
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The compound, which reacts faster with sodium methoxide in methanol in each of the given pair of compounds is to be determined and the chemical equation for the faster reaction is to be written.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic
In nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, the nucleophile substitutes a leaving group from the aryl ring.
Aryl halides bearing an electron withdrawing substituent undergo nucleophilic substitution rapidly.
The substituents attached ortho and para with respect to the halogen atom in the aryl halide react at similar rates. The substituents attached at meta position in the aryl halide react at slower rates than ortho and para substituents.
Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize the intermediate carbanion formed and thus are strongly activating substituents in the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Electron donating substituents destabilize the intermediate carbanion formed and thus are strongly deactivating substituents in the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Answer to Problem 43P
Solution:
a)
The reaction is as follows:
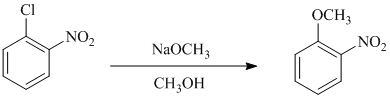
b) In between
The reaction is as follows:

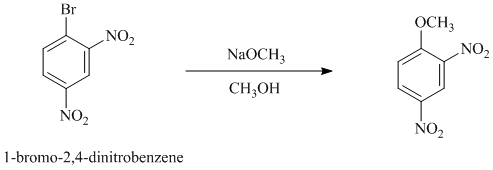
c) In between
The reaction is as follows:
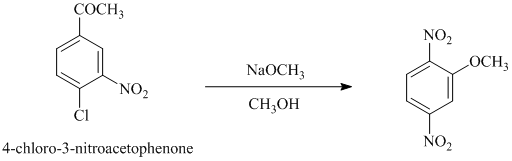
d) In between
The reaction is as follows:
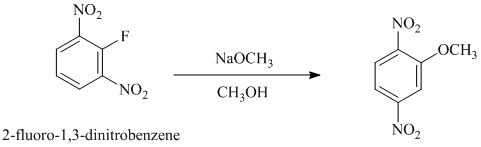
e) In between
The reaction is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
a)
In this nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, sodium methoxide is a source of the nucleophile
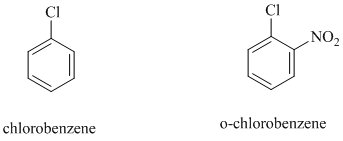
In chlorobenzene, a chlorine atom is attached to the benzene ring while in
The reaction of
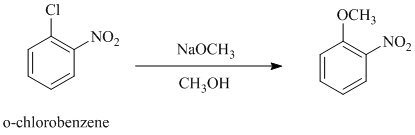
b)
In this nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, sodium methoxide is a source of the nucleophile
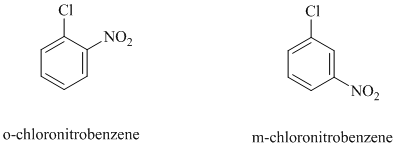
In both the given aryl halides, a strong electron withdrawing substituent is attached on the ring. In
The reaction of
c)
In this nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, sodium methoxide is a source of the nucleophile
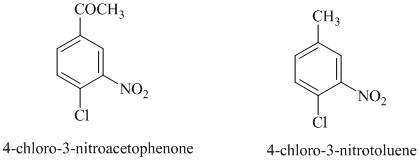
In
In
Thus, in between
The reaction of

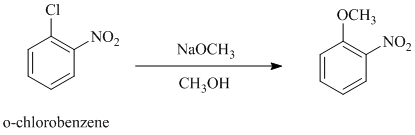
d)
In this nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, sodium methoxide is a source of the nucleophile
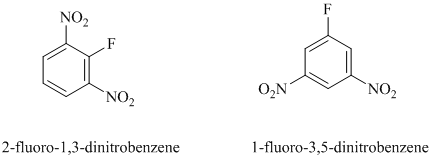
Nitro substituents are strong electron withdrawing substituents.
In
Electron withdrawing substituents at ortho and para positions activate the ring more than the electron withdrawing substituents at meta positions.
Thus, in between
The reaction of

e)
In this nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, sodium methoxide is a source of the nucleophile
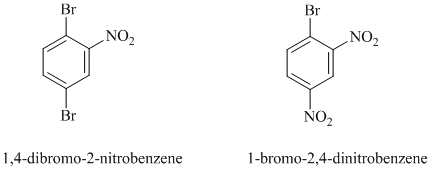
In
The reaction of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


