
Concept explainers
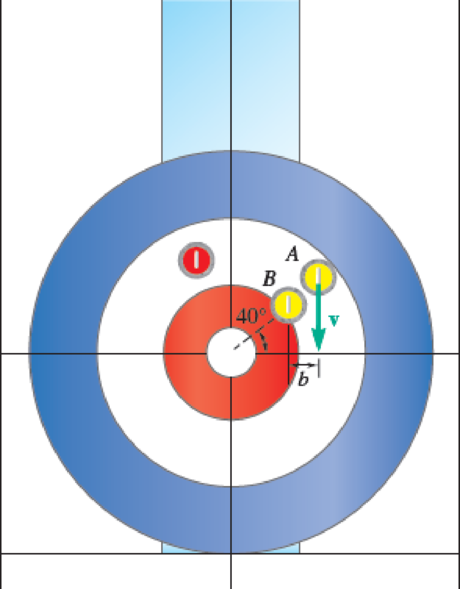
Two identical 40-lb curling stones have diameters of 11 in. and may slide on a sheet of ice. Stone B is at rest when stone A strikes it, moving it to the center of the inner circle. The distance A travels before striking B is 108 ft, and the sweepers scrubbing the ice reduce the coefficient of friction between A and the ice to 0.04, while the coefficient of kinetic friction between B and the ice is 0.1. The coefficient of restitution between A and B is 0.6. Neglecting rotation, and knowing that B travels 4 ft along the dotted line, determine (a) the distance b, (b) the speed A has when it is released 108 ft from the impact.
Fig. P13.194
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
DeGarmo's Materials and Processes in Manufacturing
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Machine Tool Practices (10th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
- 15 kg boxes are being transported around a curve via a conveyor belt as shown to the right. Assuming the curve has a radius of 3 meters and the boxes are traveling at a constant speed of 1 meter per second, what is the minimum required coefficient of friction needed to ensure the boxes don’t slip as they travel around the curve?arrow_forwardThe W1= 87.85-lb block shown rests on a smooth plane (coefficient of kinetic friction = 0) with an angle of 0 =28° from horizontal. It is connected by a flexible inextensible cord that passes around weightless, frictionless pulleys to a support. The W2 =109.85-lb weight is attached as shown. After the system is released from rest, in what distance will the block on the plain attain a speed of 6.7 ft/s? шш W2 W1arrow_forwardLuggage A is gently lowered with no initial velocity onto a moving baggage claim belt at Bradley International Airport in Hartford. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the belt and the luggage is Mk. Draw the free-body diagram (FBD) and associated kinetic diagram (KD) for Luggage A immediately after it contacts the belt.arrow_forward
- (a) Two blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown in Figure. If the system is released from rest, determine the velocity of block A after it has moved 2 m by using the data given. Assume that the coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the plane is ?k = 0.25 and that the pulley is weightless and frictionless.arrow_forwardA 10-lb bock is resting on an inclined surface at an angle of 30°, as shown. The block is in contact with a compressed spring that has a modulus of 75lb/in. The spring has an initial compression of 6 inches that is released by cutting the restraining cords. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the inclined surface and the block is 0.15, determine the speed of the block as it leaves the spring. Position B L. Position A Position C 6 in, Restraining cords ww. H = 0.15 k = 75 lb/in 30°arrow_forwardThis is not a quiz question. It is part of a review packet. Free Body Diagram and Kinetic Free Diagram needed.arrow_forward
- The blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown. If the system is released from rest, what is the tension (in Newton) produced in the cable after block A has moved 2m? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the plane is 0.25 and the pulley is weightless and frictionless. The Mass of A is 200kg; the Mass of B is 300kg.arrow_forward2.319. The two 100-lb blocks are released from rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between all contacting surfaces is ?? = 0.1. How long does it take block ? to fall 1 ft?arrow_forwardCrate A is gently placed with zero initial velocity onto a moving conveyor belt. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the belt is μk . Draw the FBD and KD for A immediately after it contacts the belt.arrow_forward
- The W1= 69.01-lb block shown rests on a smooth plane (coefficient of kinetic friction = 0) with an angle of θ=34∘ from horizontal. It is connected by a flexible inextensible cord that passes around weightless, frictionless pulleys to a support. The W2 =134.93-lb weight is attached as shown. After the system is released from rest, in what distance will the block on the plain attain a speed of 10.0 ft/s?arrow_forwardA car and its load weighs 27 kN and the center of gravity is 600 mm from the ground and midway between the front and rear wheel which are 3 m apart. The car is brought to rest from a speed of 54 kph in 5 seconds by means of the brakes. Compute the normal force on each of the front wheels of the car.arrow_forward1) The 15-kg block A and 25-kg cylinder B are connected by the light cord that passes over a 5-kg pulley with IG = 0.025 kg.m2. If the system is released from rest, (with coefficient of friction between the block and ground of 0.3) calculate the angular acceleration of the pulleyarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





