
Concept explainers
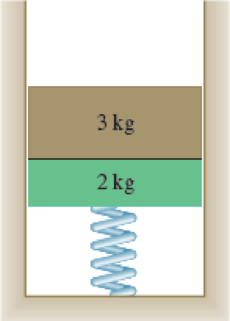
A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block supported by, but not attached to, a spring of constant 40 N/m. The upper block is suddenly removed. Determine (a) the maximum speed reached by the 2-kg block, (b) the maximum height reached by the 2-kg block.
Fig. P13.26
(a)
Find the maximum speed
Answer to Problem 13.26P
The maximum speed
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The spring constant (k) is
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Consider the position 1, the block B has been removed.
Calculate the spring stretch
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Take the position 2 be later position while the spring still in contact with block A.
Calculate the work of the force exerted
Integrate the above equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute,
Calculate the work of the gravitational force
Substitute,
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Here, the initial kinetic energy
Calculate the kinetic energy
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Write the expression for the principle of work and energy:
Substitute 0 for
At the maximum speed, differentiate the velocity equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum speed
(b)
Find the maximum height (h) reached by the
Answer to Problem 13.26P
The maximum height (h) reached by the
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The spring constant (k) is
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Consider the position 3, the block A reached the maximum height and assume that the block has separated from the spring so the spring is zero at the separation.
Calculate the work of the force exerted
Integrate the above equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute,
Calculate the work of the gravitational force
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
At the maximum height, the velocity
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the maximum height (h) reached by the
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the maximum height (h) reached by the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? n+1 6) a = 1- 2n (-1)+1 7) a = 2n-1 2n 8) an = n+1 1 9) a = sin + 2 n sin n 10) a = n 11) an = 12) a = 13) an 14) an 15) an 16) an n 2" In(n+1) = 81/n n n =(1+7)" = = 10n 3 n 1/n 17) an = In n 1/n n' 18) a =√4"narrow_forwardQu 3 Nickel (Ni) single crystal turbine blades burn less fuel at higher temperatures because blades are grown on [110] closed packed direction. Nickel (Ni) at 20°C is FCC, and has an atomic radius, R, of 0.125 nm. Draw a reduced-sphere unit cell for this crystal and draw and label the vector [I 10], starting from the origin (0, 0, 0). a) Calculate the length of the vector [| 10] in nanometers. Express your answer in nanometers to one significant figure. b) Calculate the linear density of Nickel in the [| 1 0] direction in [atom/nm]. Express your answer in atoms/nm to one significant figure. show all work problemsarrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardRequired information An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been measured and found to be εΑ = +490 μ εB=-70 μ Know that E = 200 GPa. 25 mm 30 mm 90 mm 45 mm B Determine the distance d. The distance dis 15 mm mm.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardNo use chatgptarrow_forwardProblem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





