
Concept explainers
A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the position shown, slides down the inclined rod, and compresses the spring. The direction of motion is reversed and the collar slides up the rod. Knowing that the maximum deflection of the spring is 5 in., determine (a) the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and the rod, (b) the maximum speed of the collar.
Fig. P13.29
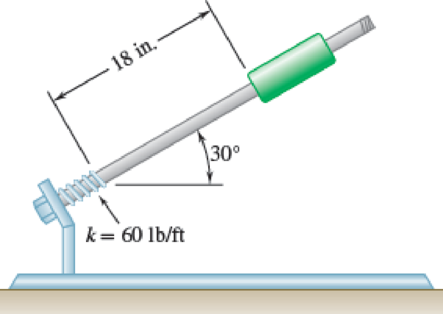
(a)
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Answer to Problem 13.29P
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the collar
The maximum deflection of the spring (x) is
The distance between the spring and collar (d) is
The spring constant (k) is
The angle of the inclined rod
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the inclined rod with the forces acting as in Figure (1).
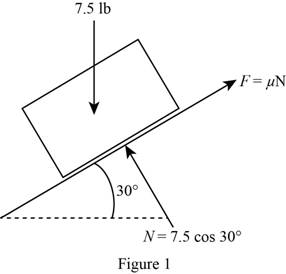
Here, the initial kinetic energy
Calculate the work done
Here, F is the frictional force.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
(b)
Find the maximum speed
Answer to Problem 13.29P
The maximum speed
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the collar
The maximum deflection of the spring (x) is
The distance between the spring and collar (d) is
The spring constant (k) is
The angle of the inclined rod
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Calculate the kinetic energy
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Here, F is the frictional force.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Substitute 0.159 for
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the maximum speed
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the maximum speed
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





