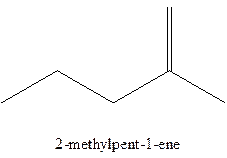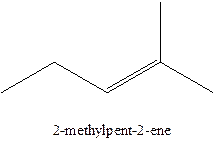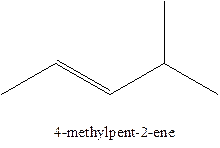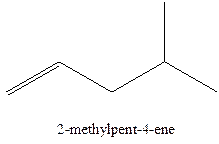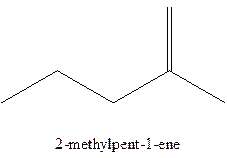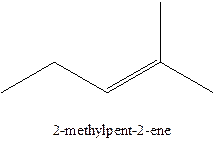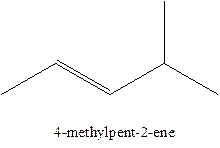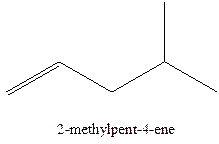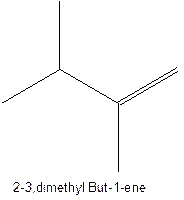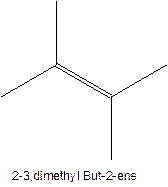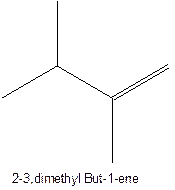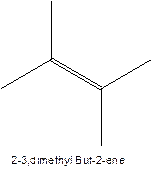Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To name and draw structural formula for
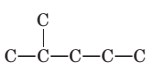
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Cis-trans isomerism arises in the compounds when there is a difference in the orientation of the two same groups.
When two same groups are along the same side of the C-C bond it is called as cis isomer, but when the same groups lie opposite to each other along the C-C bond. It is said to be trans isomer.
Example- Cis-1,2-dibromo ethane and trans-1,2, dibromo ethane are cis-trans isomers.
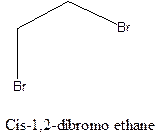
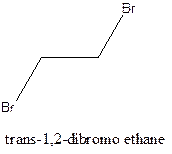
Answer to Problem 6P
The alkenes with the molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The longest chain for the given skeleton has 5 carbons therefore the root name prop- is used here. The alkenes with the molecular formula
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
(b)
Interpretation:
To name and draw structural formula for alkenes with the molecular formula
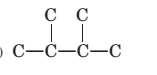
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Cis-trans isomerism arises in the compounds when there is a difference in the orientation of the two same groups.
When two same groups are along the same side of the C-C bond it is called as cis isomer, but when the same groups lie opposite to each other along the C-C bond. It is said to be trans isomer.
Example- Cis-1,2-dibromo ethane and trans-1,2, dibromo ethane are cis-trans isomers.
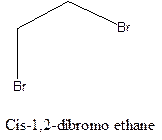
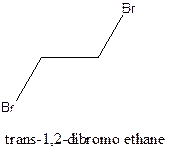
Answer to Problem 6P
The alkenes with the molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The longest chain for the given skeleton has 4 carbons therefore the root name but- is used here. The alkenes with the molecular formula
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
(c)
Interpretation:
To name and draw structural formula for alkenes with the molecular formula
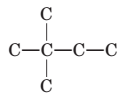
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Cis-trans isomerism arises in the compounds when there is a difference in the orientation of the two same groups.
When two same groups are along the same side of the C-C bond it is called as cis isomer, but when the same groups lie opposite to each other along the C-C bond. It is said to be trans isomer.
Example- Cis-1,2-dibromo ethane and trans-1,2, dibromo ethane are cis-trans isomers.
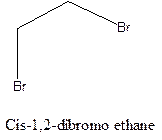
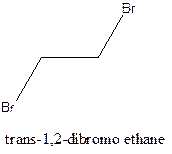
Answer to Problem 6P
The alkene with the molecular formula
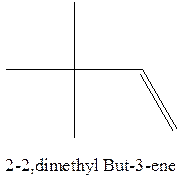
Explanation of Solution
The longest chain for the given skeleton has 4 carbons therefore the root name but- is used here. The alkene with the molecular formula
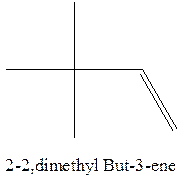
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
(c)
Interpretation:
To name and draw structural formula for alkenes with the molecular formula

Concept Introduction:
Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Cis-trans isomerism arises in the compounds when there is a difference in the orientation of the two same groups.
When two same groups are along the same side of the C-C bond it is called as cis isomer, but when the same groups lie opposite to each other along the C-C bond. It is said to be trans isomer.
Example- Cis-1,2-dibromo ethane and trans-1,2, dibromo ethane are cis-trans isomers.
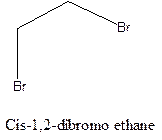
Answer to Problem 6P
The alkene with the molecular formula
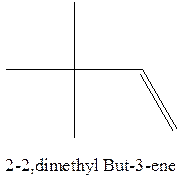
Explanation of Solution
The longest chain for the given skeleton has 4 carbons therefore the root name but- is used here. The alkene with the molecular formula
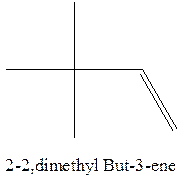
In this isomer, it contains 6 carbons and 12 hydrogen atoms, thus the molecular formula is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- + Draw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br Drawing Strong Base H Q Atoms, Bonds Charges and Rings Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Remove Done 語 Reset Undo + Drag To Panarrow_forwardDraw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Drawing Į Strong Base H Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset 謂 Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Br CH3 Q Strong Base Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Undo Reset H "Br H N Br. Remove Done .N. Drag To Panarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the product of this elementary step in an elimination mechanism. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore byproducts. + Br: .. 8 0.01 M NaOH heat Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges and Lone Pairs Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset Remove Done + Drag To Panarrow_forward+ Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Ph CH2CH3 H H3C H Br DBN [૪] Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings H | OH Charges ―00 H. C | Undo Reset Br I Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardReaction A Now the production A Œ In the product of reaction i 12 Dear the product of actionarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learnin When an unknown amine reacts with an unknown acid chloride, an amide with a molecular mass of 163 g/mol (M* = 163 m/z) is formed. In the infrared spectrum, important absorptions appear at 1661, 750 and 690 cm-1. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra are provided. Draw the structure of the product as the resonance contributor lacking any formal charges. 13C NMR DEPT 90 200 160 120 80 40 0 200 160 120 80 DEPT 135 200 160 120 80 40 0 Draw the unknown amide. 40 40 0arrow_forwardDraw the major product karmed when I reach with the epoxide. Use walge dah bonds, including hydrogen al alcach genic center, to show the chemistry of the product Beeldraw any hydrogen akams on coxygen where applicablearrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H I Select to Add Arrows + H H 'H Q H2O H2O CI:O .H H H H I Select to Add Arrows I : C H2O H H H Select to Add Arrows 'Harrow_forward
- + Draw an alkyl halide that produces ONLY the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Drawing Strong Base Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges HO Br H2N Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Panarrow_forwardFor the dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction shown, draw the major organic product. Хок Br tert-butanol heat Select Drew Templates More Erase CH QQQarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Draw the major, neutral organic product for each substitution reaction. For this question, assume that each substitution reaction goes to completion. Disregard elimination. Reaction A. CI H₂O Select Draw Templates More Erase C Harrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning