
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula,
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula,
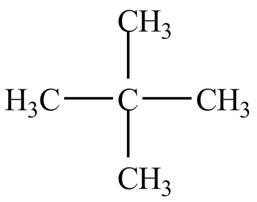
Explanation of Solution
There is only one signal in the compound that means all the protons are equivalent and all the protons are from methyl group as per chemical shift value of
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.
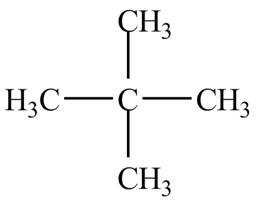
Figure 1
The structure of the compound having molecular formula,
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
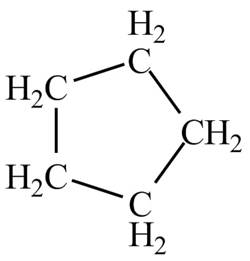
Explanation of Solution
There is only one signal in the compound that means all the protons are equivalent and all the protons are from methylene group as per chemical shift value of
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.
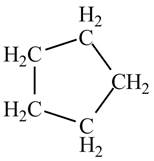
Figure 2
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
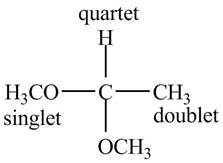
Explanation of Solution
There are three signals in the compound. One is at
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 3
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
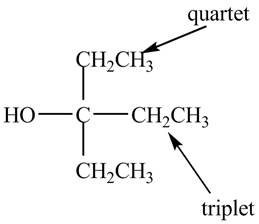
Explanation of Solution
The given spectrum is shown below.
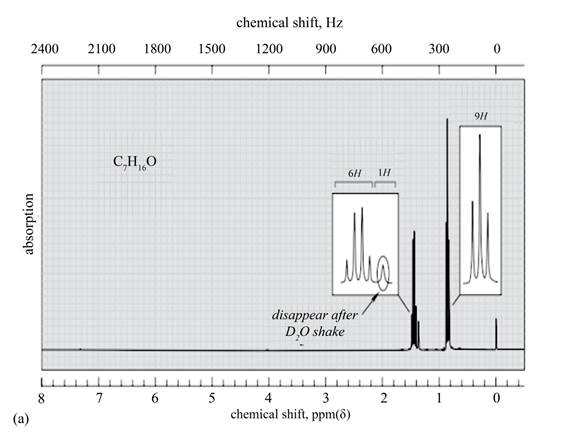
Figure 4
There are three signals in the compound. One is at
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 5
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
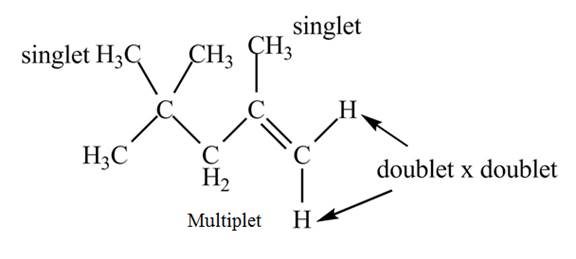
Explanation of Solution
The given spectrum is shown below.
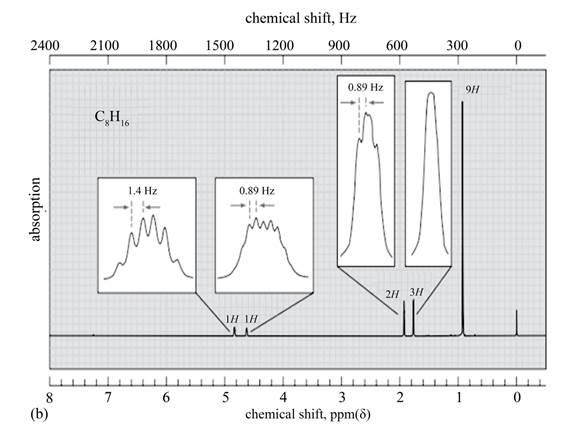
Figure 6
It is given that the
The
Figure 7
There are five signals in the compound. The two signal at
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 8
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
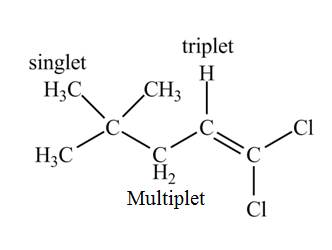
Explanation of Solution
There are three signals in the compound. The signal at
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponds to NMR data as shown below.

Figure 9
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
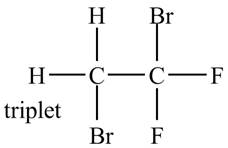
Explanation of Solution
There is only one signal in the compound for two hydrogens that means both are equivalent. The triplet signal is given by the two protons that means the splitting of the signal is done by two equivalent fluorine groups.
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 10
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
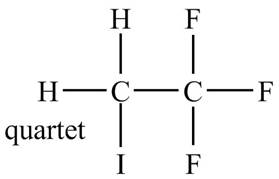
Explanation of Solution
There is only one signal in the compound for two hydrogens that means both are equivalent. The quartet signal is given by the two protons that means the splitting of the signal is done by three equivalent fluorine groups.
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 11
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
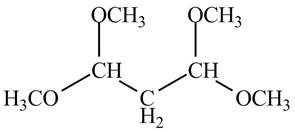
Explanation of Solution
There are three signals in the compound and total hydrogens are sixteen. The relative intergral tells about the ratio of number of hydrogen in each signal. The relative integral is
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.

Figure 12
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
(j)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.40AP
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
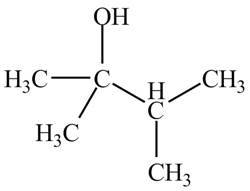
Explanation of Solution
There are three signals in the compound and total hydrogens are fourteen. The doublet signal at
The signal at
Therefore, the structure of the compound corresponding to NMR data is shown below.
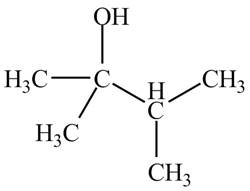
Figure 13
The structure of the compound having molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- Q Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forward
- For the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

