
You are an engineer for a plastics manufacturing company. In examining cost-saving measures, your team has brainstormed the following ideas (labeled Idea A and Idea B). It is your responsibility to evaluate these ideas and recommend which one to pursue. You have been given a graph of the current process. A copy of this graph has been provided online; you may use one of these graphs, or use graph paper as directed by your instructor.
- a. What is the selling price of the product?
Current Cost: The current process has been running for a number of years, so there are no initial fixed costs to consider.
In the operating costs, the process requires the following:
|
$2.00/pound-mass of resin |
|
S0.15/pound-mass of resin |
|
$0.10/pound-mass of resin |
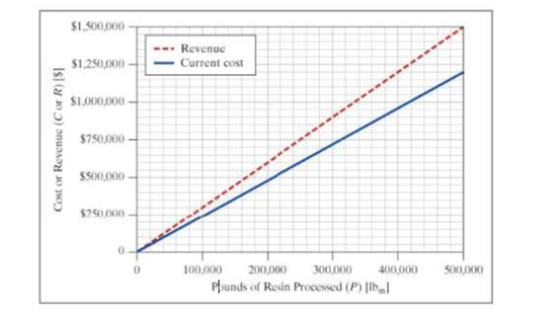
- b. There is also a cost associated with taking the scrap material to the landfill. Using the total cost determined from the graph, find the cost of landfill, in dollars per pound-mass of resin.
Idea A: Your customer will allow you to use regrind (reprocessed plastic) in the parts instead of 100% virgin plastic. Your process generates 10% scrap. Evaluate using all your scrap materials as regrind, with the regrind processed at your plant.
- c. You will need to purchase a regrind machine to process the plastic, estimated at a cost of $100,000. Using the regrind will alter the following costs, which account for using 10% scrap material:
| ■ Material cost: | $1.80/pound-mass of resin |
| ■ Energy cost: | $0.16/pound-mass of resin |
| ■ Labor cost: | $0.11/pound-mass of resin |
This idea will eliminate the landfill charge required in the current process (see part [b]). Draw the total cost curve for Idea A on the graph or on a copy.
- d. How long (in pounds of resin processed) before the company reaches breakeven on Idea A?
- e. At what minimum level of production (in pound-mass of resin processed) will Idea A begin to generate more profit than the current process?
Your customer will allow you to use regrind (reprocessed plastic) in the parts instead of 100% virgin plastic. Evaluate using 25% regrind purchased from an outside vendor.
- f. Using the regrind from the other company will alter the following costs, which account for using 25% scrap material purchased from the outside vendor:
| ■ Material cost: | $1.85/pound-mass of resin |
| ■ Energy cost: | $0.15/pound-mass of resin |
| ■ Labor cost: | $0.11/pound-mass of resin |
This idea will eliminate the landfill charge required in the current process (see part [b]) and will not require the purchase of a regrind machine as discussed in Idea A. Draw the total cost curve for Idea B on the graph or on a copy.
- g. At what minimum level of production (in pound-mass of resin processed) will Idea B begin to generate more profit than the current process?
- h. At a production level of 500,000 pound-mass of resin, which Idea (A, B, or neither) gives the most profit over the current process?
- i. If the answer to part (h) is neither machine, list the amount of profit generated by the current process at 500,000 pound-mass of resin. If the answer to part (h) is Idea A or Idea B, list the amount of profit generated by that idea at 500,000 pound-mass of resin.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Modern Database Management
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
- A 7.25-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an elevation of 17 m. If the mechanical efficiencyof the pump is 84 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of water.arrow_forwardConsider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPaarrow_forwardA race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!arrow_forward
- Figure: 06_P041 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. 400 mm 15° 20 mm A 15° 15 D B 30 mm² 80 mm 20 mm 400 mm Figure: 06_P090 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forwardFor Problems 18-22 (Table 7-27), design a V-belt drive. Specify the belt size, the sheave sizes, the number of belts, the actual output speed, and the center distance.arrow_forward
- only 21arrow_forwardonly 41arrow_forwardNormal and tangential components-relate to x-y coordinates A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I need help with finding the y component of the total acceleration. I had put -32 but its incorrect. but i keep getting figures around that numberarrow_forward
- The bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forwardConsider the angle bar shown in the given figure A W 240 mm B 80 mm Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the reactions at A and B when a = 150 mm. This problem could also be approached as a 3-force body using method of Section 4.2B.arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





