
Concept explainers
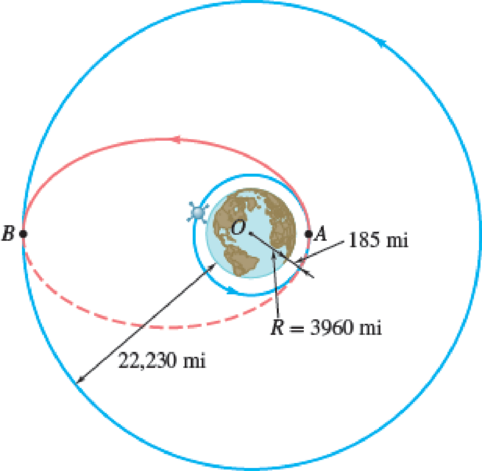
While describing a circular orbit, 185 mi above the surface of the earth, a space shuttle ejects at point A an inertial upper stage (IUS) carrying a communications satellite to be placed in a geosynchronous orbit (see Prob. 13.87) at an altitude of 22,230 mi above the surface of the earth. Determine (a) the velocity of the IUS relative to the shuttle after its engine has been fired at A, (b) the increase in velocity required at B to place the satellite in its final orbit.
Fig. P13.101
(a)
Find the velocity of the IUS relative to the shuttle after its engine has been fired at A
Answer to Problem 13.101P
The velocity of the IUS relative to the shuttle after its engine has been fired at A
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance from above the earth surface to the circular orbit (x) is
The altitude of the geosynchronous orbit (A) is
The radius of the earth (R) is
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Convert the unit of radius of earth (R) from miles to feet using the relation:
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the force acting on the spacecraft on the surface of the earth due to gravity
Write the expression for calculating the geocentric force acting on the spacecraft when it is on the surface of earth
Here, G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the earth and
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression for the centripetal force acting on the space shuttle carrying satellite rotating around the earth at the given altitude as follows:
Here, m is the mass of the space shuttle,
Write the expression for the geocentric force acting on the spacecraft rotating at the given altitude around the earth (F) as follows;
Equate the equations (1) and (2).
Calculate the altitude of the space shuttle from center of earth at position A
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of space shuttle at point A inertial upper stage
Substitute
Calculate the altitude of the space shuttle from center of earth at position A
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of space shuttle at point B
Substitute
Use the principle of conservation of angular momentum states that in the absence of external torque acting on the body, the angular momentum remains constant and no change of the momentum occurs during the entire process.
Find the velocity at B:
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the kinetic energy of the space shuttle at point A
Write the expression for the kinetic energy of the space shuttle at point B
Write the expression for the gravitational potential energy of the space shuttle at position A in the path AB
Write the expression for the gravitational potential energy of the space shuttle at position B in the path AB
Use the principle of conservation of energy states that sum of the kinetic and potential energy of a particle remains constant.
Calculate the speed of the space shuttle at position A
Write the expression for the conservation of energy as follows:
Substitute
Find the velocity at A:
Substitute
Consider the equation (1).
Find the velocity at B:
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of the IUS relative to the shuttle after the engine has been fired at point A
Substitute
Therefore, the velocity of the IUS relative to the shuttle after its engine has been fired at A
(b)
Find the increase in velocity required at B
Answer to Problem 13.101P
The increase in velocity required at B
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance from above the earth surface to the circular orbit (x) is
The altitude of the geosynchronous orbit (A) is
The radius of the earth (R) is
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Calculate the increase in the velocity required at B to place the satellite in its final orbit
Substitute
Therefore, the increase in velocity required at B
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Complet the solution: Vavg Ti Te Ts Qhexp Nuexp htheo Re Nutheo Error (m/s) (°C) (°C) (°C) (W) 2.11 18.8 21.3 45.8 2.61 18.5 20.8 46.3 Heat transfer Given data: a= 10 cm. L= 10 cm. b= 20 cm. H=40cm. ⚫ a = 10, cm: This could represent the width of the duct. ⚫b=20, cm: This might be the height of the duct. ⚫L = 10, cm: This usually stands for the length of the duct in the direction of flow. ⚫H=40, cm: This could indicate the height of some component or another duct-related dimension, but the exact meaning depends on the experiment's context.arrow_forwardplease explain each step and include drawings on the phase diagram. thanksarrow_forwardWrite clearly which points correspond to concentration of solute in front of alpha, concentration of solute in front of beta, amount of solid in the liquid in front of alpha/beta, lowest possible energy (tangent), as well as any other important information. Thank youarrow_forward
- Q3: A 4-stroke 6 litres engine is fuelled with methane (CH4) at an air-fuel ratio = 0.8. It operates at 2000 rpm with a volumetric efficiency of 80%. The exhaust (product) leaves the engine at 800 K, and the heat lost to the coolant is 3.4×105 kJ/kmol. What is the engine's output power? Assume both air and fuel (methane) inlet to the engine at 298 K. Take for methane, the molecular weight is M = 16 kg/kmol, and the heat of combustion is 50.01 MJ/kg. The ambient conditions (p = 101 kPa, T = 25 °C). (24 points)arrow_forwardTemperature (°C) 100 4. Consider the solidification of a binary Pb-10%Sn alloy. Assume that during solidification, there is complete mixing in the liquid and no diffusion in the solid. Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. (a) Draw (on the phase diagram) the compositions of the liquid and the solid at the interface as a function of temperature during solidification. (b) Illustrate on the phase diagram how one would calculate the volume fraction solidified at a given temperature. (c) (d) Indicate the temperature at which solidification is complete. Do you expect ẞ to be present in the as-cast microstructure? Explain 300 327°C 200 a (Pb) 20 20 a + L 18.3 183°C α + β 40 60 Composition (wt% Sn) Liquid 600 500 232°C B+L 400 B 61.9 97.8 300 808 100 (Sn) 200 100 Temperature (°F)arrow_forwardI tried this problem a couple of times and don't know where I'm going wrong can you help me out pleasearrow_forward
- y(0)=1, Using Laplace transforms solve the following differential equations : 11) y"-4y+4y=0, 12) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=2.1, y'(0) = 3.9 y'(0)=-3. 13) y+7y+12y=21e", y(0)=3.5, y'(0)=-10. 14) +9y=10e. y(0)=0, y'(0) = 0. 15) y+3y+2.25y=91³ +64, y(0)=1, y'(0) = 31.5 16) -6y+5y= 29 cos(21), y(0)=3.2, y'(0)=6.2 17) "+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 18) +2y+17y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=12. 19) y-4y+5y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0) = 2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3.arrow_forward4. Consider the rectangulan 2535 Let 16 a and section discussed 977b + class. in ie make a M thin" rectangle, Can you you show that Q = Go {a² = x² } . Imax = 2 Ga ты J =arrow_forward1. Consider a circular shaft in torsion that of radius r=b has a key way as shown, circle of radius a Let us try the solution x₁ (5,0) = k (6² = r²) (1- 2 awso 1.1 Does this solve the problem for the stres rer 1,2 Solve for is and 23.arrow_forward
- 3. - a For an elliptical cross that the tangent to section resultant shear can you s stress is show ellipse with the same 24 i ratio of eccentricity, in passes through to point alb that in question, it + Parrow_forward2. Consider the rod with an elliptical that strain 4 a Cross secton considered in class, Integrate the was displacement displacements, relations to obtain thearrow_forwardPlease answer Oxygen at 300 kPa and 90°C flowing at an average velocity of 3 m/s is expanded in an adiabatic nozzle. What is the maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle when the outlet pressure is 60 kPa? Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle is 532.5 Numeric ResponseEdit Unavailable. 532.5 incorrect.m/s.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





