
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds cyclohexane and
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
Explanation of Solution
The compounds cyclohexane and
The structure of
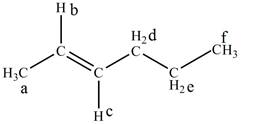
Figure 1
The structure of the cyclohexane along with its all equivalent protons peak data is shown below.
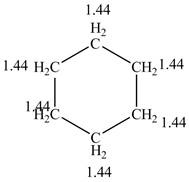
Figure 2
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
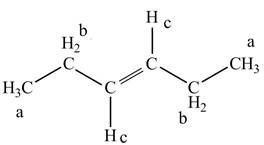
Figure 3
The structure of the
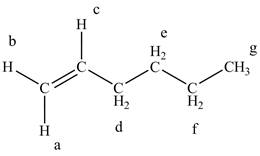
Figure 4
The
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The two compounds
The structure of
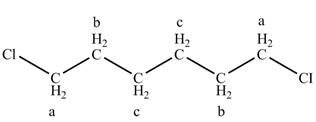
Figure 5
The structure of the
There is one signal at high chemical value at
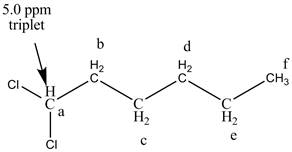
Figure 6
The structure of the
There are two signals at high chemical shift value for the compound. One at
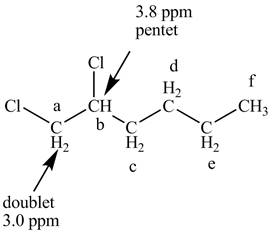
Figure 7
The
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The only signal that is different in both the compounds is for the single hydrogen of methane group attached directly to the oxygen. Also, the splitting of the protons methyl groups into doublet occurs for isopropyl group while in
The structure of
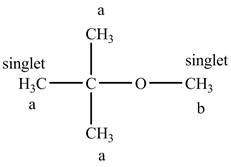
Figure 8
The structure of the isopropyl methyl ether is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
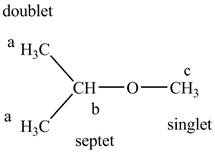
Figure 9
The
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
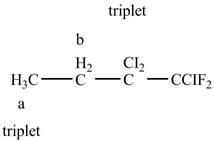
Figure 10
The structure of the
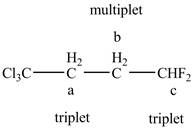
Figure 11
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

