
ORG CHEM CONNECT CARD
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264860746
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 64P
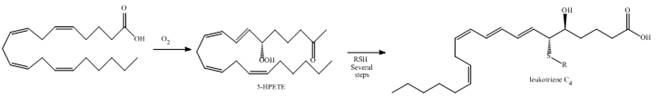
As described in Section 9.16, the leukotrienes, important components in the asthmatic response, are synthesized from arachidonic acid via the hydroperoxide
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage
A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction:
3+
3Cu²+ (aq) +2Al(s) → 3 Cu(s)+2A1³* (aq)
2+
Suppose the cell is prepared with 5.29 M Cu
in one half-cell and 2.49 M A1³+ in the other.
Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
x10
μ
☑
00.
18
Ar
И
Please help me solve this homework problem
Please help me answer this homework question
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORG CHEM CONNECT CARD
Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 13.5 - Problem 15.8 Which bond in the each compound is...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 10PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13PCh. 13.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 13 - Prob. 27PCh. 13 - Prob. 28PCh. 13 - Prob. 34PCh. 13 - 15.37 What alkane is needed to make each alkyl...Ch. 13 - 15.38 Which alkyl halides can be prepared in good...Ch. 13 - Prob. 37PCh. 13 - 15.40 Explain why radical bromination of p-xylene...Ch. 13 - a. What product(s) (excluding stereoisomers) are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 40PCh. 13 - 15.43 Draw the products formed when each alkene is...Ch. 13 - 15.44 Draw all constitutional isomers formed when...Ch. 13 - 15.45 Draw the organic products formed in each...Ch. 13 - Prob. 45PCh. 13 - 15.47 Treatment of a hydrocarbon A (molecular...Ch. 13 - 15.48 Draw the products formed in each reaction...Ch. 13 - 15.53 Consider the following bromination: .
a....Ch. 13 - 15.54 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 13 - Prob. 57PCh. 13 - 15.57 Devise a synthesis of each compound from...Ch. 13 - Prob. 59PCh. 13 - Prob. 60PCh. 13 - 15.60 Devise a synthesis of each compound using ...Ch. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - Prob. 63PCh. 13 - 15.63 As described in Section 9.16, the...Ch. 13 - 15.64 Ethers are oxidized with to form...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3+ H2(g)+2OH¯ (aq) + 2Fe³+ (aq) → 2H₂O (1)+2Fe²+ (aq) 0 kJ x10 Х ? olo 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 184.2 mL of a 0.7800M solution of dimethylamine ((CH3) NH with a 0.3000M solution of HClO4. The pK₁ of dimethylamine is 3.27. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 424.1 mL of the HClO solution to it. 2 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO 4 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ ? 000 18 Ar 1 Barrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: MnO2 (s)+4H* (aq)+2Cr²+ (aq) → Mn²+ (aq)+2H₂O (1)+2Cr³+ (aq) + 2+ 2+ 3+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 7.44 M H* and 0.485 M Cr²+ in one half-cell and 7.92 M Mn² and 3.73 M Cr³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐ x10 μ Х 5 ? 000 日。arrow_forward
- Calculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. NO (g) +H₂O (1) + Cu²+ (aq) → HNO₂ (aq) +H* (aq)+Cu* (aq) kJ - ☐ x10 x10 olo 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid b An analytical chemist is titrating 116.9 mL of a 0.7700M solution of aniline (C6H5NH2) with a 0.5300M solution of HNO3. The pK of aniline is 9.37. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 184.2 mL of the HNO 3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ 5arrow_forwardQUESTION: Find the standard deviation for the 4 different groups 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 STDEV = STDEV = STDEV = STDEV =arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression' *The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been providedarrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage Try Again Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ Ba(s) (aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) →>> Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 1.71 V ☐ x10 ☑ 5 0/5 ? 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardQuestion: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below: (x1 -x̄) 370.5 (y1 - ȳ) 5.240 (x2 - x̄) 142.5 (y2 - ȳ) 2.004 (x3 - x̄) 28.5 (y3 - ȳ) 0.390 (x4 - x̄) -85.5 (y4 - ȳ) -1.231 (x5 - x̄) -199.5 (y5 - ȳ) -2.829 (x6 - x̄) -256.5 (y6 - ȳ) -3.575arrow_forward
- Calculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY