
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399074
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 12.3CYU
Potassium chloride has the same unit cell as NaCl. Using the ion sizes in Figure 7.11, calculate the density of KCl.
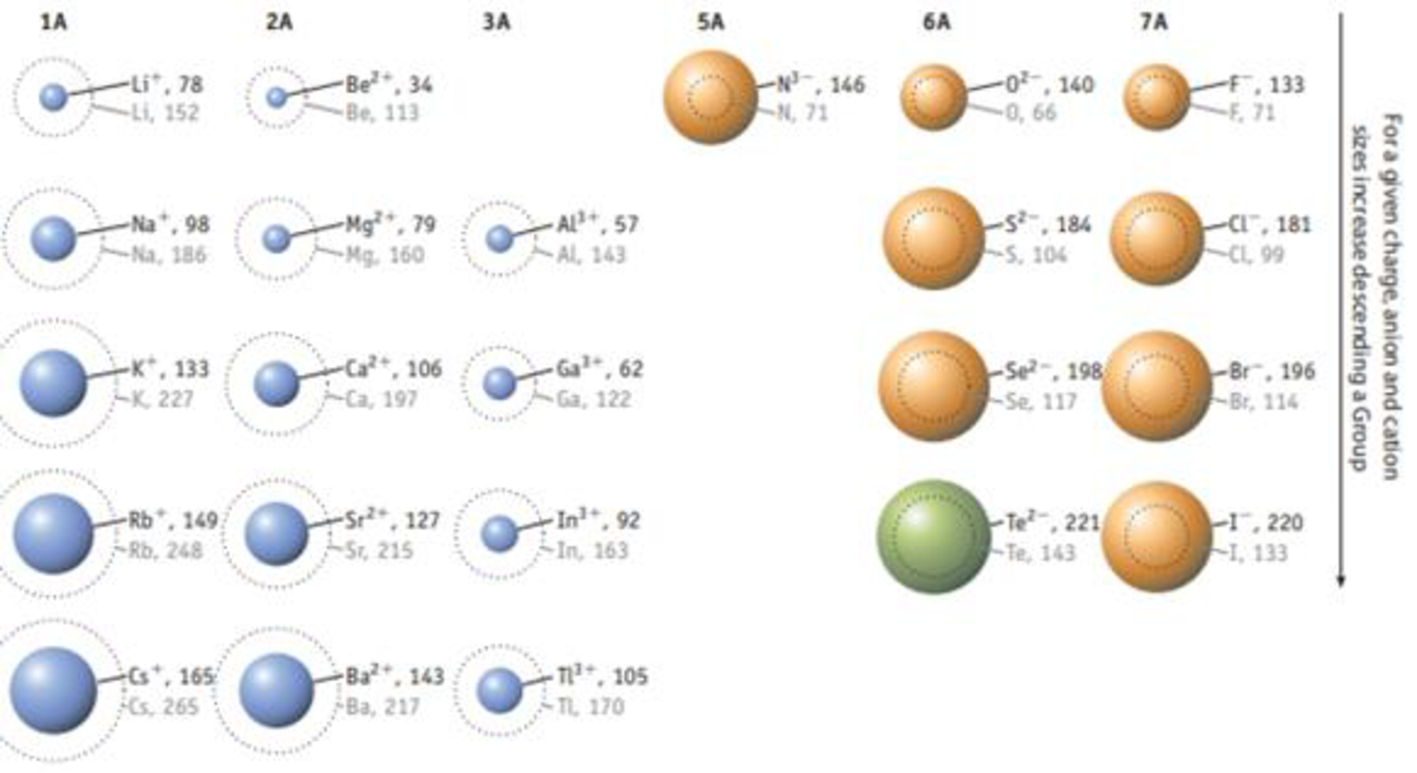
FIGURE 7.11 Relative sizes of some common ions. Rodii are given in picometers (1 pm 1 × 10‒12 m). (Data taken from J. Emsley, The Elements, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1998, 3rd edition.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
For the compound: C8H17NO2
Use the following information to come up with a plausible structure:
8
This compound has "carboxylic acid amide" and ether functional groups.
The peaks at 1.2ppm are two signals that are overlapping one another.
One of the two signals is a doublet that represents 6 hydrogens; the
other signal is a quartet that represents 3 hydrogens.
Vnk the elements or compounds in the table below in decreasing order of their boiling points. That is, choose 1 next to the substance with the highest bolling
point, choose 2 next to the substance with the next highest boiling point, and so on.
substance
C
D
chemical symbol,
chemical formula
or Lewis structure.
CH,-N-CH,
CH,
H
H 10: H
C-C-H
H H H
Cale
H 10:
H-C-C-N-CH,
Bri
CH,
boiling point
(C)
Сен
(C) B
(Choose
Please help me find the 1/Time, Log [I^-] Log [S2O8^2-], Log(time) on the data table. With calculation steps. And the average for runs 1a-1b. Please help me thanks in advance. Will up vote!
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 12.1 - (a) Determining an Atom Radius from Lattice...Ch. 12.2 - If an ionic solid has an fcc lattice of anions (X)...Ch. 12.2 - Potassium chloride has the same unit cell as NaCl....Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 1.1ACPCh. 12.6 - Describe the unit cell of lithium (see Figure).Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 1.3ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 1.4ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 2.1ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 2.2ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 2.3ACP
Ch. 12.6 - How many tin atoms are contained in the tetragonal...Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 3.2ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 3.3ACPCh. 12.6 - Prob. 3.4ACPCh. 12 - Outline a two-dimensional unit cell for the...Ch. 12 - Outline a two-dimensional unit cell for the...Ch. 12 - A portion of the crystalline lattice for potassium...Ch. 12 - The unit cell of silicon carbide, SiC, is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 5PSCh. 12 - Rutile, TiO2, crystallizes in a structure...Ch. 12 - Cuprite is a semiconductor. Oxide ions are at the...Ch. 12 - The mineral fluorite, which is composed of calcium...Ch. 12 - Calcium metal crystallizes in a face-centered...Ch. 12 - The density of copper metal is 8.95 g/cm3. If the...Ch. 12 - Potassium iodide has a face-centered cubic unit...Ch. 12 - A unit cell of cesium chloride is illustrated in...Ch. 12 - Predict the trend in lattice energy, from least...Ch. 12 - Prob. 14PSCh. 12 - To melt an ionic solid, energy must be supplied to...Ch. 12 - Which compound in each of the following pairs...Ch. 12 - Prob. 17PSCh. 12 - Prob. 18PSCh. 12 - Considering only the molecular orbitals formed by...Ch. 12 - Prob. 20PSCh. 12 - Prob. 21PSCh. 12 - Prob. 22PSCh. 12 - Prob. 23PSCh. 12 - Prob. 24PSCh. 12 - Prob. 25PSCh. 12 - Prob. 26PSCh. 12 - Prob. 27PSCh. 12 - Prob. 28PSCh. 12 - A diamond unit cell is shown here. Unit cell of...Ch. 12 - The structure of graphite is given in Figure...Ch. 12 - We have identified six types of solids (metallic,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 32PSCh. 12 - Classify each of the following materials as...Ch. 12 - Prob. 34PSCh. 12 - Benzene, C6H6, is an organic liquid that freezes...Ch. 12 - The specific heat capacity of silver is 0.235 J/g ...Ch. 12 - Prob. 37PSCh. 12 - Prob. 38PSCh. 12 - Prob. 39PSCh. 12 - If your air conditioner is more than several years...Ch. 12 - Sketch a phase diagram for O2 from the following...Ch. 12 - Tungsten crystallizes in the unit cell shown here....Ch. 12 - Silver crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit...Ch. 12 - The unit cell shown here is for calcium carbide....Ch. 12 - The very dense metal iridium has a face-centered...Ch. 12 - Vanadium metal has a density of 6.11 g/cm3....Ch. 12 - Prob. 47GQCh. 12 - Prob. 48GQCh. 12 - Prob. 49GQCh. 12 - Consider the three types of cubic units cells. (a)...Ch. 12 - The solid-state structure of silicon is shown...Ch. 12 - The solid-state structure of silicon carbide is...Ch. 12 - Spinels are solids with the general formula AB2O4...Ch. 12 - Using the thermochemical data below and an...Ch. 12 - Prob. 55GQCh. 12 - Prob. 56GQCh. 12 - Prob. 57GQCh. 12 - Prob. 58GQCh. 12 - Prob. 59GQCh. 12 - Prob. 60GQCh. 12 - Like ZnS, lead(II) sulfide, PbS (commonly called...Ch. 12 - CaTiO3, a perovskite, has the structure below. (a)...Ch. 12 - Potassium bromide has the same lattice structure...Ch. 12 - Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a...Ch. 12 - Why is it not possible for a salt with the formula...Ch. 12 - Prob. 67SCQCh. 12 - Prob. 68SCQCh. 12 - Prob. 69SCQCh. 12 - Phase diagrams for materials that have allotropes...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Genetics affects many aspects of our lives. Identify three ways genetics affects your life or the life of a ...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
More than one choice may apply. Using the terms listed below, fill in the blank with the proper term. anterior ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
Identify each of the following reproductive barriers as prezygotic or postzygotic. a. One lilac species lives o...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
How does the removal of hydrogen atoms from nutrient molecules result in a loss of energy from the nutrient mol...
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1: Answer the questions for the reaction below: ..!! Br OH a) Predict the product(s) of the reaction. b) Is the substrate optically active? Are the product(s) optically active as a mix? c) Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. d) What happens to the SN1 reaction rate in each of these instances: 1. Change the substrate to Br "CI 2. Change the substrate to 3. Change the solvent from 100% CH3CH2OH to 10% CH3CH2OH + 90% DMF 4. Increase the substrate concentration by 3-fold.arrow_forwardExperiment 27 hates & Mechanisms of Reations Method I visual Clock Reaction A. Concentration effects on reaction Rates Iodine Run [I] mol/L [S₂082] | Time mo/L (SCC) 0.04 54.7 Log 1/ Time Temp Log [ ] 13,20] (time) / [I] 199 20.06 23.0 30.04 0.04 0.04 80.0 22.8 45 40.02 0.04 79.0 21.6 50.08 0.03 51.0 22.4 60-080-02 95.0 23.4 7 0.08 0-01 1970 23.4 8 0.08 0.04 16.1 22.6arrow_forward(15 pts) Consider the molecule B2H6. Generate a molecular orbital diagram but this time using a different approach that draws on your knowledge and ability to put concepts together. First use VSEPR or some other method to make sure you know the ground state structure of the molecule. Next, generate an MO diagram for BH2. Sketch the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs of the BH2 fragment. These are called frontier orbitals. Now use these frontier orbitals as your basis set for producing LGO's for B2H6. Since the BH2 frontier orbitals become the LGOS, you will have to think about what is in the middle of the molecule and treat its basis as well. Do you arrive at the same qualitative MO diagram as is discussed in the book? Sketch the new highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs for the molecule (B2H6).arrow_forward
- Q8: Propose an efficient synthesis of cyclopentene from cyclopentane.arrow_forwardQ7: Use compound A-D, design two different ways to synthesize E. Which way is preferred? Please explain. CH3I ONa NaOCH 3 A B C D E OCH3arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward
- (10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward
- Q3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forwardQ5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardQ4: Circle the substrate that gives a single alkene product in a E2 elimination. CI CI Br Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Unit Cell Chemistry Simple Cubic, Body Centered Cubic, Face Centered Cubic Crystal Lattice Structu; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HCWwRh5CXYU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY