
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the distance (x) required to bring the train to stop.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.17P
The distance (x) required to bring the train to stop is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The initial speed of the train
The coefficient of kinetic friction
The weight of train A
The weight of train B
The weight of train C
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the train A, B and C with the forces as in Figure (1).
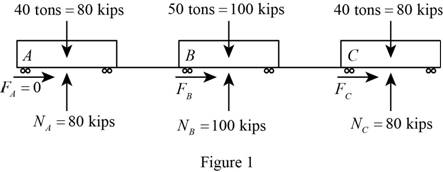
Convert the unit of initial velocity of trailer truck from
Calculate the force at A
Substitute 0.35 for
Calculate the force at B
Substitute 0.35 for
Calculate the force at C
Substitute 0.35 for
Calculate the total weight (W) using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the truck (m) using the formula:
Substitute
Calculate the initial kinetic energy
Substitute
The final kinetic energy
Calculate work done
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the distance (x) required to bring the train to stop:
Substitute
Therefore, the distance (x) required to bring the train to stop is
(b)
Find the force in each coupling.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.17P
The force in coupling AB is
The force in coupling BC is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The initial speed of the train
The coefficient of kinetic friction
The weight of train A
The weight of train B
The weight of train C
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Consider car A:
Show the free body diagram of the train A with the forces as in Figure (2).
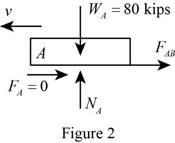
Assume
Calculate the mass of the truck (m) using the formula:
Substitute
Calculate the initial kinetic energy
Substitute
The final kinetic energy
Calculate work done
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
The expression for the principle of work and energy is as follows;
Substitute
Consider car C:
Show the free body diagram of the train C with the forces as in Figure (3).
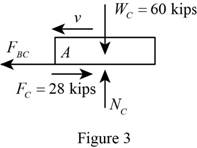
Calculate the mass of the truck (m) using the formula:
Substitute
Calculate the initial kinetic energy
Substitute
The final kinetic energy
Calculate work done
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the force in coupling BC:
Substitute
Therefore, the forces in coupling AB and BC are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
- from this problem a want you to help to draw the shear moment and the bending momentarrow_forwardreaction at a is 1.6 wL (pos) handwritten solutions only please. correct answers upvotedarrow_forward1 8 4 Add numbers so that the sum of any row or column equals .30 Use only these numbers: .1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14arrow_forward
- Uppgift 2 (9p) I77777 20 kN 10 kN/m 4 [m] 2 2 Bestäm tvärkrafts- och momentdiagram för balken i figuren ovan. Extrempunkter ska anges med både läge och värde i diagrammen.arrow_forward**Problem 8-45.** The man has a mass of 60 kg and the crate has a mass of 100 kg. If the coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is \( \mu_s = 0.4 \) and between the crate and the ground is \( \mu_c = 0.3 \), determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. **Diagram Explanation:** The diagram illustrates a scenario where a man is attempting to pull a crate using a rope-and-pulley system. The setup is as follows: - **Crate (C):** Positioned on the ground with a rope attached. - **Rope:** Connects the crate to a pulley system and extends to the man. - **Pulley on Tree:** The rope runs over a pulley mounted on a tree which redirects the rope. - **Angles:** - The rope between the crate and tree forms a \(30^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - The rope between the tree and the man makes a \(45^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - **Man (A):** Pulling on the rope with the intention of moving the crate. This arrangement tests the…arrow_forwardplease solve this problems follow what the question are asking to do please show me step by steparrow_forward
- please help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forwardplease solve this problem for me the best way that you can explained to solve please show me the step how to solvearrow_forwardplese solbe this problem and give the correct answer solve step by step find the forces and line actionarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





