ch. 13.2 - How much energy per pound should be imparted to a...Ch. 13.2 - Knowing that the velocity of an experimental space...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.90PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.91PCh. 13.2 - (a) Show that, by setting r = R + y in the...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - A governor is designed so that the valve of...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - Using the principles of conservation of energy and...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.99PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft is describing an elliptic orbit of...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit, 185 mi above...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.102PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.103PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.104PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.105PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.106PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.107PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.108PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.109PCh. 13.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit at an...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.111PCh. 13.2 - Show that the values vA and vP of the speed of an...Ch. 13.2 - Show that the total energy E of an earth satellite...Ch. 13.2 - A space probe describes a circular orbit of radius...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.115PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft of mass m describes a circular orbit...Ch. 13.2 - Using the answers obtained in Prob. 13.108, show...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.118PCh. 13.3 - A large insect impacts the front windshield of a...Ch. 13.3 - The expected damages associated with two types of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.1IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.2IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.3IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.4IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.5IMDCh. 13.3 - A 35 000-Mg ocean liner has an initial velocity of...Ch. 13.3 - A 2500-lb automobile is moving at a speed of 60...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.121PCh. 13.3 - A truck is hauling a 300-kg log out of a ditch...Ch. 13.3 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 13.3 - Steep safety ramps are built beside mountain...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.125PCh. 13.3 - The 18 000-kg F-35B uses thrust vectoring to allow...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.127PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.128PCh. 13.3 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.3 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.3 - A tractor-trailer rig with a 2000-kg tractor, a...Ch. 13.3 - The motor applies a constant downward force F =...Ch. 13.3 - An 8-kg cylinder C rests on a 4-kg platform A...Ch. 13.3 - An estimate of the expected load on...Ch. 13.3 - A 60-g model rocket is fired vertically. The...Ch. 13.3 - A 12-lb block, which can slide on a frictionless...Ch. 13.3 - A crash test is performed between an SUV A and a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.138PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.139PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.140PCh. 13.3 - The triple jump is a track-and-field event in...Ch. 13.3 - The last segment of the triple jump...Ch. 13.3 - The design for a new cementless hip implant is to...Ch. 13.3 - A 28-g steel-jacketed bullet is fired with a...Ch. 13.3 - A 120-ton tugboat is moving at 6 ft/s with a slack...Ch. 13.3 - At an intersection, car B was traveling south and...Ch. 13.3 - The 650-kg hammer of a drop-hammer pile driver...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.148PCh. 13.3 - Bullet B weighs 0.5 oz and blocks A and C both...Ch. 13.3 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand at opposite...Ch. 13.3 - A 75-g ball is projected from a height of 1.6 m...Ch. 13.3 - A ballistic pendulum is used to measure the speed...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.153PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.154PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg ball A strikes a 1-kg ball B that is...Ch. 13.4 - A sphere with a speed v0 rebounds after striking a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7IMDCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8IMDCh. 13.4 - A 10-kg ball A moving horizontally at 12 m/s...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.10IMDCh. 13.4 - Two steel blocks slide without friction on a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.156PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.157PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.158PCh. 13.4 - To apply shock loading to an artillery shell, a...Ch. 13.4 - Packages in an automobile parts supply house are...Ch. 13.4 - Three steel spheres of equal mass are suspended...Ch. 13.4 - At an amusement park, there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - At an amusement park there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.164PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.165PCh. 13.4 - A 600-g ball A is moving with a velocity of...Ch. 13.4 - Two identical hockey pucks are moving on a hockey...Ch. 13.4 - A billiard player wishes to have ball A hit ball B...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.169PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.170PCh. 13.4 - A girl throws a ball at an inclined wall from a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.172PCh. 13.4 - From experimental tests, smaller boulders tend to...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.174PCh. 13.4 - A 1-kg block B is moving with a velocity v0 of...Ch. 13.4 - A 0.25-lb ball thrown with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 13.4 - After having been pushed by an airline employee,...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.178PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 2 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 3 m...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.181PCh. 13.4 - Block A is released from rest and slides down the...Ch. 13.4 - A 23.1-kg sphere A of radius 90 mm moving with a...Ch. 13.4 - A test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb...Ch. 13.4 - Ball B is hanging from an inextensible cord. An...Ch. 13.4 - A 70-g ball B dropped from a height h0 = 1.5 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 2-kg sphere moving to the right with a velocity...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-lb...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-kg...Ch. 13 - A 34,000-lb airplane lands on an aircraft carrier...Ch. 13 - There has been renewed interest in pneumatic tube...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.192RPCh. 13 - A section of track for a roller coaster consists...Ch. 13 - Two identical 40-lb curling stones have diameters...Ch. 13 - A 300-g block is released from rest after a spring...Ch. 13 - A kicking-simulation attachment goes on the front...Ch. 13 - A 625-g basketball and a 58.5-g tennis ball are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.198RPCh. 13 - A 2-kg ball B is traveling horizontally at 10 m/s...Ch. 13 - A 2-kg block A is pushed up against a spring...Ch. 13 - The 2-lb ball at A is suspended by an inextensible...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 =6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm S 133 mm 140 mm Please solve the question above I solved the question but I'm sure the answer is wrong the link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w5UD2EPDiaKSx3W33aj Rv0olChuXtrQx/view?usp=sharingarrow_forward
- Q2: (15 Marks) A water-LiBr vapor absorption system incorporates a heat exchanger as shown in the figure. The temperatures of the evaporator, the absorber, the condenser, and the generator are 10°C, 25°C, 40°C, and 100°C respectively. The strong liquid leaving the pump is heated to 50°C in the heat exchanger. The refrigerant flow rate through the condenser is 0.12 kg/s. Calculate (i) the heat rejected in the absorber, and (ii) the COP of the cycle. Yo 8 XE-V lo 9 Pc 7 condenser 5 Qgen PG 100 Qabs Pe evaporator PRV 6 PA 10 3 generator heat exchanger 2 pump 185 absorberarrow_forwardQ5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forwardA mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forward
- my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning
Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Understanding Motor Controls
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337798686
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305494695
Author:Larry Jeffus
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Extent of Reaction; Author: LearnChemE;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__stMf3OLP4;License: Standard Youtube License