
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780357391594
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim; William H. Brown; Mary K. Campbell
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 61P
14-71 The mechanism of the acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol to an
Step 1: Add a proton.
Step 2: Break a bond to form stable molecules or ions. Step 3: Take away a proton.
These three steps are illustrated here by the dehydration of 2-butanol to give 2-butene. Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons in each step; that is, show how each bond-making or bond-breaking step occurs.
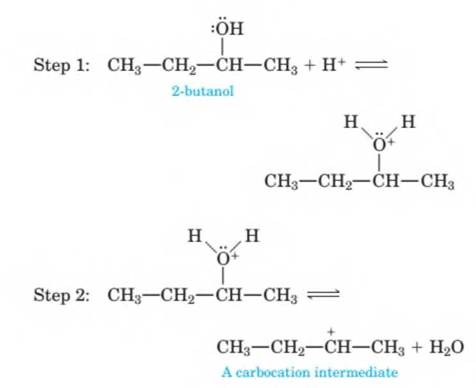
H
I +
Step 3: CH3—CH—CH—CH3
CH3—CH=CH—CH3 + H +
2-butene
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohols proceeds through an E1 mechanism. The
first step is the protonation of the alcohol oxygen to form an oxonium ion.
Dehydration of 3-methyl-2-butanol forms one major and two minor organic products. Draw the structures,
including hydrogen atoms, of the three organic products of this reaction.
н
н
:бн
н
Нас.
Нас.
CHз
CH3
ČH3
CH3
3-methyl-2-butanol
an oxonium ion
Major Product
Minor Product
Minor Product
Phenols are aromatic rings with an alcohol functional group attached directly to the ring. These compounds have unique acidity and solubility for alcohol groups. Predict the solubility of this phenol in water.
Complete the reaction shown below.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.1QCCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.2QCCh. 13.2 - Problem 14-3 Draw structural formulas for the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.4QCCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.5QCCh. 13.3 - Problem 14-6 Write the common name for each ether.Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7QCCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8QCCh. 13 - 14-8 Answer true or false. The functional group of...Ch. 13 - 14-9 What is the difference in structure between a...
Ch. 13 - 14-10 Which of the following are secondary...Ch. 13 - 14-11 Which of the alcohols in Problem 14-10 are...Ch. 13 - 14-12 Write the 1UPAC name of each compound. (e)...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6PCh. 13 - Prob. 7PCh. 13 - 14-15 Both alcohols and phenols contain an —OH...Ch. 13 - Prob. 9PCh. 13 - 14-17 Explain in terms of noncovalent interactions...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11PCh. 13 - Prob. 12PCh. 13 - 14-20 Show hydrogen bonding between methanol and...Ch. 13 - 14-21 Show hydrogen bonding between the oxygen of...Ch. 13 - 14-22 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 13 - 14-23 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 13 - 14-24 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) is commonly...Ch. 13 - Prob. 18PCh. 13 - Prob. 19PCh. 13 - Prob. 20PCh. 13 - 14-28 Give the structural formula of an alkene or...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - 14-30 Show how to distinguish between cyclohexanol...Ch. 13 - 14-31 Compare the acidity of alcohols and phenols,...Ch. 13 - 14-32 Both 2,6-diisopropylcyclohexanol and the...Ch. 13 - 14-33 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 13 - 14-34 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 13 - 14-35 Write equations for the reaction of each of...Ch. 13 - 14-36 Show how to convert cyclohexanol to these...Ch. 13 - Prob. 30PCh. 13 - Prob. 31PCh. 13 - 14-39 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 13 - 14-40 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 13 - Prob. 34PCh. 13 - 14-42 Write the common name for each ether. ch3...Ch. 13 - Prob. 36PCh. 13 - 14-44 Answer true or false. (a) The functional...Ch. 13 - Prob. 38PCh. 13 - Write the common name for each thiol in Problem 38...Ch. 13 - 14-47 Following are structural formulas for...Ch. 13 - 14-48 Explain why methanethiol, CH3SH, has a lower...Ch. 13 - 14-49 Answer true or false. Today, the major...Ch. 13 - (Chemical Connections 13A ) As stated in the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 44PCh. 13 - Prob. 45PCh. 13 - Prob. 46PCh. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - (Chemical Connections 13D ) Show that enflurane...Ch. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - 14-60 Write a balanced equation for the complete...Ch. 13 - 14-61 Knowing what you do about electronegativity,...Ch. 13 - 14-62 Draw structural formulas and write IUPAC...Ch. 13 - Prob. 53PCh. 13 - 14-64 Explain why the boiling point of ethylene...Ch. 13 - Prob. 55PCh. 13 - 14-66 1,4-Butanediol, hexane, and 1-pentanol have...Ch. 13 - 14-67 Of the three compounds given in Problem...Ch. 13 - Prob. 58PCh. 13 - 14-69 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 13 - 14-70 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 13 - 14-71 The mechanism of the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - 14-73 Lipoic acid is a growth factor for many...Ch. 13 - 14-74 Following is a structural formula for the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 65PCh. 13 - Prob. 66PCh. 13 - Prob. 67PCh. 13 - 14-78 Consider alkenes A, B, and C. each of which...Ch. 13 - Prob. 69P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 14-33 Write equations for the reaction of 1-butanol, a primary alcohol, with these reagents. H2SO4, heat K2Cr2O7, H2SO4arrow_forward14-34 Write equations for the reaction of 2-butanol with these reagents. H2SO4, heat K2Cr2O7, H2SO4arrow_forward14-36 Show how to convert cyclohexanol to these compounds. Cyclohexene Cyclohexane Cyclohexanone Bromocyclohexanearrow_forward
- 14-28 Give the structural formula of an alkene or alkenes from which each alcohol can be prepared. 2-Butanol 1-Methylcyclohexanol 3-Hexanol 2-Methyl-2-pentanol Cyclopentanolarrow_forward14-48 Explain why methanethiol, CH3SH, has a lower boiling point (6°C) than methanol, CH3OH (65°C), even though methanethiol has a higher molecular weightarrow_forward14-30 Show how to distinguish between cyclohexanol and cyclohexene by a simple chemical test. Tell what you would do, what you would expect to see, and how you would interpret your observation.arrow_forward
- 14-78 Consider alkenes A, B, and C. each of which has the same molecular formula, C(.H12. Alkenes B and C can each be separated into cis and trans isomers. Upon catalytic reduction using H,, in the presence of a transition metal catalyst (Ni, Pd, or Pt>, alkenes A, B, and C all give hexane as the only product. Acid- catalyzed hydration of alkene C gives one alcohol with the molecular formula CeH14O. Acid catalyzed- hydration of alkene B gives an equal mixture of two alcohols, each with the molecular formula C6H14O. Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkene C gives only a single alcohol with the molecular formula C6H14O. Propose structural formulas for alkenes A, B, and C and the alcohols formed by acid-catalyzed hydration of each, consistent with these experimental results.arrow_forward14-20 Show hydrogen bonding between methanol and water in the following ways. Between the oxygen of methanol and a hydrogen of water Between the hydrogen of methanol’s OH group and the oxygen of waterarrow_forward14-31 Compare the acidity of alcohols and phenols, which are both classes of organic compounds that contain an —OH group.arrow_forward
- 14-9 What is the difference in structure between a primary, a secondary, and a tertiary alcohol?arrow_forward14-69 Show how to prepare each compound from 2-methyl-1 -propanol. 2-Methylpropene 2-Methyl-2-propanol 2-Methylpropanoic acid, (CH3)2CHCOOHarrow_forward14-55 (Chemical Connections 140 The legal definition of being under the influence of alcohol is based on blood alcohol content. What is the relationship between breath alcohol content and blood alcohol content?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Acid-Base Titration | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFqx6_Y6c2M;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY