Concept explainers
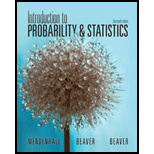
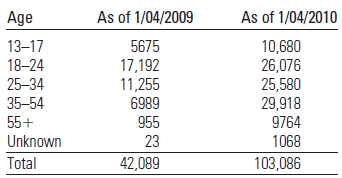
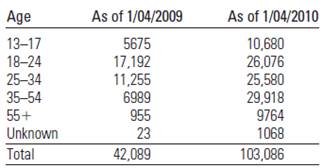
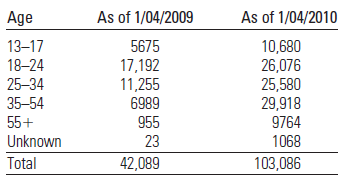
Facebook Fanatics The social networking site called Facebook has grown quickly since its inception in 2004. In fact, Facebook’s United States user base grew from 42 million users to 103 million users between 2009 and 2010. The table below shows the age distribution of Facebook users (in thousands) as it changed from January 2009 to January 2010.3
a. Define the variable that has been measured in this table.
b. Is the variable quantitative or qualitative?
c. What do the numbers represent?
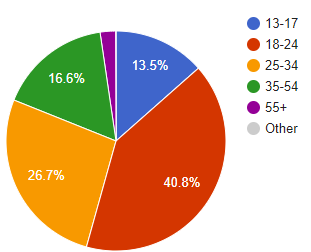
d. Construct a pie chart to describe the age distribution of Facebook users as of January 4, 2009.
e. Construct a pie chart to describe the age distribution of Facebook users as of January 4, 2010.
f. Refer to parts d and e. How would you describe the changes in the age distributions of Facebook users during this 1-year period?
a.
Todefine: thevariable that has been measured in the table.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
Concept used:
The variables are the topic that were investigated.
Categorical/quantitative variables place the industry into a category while a quantitative variable is a numerical variable.
Calculation:
The table shows the age distributions of Facebook users and thus the variable that has been measuring the age.
b.
To check: whether that it is quantitative and qualitative.
Answer to Problem 1.14E
Qualitative.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
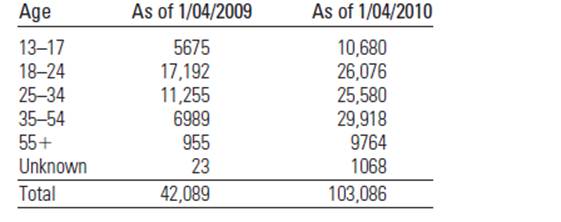
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
Concept used:
The variables are the topic that were investigated.
Categorical/quantitative variables place the industry into a category while a quantitative variable is a numerical variable.
Calculation:
In the table, it is noted that the place of the people in different age group
c.
To find: that the number represent.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
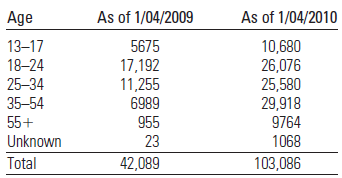
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
Calculation:
The numbers in the table above represents the number of Facebook user that fall within the corresponding age category.
d.
To construct: a pie chart to describe the age distribution of Facebook user in
Explanation of Solution
Given:
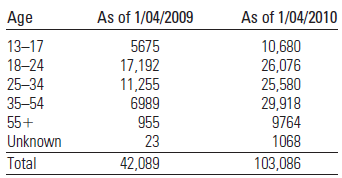
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
Calculation:
The percentage is the frequency divided by the total frequency. Note that the table describes a total of
| Category | Frequency | Percent |
| Unknown |
The slice (central angle) is the product
| Category | Frequency | Percent | Slice size |
| Unknown |
Draw a circle for each category using the determined slice size.
January 2009
e.
To construct: a pie chart to describe the age distribution of Facebook user in
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
Calculation:
The percentage is the frequency divided by the total frequency. Note that the table describes a total of
| Category | Frequency | Percent |
| Unknown |
The slice (central angle) is the product
| Category | Frequency | Percent | Slice size |
| Unknown |
Draw a circle for each category using the determined slice size.
January 2010
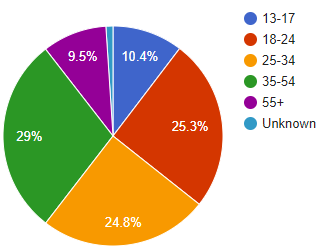
f.
To describe: the changes in the age distribution of Facebook users in 1-year period in part (d) and part (e).
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given table below shows that the age distribution of Facebook users as it changes from January 2009 to January 2010:
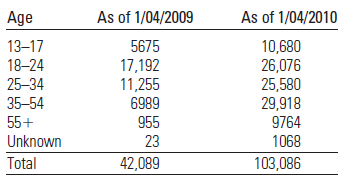
Calculation:
It appears that a lot of older people signed up as Facebook user between 2009 to 2010, because the percentage of first three categories are larger in 2009 compared to 2010, while the other age categories contain a smaller percentage in 2009 compared to 2010.
The largest decrease in percentage occurred in the 18-24 age category, while the largest increase in percentage occurred in the 35-54 age category.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction to Probability and Statistics
- Theorem 2.6 (The Minkowski inequality) Let p≥1. Suppose that X and Y are random variables, such that E|X|P <∞ and E|Y P <00. Then X+YpX+Yparrow_forwardTheorem 1.2 (1) Suppose that P(|X|≤b) = 1 for some b > 0, that EX = 0, and set Var X = 0². Then, for 0 0, P(X > x) ≤e-x+1²² P(|X|>x) ≤2e-1x+1²² (ii) Let X1, X2...., Xn be independent random variables with mean 0, suppose that P(X ≤b) = 1 for all k, and set oσ = Var X. Then, for x > 0. and 0x) ≤2 exp Σ k=1 (iii) If, in addition, X1, X2, X, are identically distributed, then P(S|x) ≤2 expl-tx+nt²o).arrow_forwardTheorem 5.1 (Jensen's inequality) state without proof the Jensen's Ineg. Let X be a random variable, g a convex function, and suppose that X and g(X) are integrable. Then g(EX) < Eg(X).arrow_forward
- Can social media mistakes hurt your chances of finding a job? According to a survey of 1,000 hiring managers across many different industries, 76% claim that they use social media sites to research prospective candidates for any job. Calculate the probabilities of the following events. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) answer parts a-c. a) Out of 30 job listings, at least 19 will conduct social media screening. b) Out of 30 job listings, fewer than 17 will conduct social media screening. c) Out of 30 job listings, exactly between 19 and 22 (including 19 and 22) will conduct social media screening. show all steps for probabilities please. answer parts a-c.arrow_forwardQuestion: we know that for rt. (x+ys s ا. 13. rs. and my so using this, show that it vye and EIXI, EIYO This : E (IX + Y) ≤2" (EIX (" + Ely!")arrow_forwardTheorem 2.4 (The Hölder inequality) Let p+q=1. If E|X|P < ∞ and E|Y| < ∞, then . |EXY ≤ E|XY|||X|| ||||qarrow_forward
- Theorem 7.6 (Etemadi's inequality) Let X1, X2, X, be independent random variables. Then, for all x > 0, P(max |S|>3x) ≤3 max P(S| > x). Isk≤narrow_forwardTheorem 7.2 Suppose that E X = 0 for all k, that Var X = 0} x) ≤ 2P(S>x 1≤k≤n S√2), -S√2). P(max Sk>x) ≤ 2P(|S|>x- 1arrow_forwardThree players (one divider and two choosers) are going to divide a cake fairly using the lone divider method. The divider cuts the cake into three slices (s1, s2, and s3).If the chooser's declarations are Chooser 1: {s3} and Chooser 2: {s3}, which of the following is a fair division of the cake?arrow_forwardTheorem 1.4 (Chebyshev's inequality) (i) Suppose that Var X x)≤- x > 0. 2 (ii) If X1, X2,..., X, are independent with mean 0 and finite variances, then Στη Var Xe P(|Sn| > x)≤ x > 0. (iii) If, in addition, X1, X2, Xn are identically distributed, then nVar Xi P(|Sn> x) ≤ x > 0. x²arrow_forwardTheorem 2.5 (The Lyapounov inequality) For 0arrow_forwardTheorem 1.6 (The Kolmogorov inequality) Let X1, X2, Xn be independent random variables with mean 0 and suppose that Var Xk 0, P(max Sk>x) ≤ Isk≤n Σ-Var X In particular, if X1, X2,..., X, are identically distributed, then P(max Sx) ≤ Isk≤n nVar X₁ x2arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning