
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The NMR stands for nuclear magnetic resonance. NMR spectroscopy deals with the interaction between
Answer to Problem 13.44AP
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the compound A and compound B is that compound A contains a doublet and septet and compound B contains only singlet.
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
The formula used to determine NMR splitting is shown below.
Where
• n is the number of hydrogen atom on the adjacent atom.
The structure of compound A is shown below.
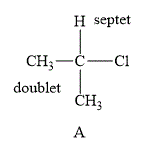
Figure 1
The compound A shown in Figure 1 contains six methyl protons and one methyne proton. The number of hydrogen atoms on adjacent atom of methyl protons
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons splits into a doublet as the number of peaks is
NMR spectra of methyne protons splits into septet as the number of peaks is
The structure of the compound
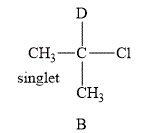
Figure 2
The compound B shown in Figure 2 contains six methyl protons. The number of hydrogen atoms on adjacent atom of methyl protons
The NMR spectra of methyl protons splits into singlet as the number of peaks is 0. As a result, there is no coupling. Therefore, the methyl protons give a singlet peak.
The compound A gives septet and doublet whereas compound B gives a singlet in proton NMR spectra.
(b)
Interpretation:
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The NMR stands for nuclear magnetic resonance. NMR spectroscopy deals with the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nucleus of an atom. NMR spectroscopy is used to determine the structural information about compounds.
Answer to Problem 13.44AP
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the compound A and compound B is that compound A contains two triplets and compound B contains two triplets and one quintet (multiplet).
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
The formula used to determine NMR splitting is shown below.
Where
• n is the number of hydrogen atom on the adjacent atom.
The structure of compound A is shown below.
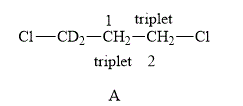
Figure 3
The compound A shown in Figure 3 contains four methylene protons. The methylene protons are adjacent to each other. Therefore, both of them couple with each other. The value of hydrogen atoms
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
The structure of compound B is shown below.
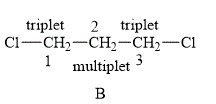
Figure 4
The compound B shown in Figure 4 contains six methylene protons. The methylene protons are adjacent to each other. The value of hydrogen atoms
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
The protons on the adjacent of
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
The compound A gives triplet at both the carbons whereas compound B gives triplet on
(c)
Interpretation:
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The NMR stands for nuclear magnetic resonance. NMR spectroscopy deals with the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nucleus of an atom. NMR spectroscopy is used to determine the structural information about compounds.
Answer to Problem 13.44AP
The difference in the proton NMR spectra of the compound A and compound B is that compound A contains a doublet and septet and compound B contains only singlet.
Explanation of Solution
The formula used to determine NMR splitting is shown below.
Where
• n is the number of hydrogen atom on the adjacent atom.
The structure of compound A and B are shown below.
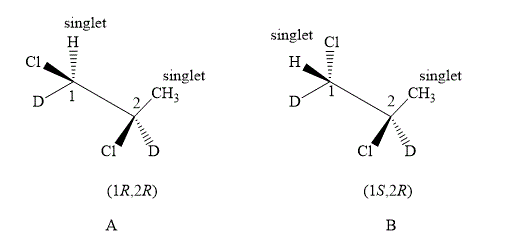
Figure 5
The compound A and B shown in Figure 5 both have similar spectrums. In the compound A, the value of number of methyl protons on adjacent to
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
Compound A and compound B both are diastereotopic. The chemical shift value of both the compounds is slightly different. The spectrum of both compounds is the same as there are diastereoisomers. Therefore, compound B also forms singlet on both the carbons.
The structure of compound C is shown below.
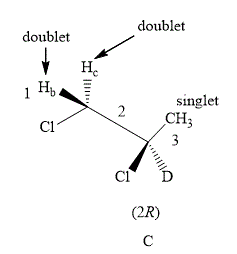
Figure 6
The compound C shown in Figure 6 contains five equivalent protons. The value of hydrogen atoms
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
The number of peaks of both
Therefore, the NMR spectra of methyl protons of
The compound A gives triplet at both the carbons whereas compound B gives triplet on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardHelp me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forward
- Is an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forwardHelp me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forward
- V Consider this step in a radical reaction: Br: ? What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ⚫ionization termination initialization neutralization none of the abc Explanation Check 80 Ο F3 F1 F2 2 F4 01 % do5 $ 94 #3 X 5 C MacBook Air 25 F5 F6 66 ©2025 ˇ F7 29 & 7 8arrow_forwardShow how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardno aiarrow_forward
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw a tetramer if this alternating copolymer pleasearrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





