
Concept explainers
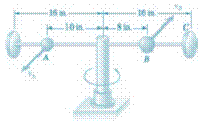
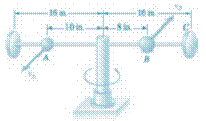
A 1-Ib ball A and a 2-Ib ball B are mounted on a horizontal rod that rotates freely about a vertical shaft. The balls are held in the positions shown by pins. The pin holding B is suddenly removed and the ball moves to position C as the rod rotates. Neglecting friction and the mass of the rod and knowing that the initial speed of A is
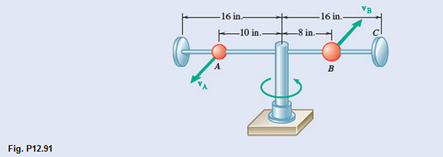
(a)
Radial and transverse component of acceleration of ball B immediately after the pin is removed.
Answer to Problem 12.91P
Radial component:
Transverse component:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
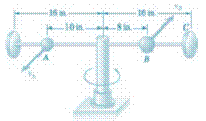
Let
Constraint of rod:
Components of acceleration:
Sketch the free body diagrams of the balls showing the radial and transverse components of the forces acting on them.
Owing to frictionless sliding of B along the rod,
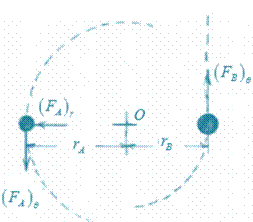
Radial component of acceleration of B.
Transverse components of acceleration,
Since the rod has no mass, it must be in equilibrium.
Draw its free body diagram, applying Newton’s third law:
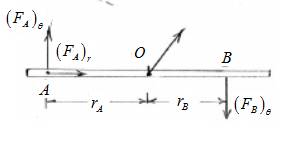
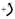 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
At
So that
From Eq. (1),
(b)
Acceleration of ball B relative to rod.
Answer to Problem 12.91P
Acceleration of ball B relative to rod:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Acceleration of B relative to the rod,
At
(c)
Acceleration of ball B relative to rod.
Answer to Problem 12.91P
Acceleration of ball B relative to rod:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Speed of A:
Substituting
Integrating with respect to time,
Applying to the final state with ball B moved to the stop at C,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- Qu 4 A cylindrical metal specimen 15.0 mm in diameter and 150 mm long is to be subjected to a tensile stress of 50 MPa; at this stress level, the resulting deformation will be totally elastic. If the elongation must be less than 0.072 mm, which of the metals in Table 1 are suitable candidates? If, in addition, the maximum permissible diameter decrease is 2.3 × 10-3 mm when the tensile stress of 50 MPa is applied, which of the metals that satisfy the criterion in part (a) are suitable candidates? see on the tables given part a and b i need to show all work problems formula step by step please make sure is correctly material sciencearrow_forwardZ4 please help on the attached question.arrow_forwardB4 Please help on the attached question.arrow_forward
- B9 Please help on the attached question.arrow_forwardB7 Please help on the attached question.arrow_forwardFrom dynamics CHAPTER 12: Rectilinear Kinematics. Continuous Motion. Qu. 1 The velocity of a particle traveling along a straight line is v = (3t2 - 6t)ft/s, where t is in seconds. If s = 4ft when t = 0, determine the position of the particle when t = 4s. What is the total distance traveled during the time interval t = 0 to t = 4s? Also, what is the acceleration when t = 2 s?I want to show all work step by step problemsarrow_forward
- Z1 please help on the attached question.arrow_forwardProblem 3 (10 pts). When using linear shape functions to solve the multiphysics thermoelastic problem considered in class, we found that the stress in the rod is affected by unphysical oscillations like the following plot(a) [10pts] What is the origin of this issue and how can we fix it?arrow_forwardZ6 please help on the attached question.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





