
Concept explainers
(a)
The magnitude of force P.
Answer to Problem 12.28P
Explanation of Solution
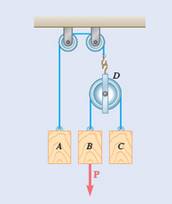
Given information:
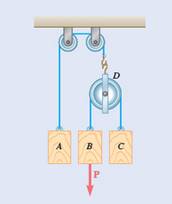
Mass of block A
Mass of block B=C
Time
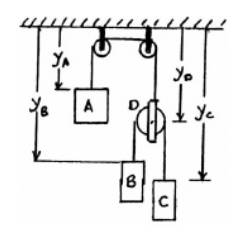
Let the position co-ordinate be Y and it is positive towards downwards.
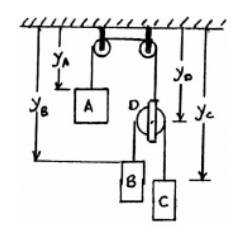
Now, constraint of cord AD:
Then,
Similarly, constraint of cord BC:
Then,
Now, from equation (1) and (2);
As all of the forces are constant then, we have uniformly accelerated motions.
Then,
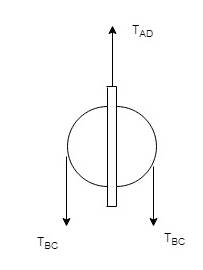
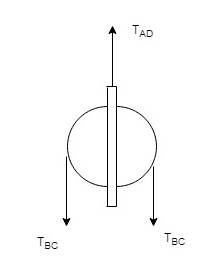
Now, calculate all the forces for pulley D,
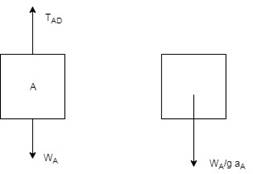
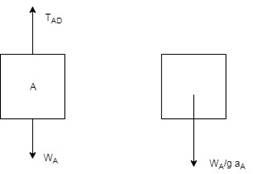
Now, calculate all the forces for block A, for this the draw the free body and kinetic diagram of the block A:
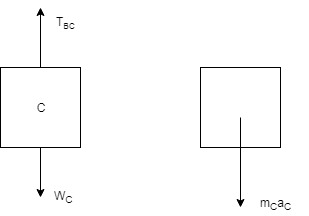
Calculate all the forces for block C, for this the draw the free body and kinetic diagram of block C:
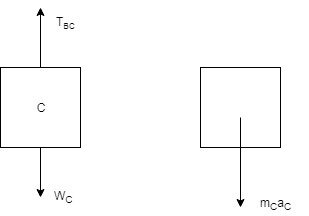
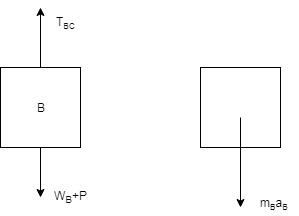
Calculate all the forces for block B, for this the draw the free body and kinetic diagram of block B:
Substituting the values of equation (4) and (5) into equation (3);
Putting all the values in equation (6);
(b)
The tension in cord AD.
Answer to Problem 12.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass of block A
Mass of block B=C
Time
Let the position co-ordinate be Y and it is positive towards downwards.
Now, constraint of cord AD:
Then,
Similarly, constraint of cord BC:
Then,
Now, from equation (1) and (2);
As all of the forces are constant then we have uniformly accelerated motions.
Then,
Now, calculate all the forces for pulley D,
Now, calculate all the forces for block A, for this the draw the free body and kinetic diagram of the block A:
Calculate all the forces for block C, for this the draw the free body and kinetic diagram of the block C:
Substituting the values of equation (4) and (5) into equation (3);
Now, tension in cord AD;
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- Hello I was going over the solution for this probem and I'm a bit confused on the last part. Can you please explain to me 1^4 was used for the Co of the tubular cross section? Thank you!arrow_forwardBlood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cParrow_forwardQ2: Find the shear load on bolt A for the connection shown in Figure 2. Dimensions are in mm Fig. 2 24 0-0 0-0 A 180kN (10 Markarrow_forward
- determine the direction and magnitude of angular velocity ω3 of link CD in the four-bar linkage using the relative velocity graphical methodarrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forward
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forward(Read image) (Answer given)arrow_forwardProblem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and (y2), respectively. Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s]. Givens: y1 = 4.112 m y2 = 0.387 m b = 0.942 m Answers: ( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s ( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s ( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s ( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/sarrow_forward
- Problem (14): A pump is being used to lift water from an underground tank through a pipe of diameter (d) at discharge (Q). The total head loss until the pump entrance can be calculated as (h₁ = K[V²/2g]), h where (V) is the flow velocity in the pipe. The elevation difference between the pump and tank surface is (h). Given the values of h [cm], d [cm], and K [-], calculate the maximum discharge Q [Lit/s] beyond which cavitation would take place at the pump entrance. Assume Turbulent flow conditions. Givens: h = 120.31 cm d = 14.455 cm K = 8.976 Q Answers: (1) 94.917 lit/s (2) 49.048 lit/s ( 3 ) 80.722 lit/s 68.588 lit/s 4arrow_forwardProblem (13): A pump is being used to lift water from the bottom tank to the top tank in a galvanized iron pipe at a discharge (Q). The length and diameter of the pipe section from the bottom tank to the pump are (L₁) and (d₁), respectively. The length and diameter of the pipe section from the pump to the top tank are (L2) and (d2), respectively. Given the values of Q [L/s], L₁ [m], d₁ [m], L₂ [m], d₂ [m], calculate total head loss due to friction (i.e., major loss) in the pipe (hmajor-loss) in [cm]. Givens: L₁,d₁ Pump L₂,d2 오 0.533 lit/s L1 = 6920.729 m d1 = 1.065 m L2 = 70.946 m d2 0.072 m Answers: (1) 3.069 cm (2) 3.914 cm ( 3 ) 2.519 cm ( 4 ) 1.855 cm TABLE 8.1 Equivalent Roughness for New Pipes Pipe Riveted steel Concrete Wood stave Cast iron Galvanized iron Equivalent Roughness, & Feet Millimeters 0.003-0.03 0.9-9.0 0.001-0.01 0.3-3.0 0.0006-0.003 0.18-0.9 0.00085 0.26 0.0005 0.15 0.045 0.000005 0.0015 0.0 (smooth) 0.0 (smooth) Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.00015 Drawn…arrow_forwardThe flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





