
Note: Exercises marked * are based on optional material.
Instructions for Data Sets: Choose one of the data sets A–K below or as assigned by your instructor. Only the first three and last three observations are shown for each data set. In each data set, the dependent variable (response) is the first variable. Choose the independent variables (predictors) as you judge appropriate. Use a spreadsheet or a statistical package (e.g., MegaStat or Minitab) to perform the necessary regression calculations and to obtain the required graphs. Write a concise report answering questions 13.25 through 13.41 (or a subset of these questions assigned by your instructor). Label sections of your report to correspond to the questions. Insert tables and graphs in your report as appropriate. You may work with a partner if your instructor allows it.
If you did not already do so, request leverage statistics. Are any observations influential? Explain.
Find leverage statistics.
Identify any of the observations are influential.
Answer to Problem 38CE
The leverage statistics are,
| Observation | Sales/SqFt | Predicted | Residual | Leverage |
| 1 | 702 | 505.5378 | 196.4622 | 0.0659 |
| 2 | 210 | 388.0933 | –178.093 | 0.0818 |
| 3 | 365 | 419.7986 | –54.7986 | 0.0789 |
| 4 | 443 | 419.2017 | 23.79828 | 0.0458 |
| 5 | 399 | 336.1339 | 62.86605 | 0.0798 |
| 6 | 265 | 524.3932 | –259.393 | 0.0816 |
| 7 | 572 | 365.8614 | 206.1386 | 0.0655 |
| 8 | 642 | 491.9392 | 150.0608 | 0.0935 |
| 9 | 461 | 422.9892 | 38.0108 | 0.0225 |
| 10 | 639 | 458.365 | 180.635 | 0.0703 |
| 11 | 484 | 502.2794 | –18.2794 | 0.0715 |
| 12 | 581 | 466.1341 | 114.8659 | 0.0478 |
| 13 | 268 | 432.9745 | –164.974 | 0.0586 |
| 14 | 573 | 497.5596 | 75.44042 | 0.2737 |
| 15 | 586 | 525.2306 | 60.76944 | 0.1168 |
| 16 | 369 | 398.5007 | –29.5007 | 0.0584 |
| 17 | 351 | 498.6047 | –147.605 | 0.0985 |
| 18 | 458 | 429.3871 | 28.61286 | 0.0535 |
| 19 | 987 | 614.5091 | 372.4909 | 0.1820 |
| 20 | 357 | 454.3592 | –97.3592 | 0.0429 |
| 21 | 406 | 417.2942 | –11.2942 | 0.0250 |
| 22 | 681 | 391.1612 | 289.8388 | 0.0493 |
| 23 | 368 | 492.4983 | –124.498 | 0.2093 |
| 24 | 304 | 460.1672 | –156.167 | 0.0604 |
| 25 | 394 | 415.2689 | –21.2689 | 0.0913 |
| 26 | 562 | 486.68 | 75.31997 | 0.0580 |
| 27 | 495 | 423.7816 | 71.21836 | 0.0942 |
| 28 | 310 | 388.496 | –78.496 | 0.1363 |
| 29 | 373 | 422.8679 | –49.8679 | 0.0227 |
| 30 | 236 | 345.16 | –109.16 | 0.1516 |
| 31 | 413 | 406.2904 | 6.709589 | 0.1565 |
| 32 | 625 | 543.4075 | 81.59252 | 0.1197 |
| 33 | 274 | 397.4102 | –123.41 | 0.0526 |
| 34 | 543 | 558.9323 | –15.9323 | 0.1372 |
| 35 | 179 | 297.105 | –118.105 | 0.0794 |
| 36 | 375 | 361.7308 | 13.26922 | 0.0837 |
| 37 | 329 | 433.9038 | –104.904 | 0.0659 |
| 38 | 297 | 430.0182 | –133.018 | 0.0682 |
| 39 | 323 | 455.7566 | –132.757 | 0.0800 |
| 40 | 469 | 404.899 | 64.101 | 0.0291 |
| 41 | 353 | 497.4495 | –144.449 | 0.0837 |
| 42 | 380 | 491.0586 | –111.059 | 0.0696 |
| 43 | 398 | 408.7628 | –10.7628 | 0.0353 |
| 44 | 312 | 318.6083 | –6.60827 | 0.0574 |
| 45 | 452 | 432.4409 | 19.55915 | 0.0731 |
| 46 | 699 | 362.4679 | 336.5321 | 0.0617 |
| 47 | 367 | 347.5704 | 19.42961 | 0.0801 |
| 48 | 432 | 380.8856 | 51.11438 | 0.0736 |
| 49 | 367 | 355.4863 | 11.51368 | 0.0922 |
| 50 | 401 | 381.559 | 19.44102 | 0.0432 |
| 51 | 414 | 481.2256 | –67.2256 | 0.0375 |
| 52 | 481 | 428.1006 | 52.89939 | 0.0183 |
| 53 | 538 | 415.7548 | 122.2452 | 0.0271 |
| 54 | 330 | 359.279 | –29.279 | 0.0356 |
| 55 | 250 | 438.5112 | –188.511 | 0.0532 |
| 56 | 292 | 396.9591 | –104.959 | 0.0582 |
| 57 | 517 | 411.7635 | 105.2365 | 0.0231 |
| 58 | 552 | 470.1005 | 81.89945 | 0.0275 |
| 59 | 387 | 361.7699 | 25.23009 | 0.0832 |
| 60 | 427 | 408.3022 | 18.69777 | 0.0631 |
| 61 | 454 | 497.6884 | –43.6884 | 0.0887 |
| 62 | 512 | 441.1052 | 70.89483 | 0.0793 |
| 63 | 345 | 375.7731 | –30.7731 | 0.1071 |
| 64 | 234 | 334.17 | –100.17 | 0.0622 |
| 65 | 348 | 333.4539 | 14.54613 | 0.1051 |
| 66 | 348 | 458.6665 | –110.666 | 0.1285 |
| 67 | 295 | 315.655 | –20.655 | 0.1077 |
| 68 | 361 | 376.5859 | –15.5859 | 0.0450 |
| 69 | 468 | 232.9942 | 235.0058 | 0.2319 |
| 70 | 404 | 393.7594 | 10.24059 | 0.1052 |
| 71 | 246 | 373.6202 | –127.62 | 0.1022 |
| 72 | 340 | 403.9505 | –63.9505 | 0.1144 |
| 73 | 401 | 413.2786 | –12.2786 | 0.0619 |
| 74 | 327 | 316.5622 | 10.43785 | 0.1045 |
The observations 14, 19, 23 and 69 are considered to have higher leverage values.
The influential observation is 23.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation
The given information is that, the dataset of ‘Noodles & Company Sales, Seating, and Demographic data’ contains
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain regression output using MegaStat software is given as,
- • Choose MegaStat >Correlation/Regression>Regression Analysis.
- • SelectInput ranges, enter the variable range for ‘Seats-Inside, Seats-Patio, MedIncome, MedAge, BachDeg%’ as the column of X, Independent variable(s)
- • Enter the variable range for ‘Sales/SqFt’ as the column of Y, Dependent variable.
- • In Options> Residuals chooseDiagnostics and influential residuals.
- • Click OK.
Output using MegaStatsoftware is given below:
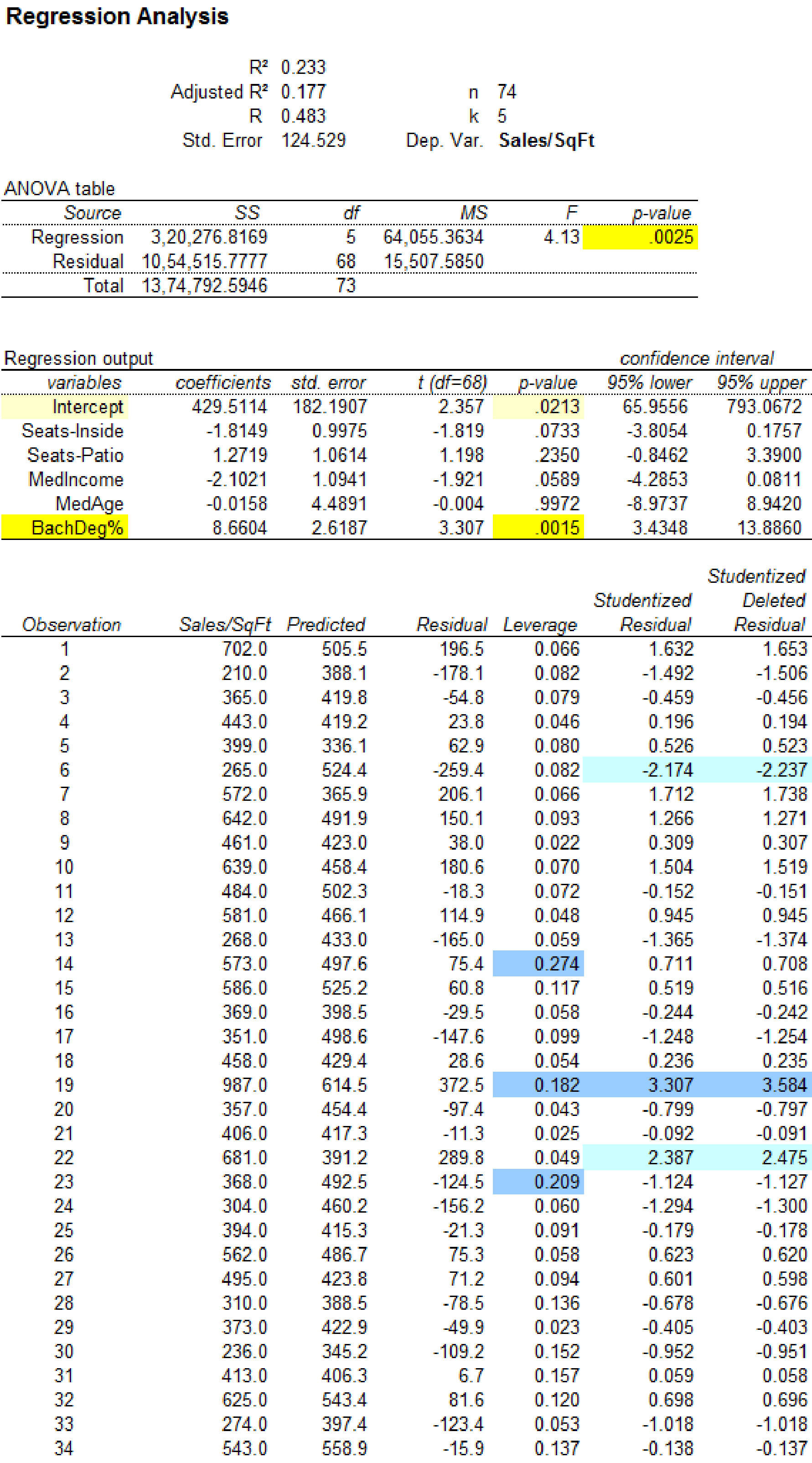
Influential observation:
The influential observation has a great effect on the parameters of the regression line when it is removed from the data set.
The influential observations can be identified using the leverage values. If the observation have the high leverage value, that is any leverage statistic is greater than value of
Substitute,
The leverage statistics greater than 0.1622 are, 0.274 corresponding to observation 14, 0.182 corresponding to observation 19, 0.209 corresponding to observation 23 and 0.232 corresponding to observation 69
The observations 14, 19, 23 and 69 are considered to have higher leverage values.
Regression conclusion including all observations:
Let
The p-value for predictor seats-inside is 0.0733.
The p-value for predictor seats-patio is 0.2350.
The p-value for predictor MedIncome is 0.0589.
The p-value for predictor MedAge is 0.9972.
The p-value for predictor BachDeg% is 0.0015.
Null hypothesis:
The predictor variable j is not related to annual sales.
Alternative hypothesis:
The predictor variable j is related to annual sales.
Rejection rules:
- • If p-value is less than the level of significance then the null hypothesis is rejected. The predictor is significant.
- • If p-value is greater than the level of significance then the null hypothesis is not rejected. The predictor is not significant.
Conclusion for seats-inside:
The p-value for predictor seats-inside is 0.0733.
The level of significance is 0.05.
The p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
The null hypothesis is not rejected.
The predictor variable seats-inside is not related to annual sales.
The predictor seats-inside is not significant.
Conclusion for seats-patio:
The p-value for predictor seats-patio is 0.2350.
The level of significance is 0.05.
The p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
The null hypothesis is not rejected.
The predictor variable seats-patio is not related to annual sales.
The predictor seats-patio is not significant.
Conclusion for median income:
The p-value for predictor median income is 0.0589.
The level of significance is 0.05.
The p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
The null hypothesis is not rejected.
The predictor variable median income is not related to annual sales.
The predictor median income is not significant.
Conclusion for median age:
The p-value for predictor median age of population is 0.9972.
The level of significance is 0.05.
The p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
The null hypothesis is not rejected.
The predictor variable median age of population is not related to annual sales.
The predictor median age of population is not significant.
Conclusion for ‘% with Bachelor's Degree’:
The p-value for predictor ‘% with Bachelor's Degree’ is 0.0015.
The level of significance is 0.05.
The p-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
The null hypothesis is rejected.
The predictor variable ‘% with Bachelor's Degree’ is related to annual sales.
The predictor ‘% with Bachelor's Degree’of population is significant.
The p-value for ‘% with Bachelor's Degree’ indicates predictor significance at
Regression analysis by removing the observation 14:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain regression equation using MegaStat software is given as,
- • Choose MegaStat >Correlation/Regression>Regression Analysis.
- • SelectInput ranges, enter the variable range for ‘Seats-Inside, Seats-Patio, MedIncome, MedAge, BachDeg%’ as the column of X, Independent variable(s)
- • Enter the variable range for ‘Sales/SqFt’ as the column of Y, Dependent variable.
- • Click OK.
Output using MegaStatsoftware is given below:
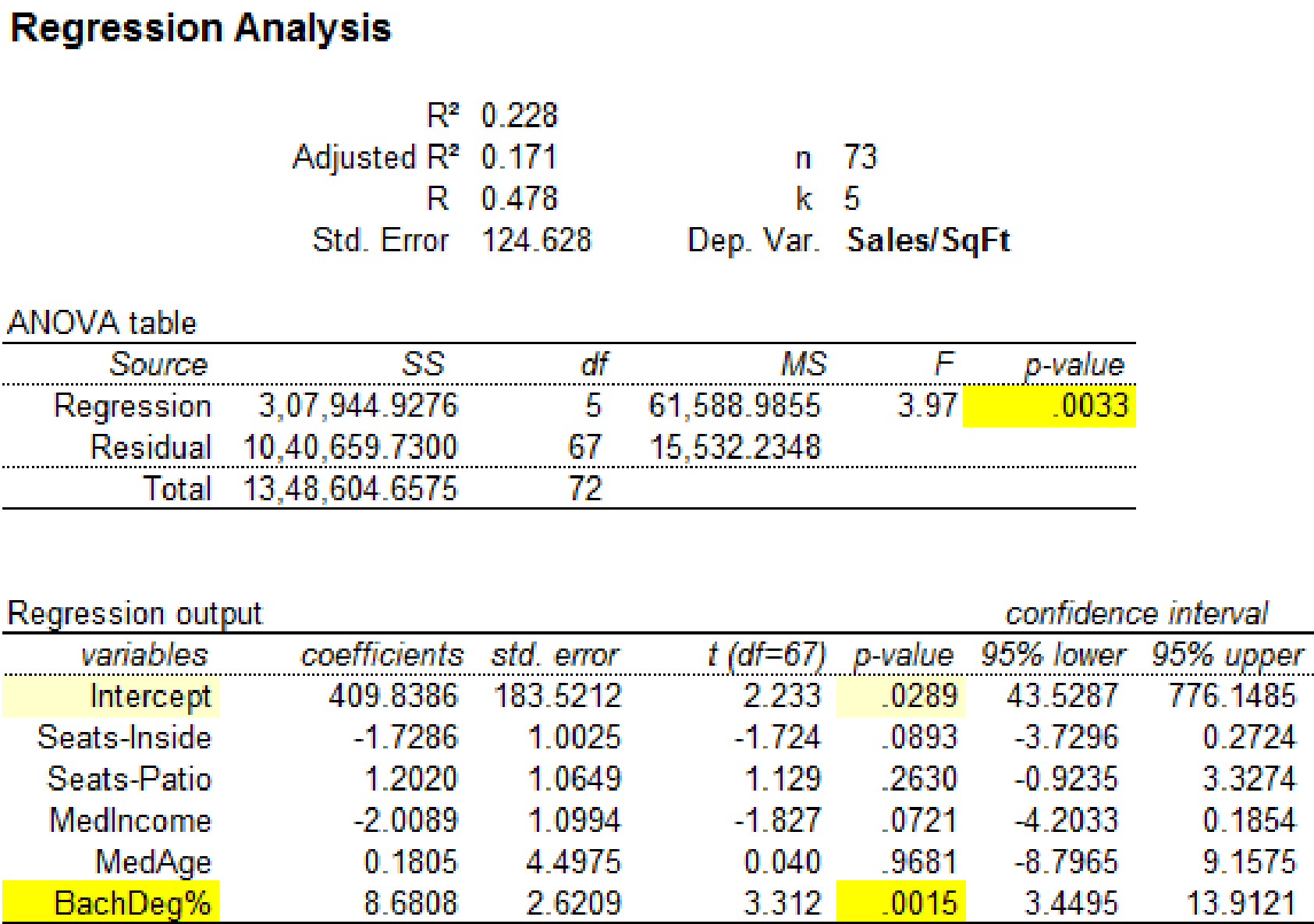
It is clear that the predictor variable ‘BachDeg%’ with p-value 0.0015 is significant at
Regression analysis by removing the observation 19:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain regression equation using MegaStat software is given as,
- • Choose MegaStat >Correlation/Regression>Regression Analysis.
- • SelectInput ranges, enter the variable range for ‘Seats-Inside, Seats-Patio, MedIncome, MedAge, BachDeg%’ as the column of X, Independent variable(s)
- • Enter the variable range for ‘Sales/SqFt’ as the column of Y, Dependent variable.
- • Click OK.
Output using MegaStatsoftware is given below:
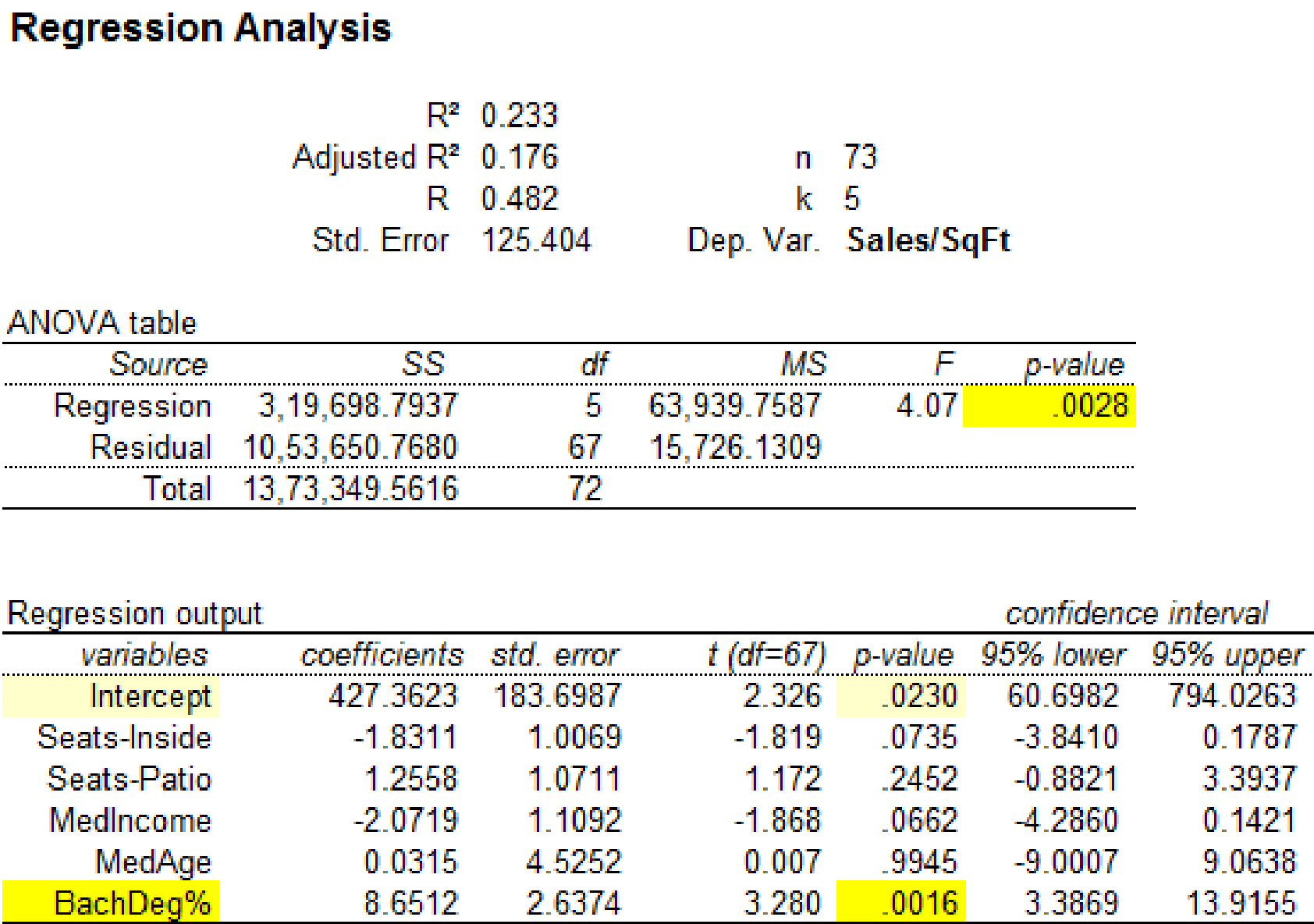
It is clear that the predictor variable ‘BachDeg%’ with p-value 0.0016 is significant at
Regression analysis by removing the observation 23:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain regression equation using MegaStat software is given as,
- • Choose MegaStat >Correlation/Regression>Regression Analysis.
- • SelectInput ranges, enter the variable range for ‘Seats-Inside, Seats-Patio, MedIncome, MedAge, BachDeg%’ as the column of X, Independent variable(s)
- • Enter the variable range for ‘Sales/SqFt’ as the column of Y, Dependent variable.
- • Click OK.
Output using MegaStatsoftware is given below:
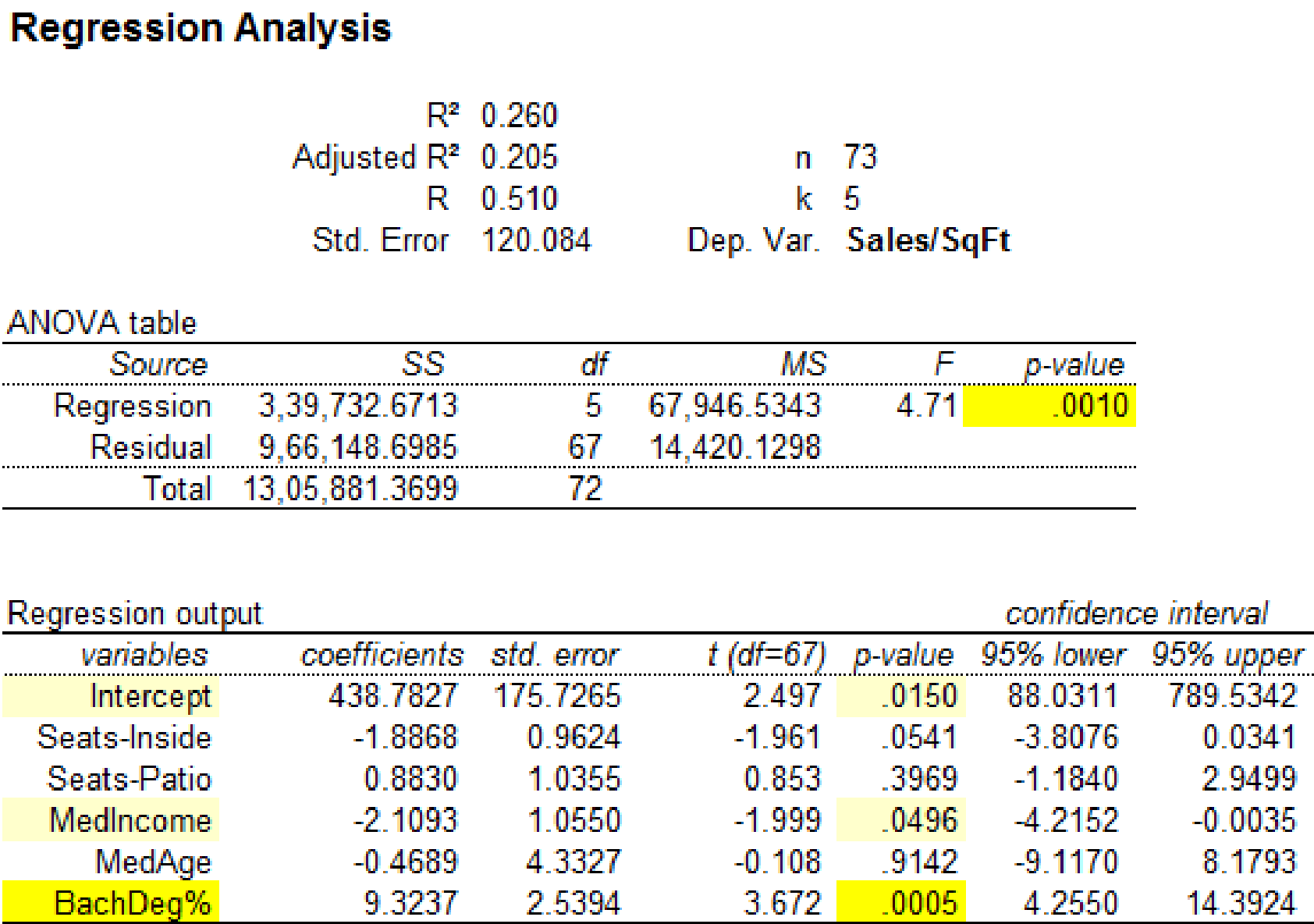
It is clear that the predictor variables ‘MedIncome’ with p-value 0.0496 and ‘BachDeg%’ with p-value 0.0016 are significant at
Regression analysis by removing the observation 69:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain regression equation using MegaStat software is given as,
- • Choose MegaStat >Correlation/Regression>Regression Analysis.
- • SelectInput ranges, enter the variable range for ‘Seats-Inside, Seats-Patio, MedIncome, MedAge, BachDeg%’ as the column of X, Independent variable(s)
- • Enter the variable range for ‘Sales/SqFt’ as the column of Y, Dependent variable.
- • Click OK.
Output using MegaStatsoftware is given below:
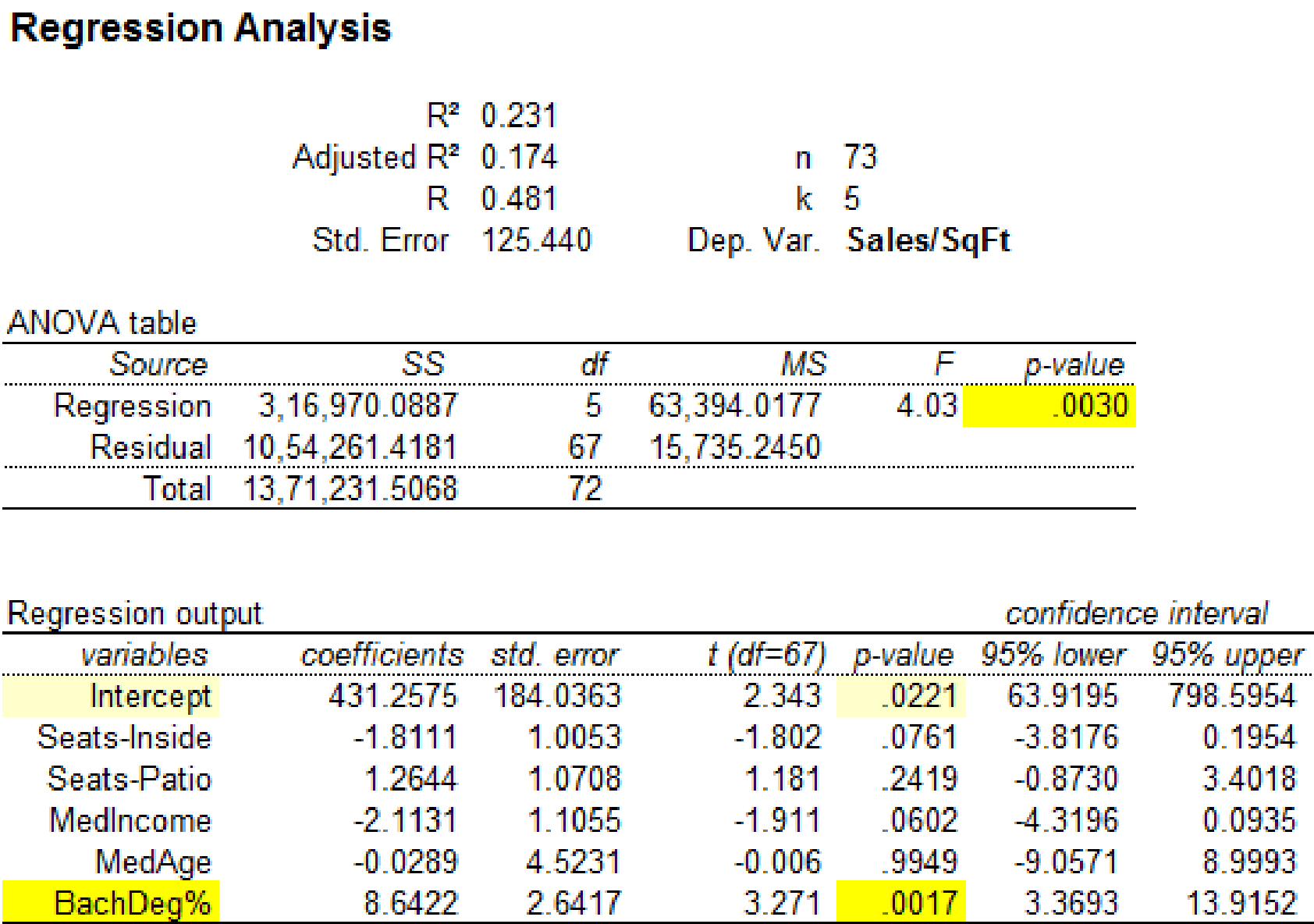
It is clear that the predictor variable ‘BachDeg%’ with p-value 0.0017 is significant at
The significance for the regression statistics has changed when the observation 23 is removed from the data set. Hence, the influential observation is 23.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- You’re scrolling through Instagram and you notice that a lot of people are posting selfies. This piques yourcuriosity and you want to estimate the percentage of photos on Instagram that are selfies.(a) (5 points) Is there a “ground truth” for the percentage of selfies on Instagram? Why or why not?(b) (5 points) Is it possible to estimate the ground truth percentage of selfies on Instagram?Irrespective of your answer to the previous question, you decide to pull up n = 250 randomly chosenphotos from your friends’ Instagram accounts and find that 32% of these photos are selfies.(c) (15 points) Determine which of the following is an observation, a variable, a sample statistic (valuecalculated based on the observed sample), or a population parameter.• A photo on Instagram.• Whether or not a photo is a selfie.• Percentage of all photos on Instagram that are selfies.• 32%.(d) (5 points) Based on the sample you collected, do you think 32% is a reliable ballpark estimate for theground truth…arrow_forwardCan you explain this statement below in layman's terms? Secondary Analysis with Generalized Linear Mixed Model with clustering for Hospital Center and ICUvs Ward EnrolmentIn a secondary adjusted analysis we used generalized linear mixed models with random effects forcenter (a stratification variable in the primary analyses). In this analysis, the relative risk for the primaryoutcome of 90-day mortality for 7 versus 14 days of antibiotics was 0.90 (95% Confidence Interval [CI]0.78, 1.05).arrow_forwardIn a crossover trial comparing a new drug to a standard, π denotes the probabilitythat the new one is judged better. It is desired to estimate π and test H0 : π = 0.5against H1 : π = 0.5. In 20 independent observations, the new drug is better eachtime.(a) Find and plot the likelihood function. Give the ML estimate of π (Hint: youmay use the plot function in R)arrow_forward
- Can you explain what this analysis means in layman's terms? - We calculated that a target sample size of 3626, which was based on anticipated baseline 90-day mortality of 22% and a noninferiority margin of no more than 4 percentage points, would give the trial 80% power, at a one-sided alpha level of 2.5%, accounting for a maximum of 5% loss to follow-up and for early stopping rules for three interim analyses.-arrow_forwardCan you help me understand this analysis? A 95.7% confidence interval is shown for the intention-to-treat analysis (accounting for alpha spending in interim analyses), and 95% confidence intervals are shown for the other two analyses. The widths of the confidence intervals have not been adjusted for multiplicity. The dashed line indicates the noninferiority margin of 4 percentage points.arrow_forwardTitle: Analyzing Customer Satisfaction for UnileverAs a member of Unilever's Customer Experience Management team, you are responsible forevaluating customer satisfaction levels and monitoring competitive moves. This case studyinvolves analyzing satisfaction data to test two key hypotheses about Unilever's performancerelative to its main competitor, Procter & Gamble (P&G).Unilever’s leadership team has emphasized the importance of customer satisfaction inmaintaining competitive advantage and market leadership. As part of this initiative, yourteam regularly monitors satisfaction scores and benchmarks them against competitors likeP&G.You are tasked with analyzing the provided dataset to answer the following questions:1. Does Unilever’s average customer satisfaction score meet the minimum threshold of2. 75%?Is there no significant difference between Unilever’s overall average satisfaction scoreand P&G’s average satisfaction score?arrow_forward
- Need help answering wuestionarrow_forwardThe following table shows a data set containing information for 25 of the shadow stocks tracked by the American Association of Individual Investors (aaii.com, February 2002). Shadow stocks are common stocks of smaller companies that are not closely followed by Wall Street analysts. Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Company DeWolfe Companies Exchange Ticker Symbol Market Cap ($ millions) Price/ Gross Profit Earnings Ratio Margin (%) AMEX DWL 36.4 8.4 36.7 North Coast Energy OTC NCEB 52.5 6.2 59.3 Hansen Natural Corp. OTC HANS 41.1 14.6 44.8 MarineMax, Inc. NYSE HZO 111.5 7.2 23.8 Nanometrics Incorporated OTC NANO 228.6 38.0 53.3 TeamStaff, Inc. OTC TSTF 92.1 33.5 4.1 Environmental Tectonics AMEX ETC 51.1 35.8 35.9 Measurement Specialties AMEX MSS 101.8 26.8 37.6 SEMCO Energy, Inc. NYSE SEN 193.4 18.7 23.6 Party City Corporation OTC PCTY 97.2 15.9 36.4 Embrex, Inc. OTC EMBX 136.5 18.9 59.5 Tech/Ops Sevcon, Inc. AMEX ΤΟ 23.2 20.7 35.7 ARCADIS NV OTC ARCAF 173.4…arrow_forwardThe following table shows a data set containing information for 25 of the shadow stocks tracked by the American Association of Individual Investors (aaii.com, February 2002). Shadow stocks are common stocks of smaller companies that are not closely followed by Wall Street analysts. Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Company DeWolfe Companies Exchange AMEX Ticker Symbol Market Cap Price/ Gross Profit Earnings Margin ($ millions) Ratio (%) DWL 36.4 8.4 36.7 North Coast Energy OTC NCEB 52.5 6.2 59.3 Hansen Natural Corp. OTC HANS 41.1 14.6 44.8 MarineMax, Inc. NYSE HZO 111.5 7.2 23.8 Nanometrics Incorporated OTC NANO 228.6 38.0 53.3 TeamStaff, Inc. OTC TSTF 92.1 33.5 4.1 Environmental Tectonics AMEX ETC 51.1 35.8 35.9 Measurement Specialties AMEX MSS 101.8 26.8 37.6 SEMCO Energy, Inc. NYSE SEN 193.4 18.7 23.6 Party City Corporation OTC PCTY 97.2 15.9 36.4 Embrex, Inc. OTC EMBX 136.5 18.9 59.5 Tech/Ops Sevcon, Inc. AMEX ΤΟ 23.2 20.7 35.7 ARCADIS NV OTC ARCAF 173.4…arrow_forward
- The following data show the year to date percent change (YTD % Change) for 30 stock-market indexes from around the word (The Wall Street Journal, August 26, 2013). a. What index has the largest positive YTD % Change? Round your answer to once decimal place. index with a YTD % Change of % b. Using a class width of 5 beginning with -20 and going to 40, develop a frequency distribution for the data. YTD % Change Frequency -20 - -15 -15 - -10 -10 - -5 -5 - 0 0 - 5 5 - 10 10 - 15 15 - 20 20 - 25 30 - 35 c. 1. 2. 3. 4.arrow_forwardThe following data show the year to date percent change (YTD % Change) for 30 stock-market indexes from around the word (The Wall Street Journal, August 26, 2013). Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Country Australia Index S&P/ASX200 YTD % Change 10.2 Belgium Bel-20 12.6 Brazil São Paulo Bovespa -14.4 Canada S&P/TSX Comp 2.6 Chile Santiago IPSA -16.3 China Shanghai Composite -9.3 Eurozone EURO Stoxx 10.0 France CAC 40 11.8 Germany DAX 10.6 Hong Kong Hang Seng -3.5 India S&P BSE Sensex -4.7 Israel Tel Aviv 1.3 Italy FTSE MIB 6.6 Japan Nikkei 31.4 Mexico IPC All-Share -6.4 Netherlands AEX 9.3 Singapore Straits Times -2.5 South Korea Kospi -6.4 Spain IBEX 35 6.4 Sweden Switzerland SX All Share 13.8 Swiss Market 17.4 Taiwan Weighted 2.3 U.K. FTSE 100 10.1 U.S. S&P 500 16.6 U.S. DJIA 14.5 U.S. Dow Jones Utility 6.6 U.S. Nasdaq 100 17.4 U.S. Nasdaq Composite 21.1 World DJ Global ex U.S. 4.2 World DJ Global Index 9.9 a. What index has the largest positive YTD %…arrow_forwardDescribe a three step process you choose to determine how many elementary schools there are in the city of 5 million people.arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning



