
Concept explainers
During the week of May 10, Hyrum Manufacturing produced and shipped 16,000 units of its aluminum wheels: 4,000 units of Model A and 12,000 units of Model B. The cycle time for Model A is 1.09 hours and for Model B is 0.47 hour. The following costs and production hours were incurred:
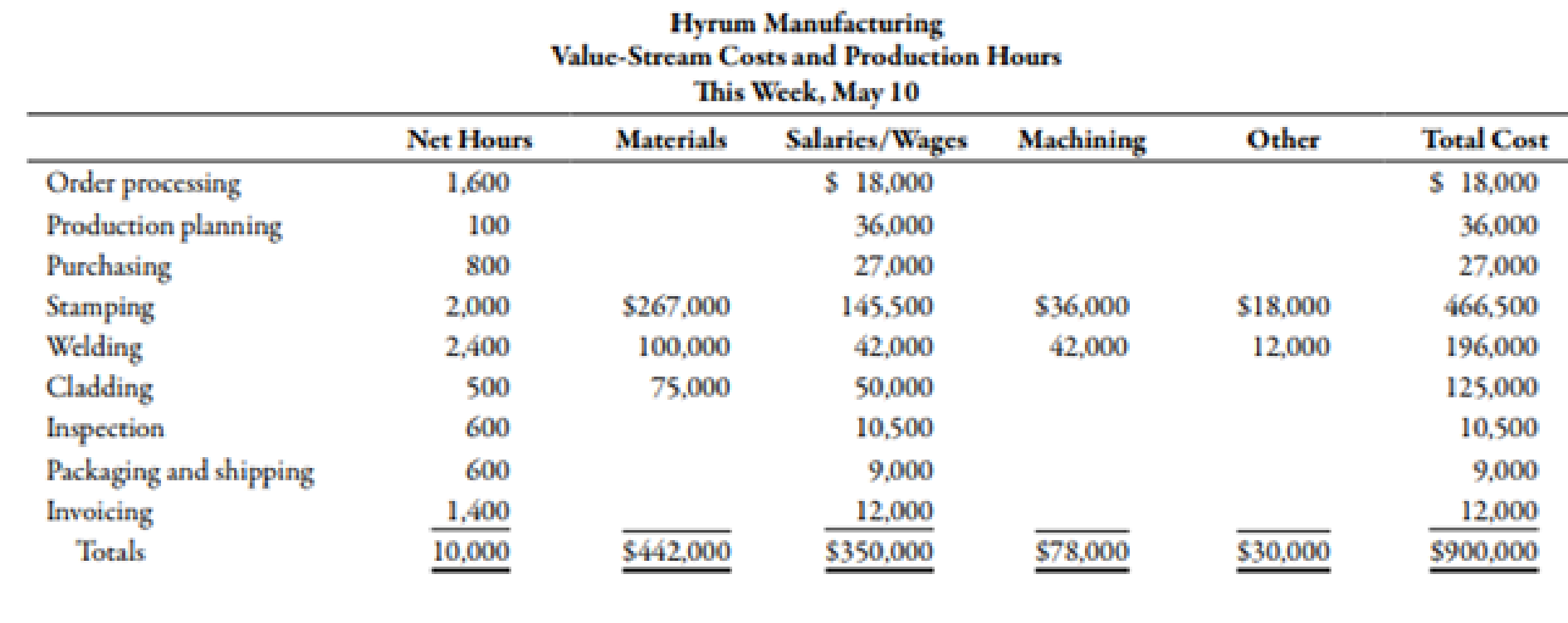
Required:
- 1. Assume that the value-stream costs and total units shipped apply only to one model (a single-product value stream). Calculate the unit cost, and comment on its accuracy.
- 2. Assume that Model A is responsible for 40% of the materials cost. Calculate the unit cost for Models A and B, and comment on its accuracy. Explain the rationale for using units shipped instead of units produced in the calculation.
- 3. Calculate the unit cost for the two models, using DBC. Explain when and why this cost is more accurate than the unit cost calculated in Requirement 2.
1.
Compute unit cost assuming that the value-stream cost and total units shipped apply to a single model.
Answer to Problem 25BEA
Unit cost is $56.25
Explanation of Solution
Value Stream:
Value stream consists of the processes through which a product goes; that is from procurement to delivery. In value stream, all processes are covered whether or not they add value to the product.
Computation of unit cost:
Unit cost can be computed by using formula:
Substitute $900,000 for total value stream cost and 16,000 for total units in the above formula.
In case, there is only one product and all the costs are directly attributable to that product, then unit cost computed would provide accurate result.
Therefore, assuming that the value-stream cost and total units shipped apply to a single model, unit cost is $56.25
2.
Compute unit cost of both the models in case, Model A is responsible for 40% of the material cost. Comment on accuracy of the results and provide the rationale behind using units shipped instead of units produced.
Answer to Problem 25BEA
Unit cost of model A and B is $72.825 and $50.725 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of unit cost:
| Particulars | Model A ($) | Model B ($) |
| Units shipped | 4,000 | 12,000 |
| Material cost |
176,800 |
265,200 |
|
Material cost per unit (A) |
44.20 |
22.10 |
| Conversion cost per unit1 (B) | 28.625 | 28.625 |
| Unit cost | 72.825 | 50.725 |
Table (1)
Units shipped are used to compute per unit cost rather than units produced. This is done to encourage the reduction of goods produced, in excess of units to be shipped.
This would happen because value stream cost includes goods that are produced and unit cost would increase if goods shipped are lesser than goods produced.
Therefore, unit cost of model A and B is $72.825 and $50.725 respectively.
Working Notes:
1. Computation of conversion cost per unit:
3.
Compute unit cost for each model using duration based costing.
Answer to Problem 25BEA
Unit cost of model A and B would be $94.122 and $43.626 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Duration Based Costing:
In duration based costing, value stream conversion cost is distributed amongst products in proportion of the cycle time.
Computation of unit cost:
| Particulars | Model A ($) | Model B ($) |
| Units shipped | 4,000 | 12,000 |
| Material cost |
176,800 |
265,200 |
|
Material cost per unit (A) |
44.20 |
22.10 |
| Conversion cost rate per hour1 | 45.8 | 45.8 |
| Cycle time per unit (hours) | 1.09 | 0.47 |
| Conversion cost per unit (B) |
49.922 |
21.526 |
| Unit cost | 94.122 | 43.626 |
Table (2)
Duration bond costing would provide better results when products are not homogeneous and time taken by each type of product varies.
Therefore, unit cost of model A and B would be $94.122 and $43.626 respectively.
Working Notes:
1. Computation of conversion cost rate:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making, Loose-Leaf Version, 7th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- 1. Steve works in an insurance office and in 2013 was provided with uniforms by her employer which cost $15,000. Which of the following tax treat of the uniform allowance is incorrect? A. Any amount exceeding $5739 is taxable at a rate of 25% B. She cannot claim uniform and laundry allowance C. The amount is added to her salary and taxed at 25% D. If the company provided uniform allowance, then it would regarded as a taxable benefit 2. Which of the following is false in describing a contract of service A. Individual can conduct business on his/her own account B.Tools, materials and work place are provided by the payer C. Individual is subject to the supervision, direction and control of another person D. Contract is a legally binding exclusive service agreement between the performer and payer. 3. What year was the tax threshold system established in Jamaica? A.1960 B.1986 C.1990 D.1953 4. Mr. Williams did a presentation explaining Adam Smith’s initial Canons of Taxation to his…arrow_forwardEckhart Corp. reports that at an activity level of 5,800 machine-hours in a month, its total variable inspection cost is $348,240 and its total fixed inspection cost is $128,500. What would be the total variable inspection cost at an activity level of 6,100 machine-hours in a month? Assume that this level of activity is within the relevant range.arrow_forwardFinancial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Need help with this question solution general accountingarrow_forwardKay works in an insurance office and in 2013 was provided with uniforms by her employer which cost $15,000. Which of the following tax treat of the uniform allowance is incorrect? A.Any amount exceeding $5739 is taxable at a rate of 25% B.She cannot claim uniform and laundry allowance C.The amount is added to her salary and taxed at 25% D.If the company provided uniform allowance, then it would regarded as a taxable benefitarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Steven works in an insurance office and in 2013 was provided with uniforms by her employer which cost $15,000. Which of the following tax treat of the uniform allowance is incorrect? A. Any amount exceeding $5739 is taxable at a rate of 25% B. She cannot claim uniform and laundry allowance C.The amount is added to her salary and taxed at 25% D. If the company provided uniform allowance, then it would regarded as a taxable benefitarrow_forwardWhat are its 2022 earnings per share for this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardnot use ai solve this question do fastarrow_forward
- Emoluments refer to the salary and other benefits an individual receives as a result of being employed. All of the following are emoluments except: A. All annuities, pensions, superannuation or other allowances payable in respect of past services in any office or employment of profit. B. Salaries, wages, overtime pay C. Lump sum paid out of the Consolidated Fund D. Utilities and other benefits of employment in money, kind or otherwisearrow_forwardH. Smith is employed at a rate of $35 (USD) PER HOUR FOR A FORTY HOUR WORK WEEK:any hour over the forty smith is paid an additional $5usd. during the month of march 2016 smith worked the following schedule: Work week hours worked benefits Value of benefits March 1-4 40 cell phone 15000.00TT$ March 7-11 45 Housing 40,000 March 14-18 42 Motor car 45,000 March 28-31 41 Cash Allowance 100,000 Tax Credits: Personal allowance 75,000, NIC 9% OF BASIC PAY, PAYE rate vv25%. using an exchange rate of $1.50tt$ for us $1, compute the net pay of mr smith formonth ending march 31,2016 in TT currency.arrow_forwardKindly help me with accounting questionsarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



