
Concept explainers
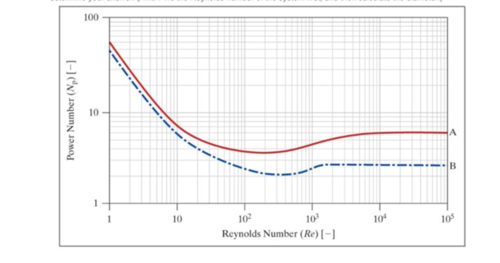
The relationship of the power required by a propeller (show as the power number, on the ordinate) and the Reynolds number (abscissa) is shown in the following graph. For a propeller, the Reynolds number (Re) is written slightly differently as
where D is the blade diameter [meters] and n is the shaft speed [hertz]. The power number (Nρ) is given by the following, where P is the power required [watts].
Use the following chart to answer questions (a) through (d).
- a. If the Reynolds number is 500, what is the power number for a system described by curve A?
- b. If the power number (Nρ) is 30, what is the Reynolds number for a system described by curve A?
- c. If the Reynolds number is 4000, what is the power (P) required in units of watts at a shaft speed (n) of 0.03 hertz? Assume the system contains acetone, with a kinematic viscosity of 0.419 stokes. The density of acetone is 0.785 grams per cubic centimeters. Use curve B in the graph to determine your answer. (Hint: Use the Reynolds number of the system to first calculate the diameter, then find the power number, and then calculate the power.)
- d. If the power number (Nρ) is 5, what is the diameter (D) of the blade in units of centimeters at a shaft speed (n) of 0.02 hertz? Assume the system contains brine, with a kinematic viscosity of 0.0102 stokes. Use curve A in the graph to determine your answer. (Hint: Find the Reynolds number of the system first, and then calculate the diameter.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- w1 Three distributed loads act on a beam as shown. The load between A and B increases linearly from 0 to a maximum intensity of w₁ = 12.8 lb/ft at point B. The load then varies linearly with a different slope to an intensity of w₂ = 17.1 lb/ft at C. The load intensity in section CD of the beam is constant at w3 10.2 lb/ft. For each load region, determine the resultant force and the location of its line of action (distance to the right of A for all cases). cc 10 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl = WI W2 W3 -b- C Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 4.50 ft b 5.85 ft с 4.28 ft The resultant load in region AB is FR₁ = lb and acts ft to the right of A. The resultant load in region BC is FR2 lb and acts = ft to the right of A. The resultant load in region CD is FR3 = lb and acts ft to the right of A.arrow_forwardThe T-shaped structure is embedded in a concrete wall at A and subjected to the force F₁ and the force-couple system F2 1650 N and M = 1,800 N-m at the locations shown. Neglect the weight of the structure in your calculations for this problem. = a.) Compute the allowable range of magnitudes for F₁ in the direction shown if the connection at A will fail when subjected to a resultant moment with a magnitude of 920 N- m or higher. b.) Focusing on the forces and igonoring given M for now. Using the value for F1, min that you calculated in (a), replace the two forces F₁ and F2 with a single force that has equivalent effect on the structure. Specify the equivalent →> force Feq in Cartesian components and indicate the horizontal distance from point A to its line of action (note this line of action may not intersect the structure). c.) Now, model the entire force system (F1,min, F2, and M) as a single force and couple acting at the junction of the horizontal and vertical sections of the…arrow_forwardThe heated rod from Problem 3 is subject to a volumetric heating h(x) = h0 x L in units of [Wm−3], as shown in the figure below. Under the heat supply the temperature of the rod changes along x with the temperature function T (x). The temperature T (x) is governed by the d following equations: − dx (q(x)) + h(x) = 0 PDE q(x) =−k dT dx Fourier’s law of heat conduction (4) where q(x) is the heat flux through the rod and k is the (constant) thermal conductivity. Both ends of the bar are in contact with a heat reservoir at zero temperature. Determine: 1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem. 2. The temperature function T (x). 3. The heat flux function q(x). Side Note: Please see that both ends of bar are in contact with a heat reservoir at zero temperature so the boundary condition at the right cannot be du/dx=0 because its not thermally insulated. Thank youarrow_forward
- The elastic bar from Problem 1 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω2x. Under this radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement d u(x) is governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (2) where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ is the mass density, and E is the (constant) Young’s modulus. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0 and it is also pinned at x = L. Determine: 1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem. 2. The displacement function u(x). 3. The stress function σ(x). SIDE QUESTION: I saw a tutor solve it before but I didn't understand why the tutor did not divide E under the second term (c1x) before finding u(x). The tutor only divided E under first term. please explain and thank youarrow_forwardcalculate the total power required to go 80 mph in a VW Type 2 Samba Bus weighing 2310 lbs. with a Cd of 0.35 and a frontal area of 30ft^2. Consider the coefficient of rolling resistance to be 0.018. What is the increase in power required to go the same speed if the weight is increased by 2205 pounds (the rated carrying capacity of the vehicle). If the rated power for the vehicle is 49 bhp, will the van be able to reach 80 mph at full carrying capacity?arrow_forwardA distillation column with a total of 13 actual stages (including a partial condenser) is used to perform a separation which requires 7 ideal stages. Calculate the overall column efficiency, and report your answer in %arrow_forward
- 6. Consider a 10N step input to the mechanical system shown below, take M = 15kg, K = 135N/m, and b = 0.4 Ns/m. (a) Assume zero initial condition, calculate the (i) System pole (ii) System characterization, and (iii) The time domain response (b) Calculate the steady-state value of the system b [ www K 个 х M -F(+)arrow_forward2. Solve the following linear time invariant differential equations using Laplace transforms subject to different initial conditions (a) y-y=t for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 1 (b) ÿ+4y+ 4y = u(t) for y(0) = 0 and y(0) = 1 (c) y-y-2y=0 for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 0arrow_forward3. For the mechanical systems shown below, the springs are undeflected when x₁ = x2 = x3 = 0 and the input is given as fa(t). Draw the free-body diagrams and write the modeling equations governing each of the systems. K₁ 000 K₂ 000 M₁ M2 -fa(t) B₂ B₁ (a) fa(t) M2 K₂ 000 B K₁ x1 000 M₁ (b)arrow_forward
- This question i m uploading second time . before you provide me incorrect answer. read the question carefully and solve accordily.arrow_forward1. Create a table comparing five different analogous variables for translational, rotational, electrical and fluid systems. Include the standard symbols for each variable in their respective systems.arrow_forward2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities v₁ and v₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 m2 βarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





