
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the product for the
Concept Introduction:
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,
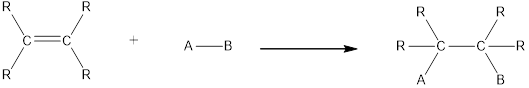
Halogenation is an example of addition reaction. In this reaction, a halogen molecule is incorporated into the molecules of organic compound. Halogenation of alkene results in the formation of dihaloalkane, where both carbon atoms bonded by double bond gets halogen atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the product for the alkene addition reaction has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,
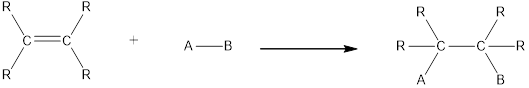
Hydrohalogenation is an example of addition reaction. In this reaction, a hydrogen halide molecule is incorporated into the molecules of organic compound. Hydrohalogenation of alkene results in the formation of
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the product for the alkene addition reaction has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,
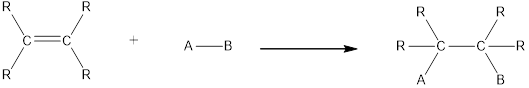
Hydrogenation is an example of addition reaction. In this reaction, a hydrogen molecule is incorporated into the molecules of organic compound. Hydrogenation of alkene results in the formation of alcohol, where both carbon atoms bonded by double bond gets hydrogen atom. This reaction requires a metal as catalyst.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the product for the alkene addition reaction has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,
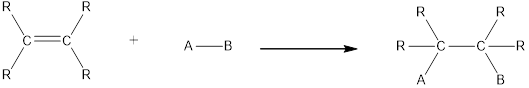
Hydration is an example of addition reaction. In this reaction, a water molecule is incorporated into the molecules of organic compound. Hydration of alkene results in the formation of alcohol, where one carbon atom gets hydrogen atom added and the other carbon atom gets hydroxyl group added to it. This reaction requires a small amount of sulphuric acid as catalyst.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry, Hybrid (with Owlv2 Quick Prep For General Chemistry Printed Access Card)
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





