
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119776741
Author: Klein
Publisher: WILEY CONS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 12, Problem 69IP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
A proper mechanism for the following transformation is to be determined.
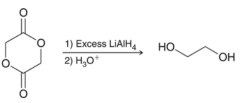
Concept introduction:
Hydride transfer is the migration of a hydrogen nucleus from one atom to another atom, accompanied by two electrons. The
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Hand written equations please
>
each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that:
1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and
2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers.
Substrate A
Substrate B
Faster Rate
X
Ś
CI
(Choose one)
(Choose one)
CI
Br
Explanation
Check
Br
(Choose one)
© 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights F
NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at
4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer.
The
H
O
HỌC—C—0—CH, CH,
2
A
ethyl acetate
H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm
Check
OA
B
OC
ch
B
C
Save For Later
Submit Ass
© 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 12.1 - Prob. 1PTSCh. 12.1 - Prob. 2ATSCh. 12.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 12.2 - Prob. 4CCCh. 12.3 - Prob. 8CCCh. 12.3 - Prob. 9CCCh. 12.4 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 12.4 - Prob. 10PTSCh. 12.4 - Prob. 11ATS
Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 12.4 - Prob. 12PTSCh. 12.4 - Prob. 13ATSCh. 12.6 - Prob. 14CCCh. 12.6 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 12.6 - Prob. 15PTSCh. 12.6 - Prob. 16PTSCh. 12.7 - Prob. 18CCCh. 12.9 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 12.9 - Prob. 19PTSCh. 12.9 - Prob. 20ATSCh. 12.9 - Prob. 21CCCh. 12.10 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 12.10 - Prob. 22PTSCh. 12.10 - Prob. 23ATSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 8LTSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 24PTSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 25ATSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 26CCCh. 12.13 - Prob. 9LTSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 27PTSCh. 12.13 - Prob. 28ATSCh. 12 - Prob. 29PPCh. 12 - Prob. 30PPCh. 12 - Prob. 31PPCh. 12 - Prob. 32PPCh. 12 - Prob. 33PPCh. 12 - Prob. 34PPCh. 12 - Prob. 35PPCh. 12 - Prob. 36PPCh. 12 - Prob. 37PPCh. 12 - Prob. 38PPCh. 12 - Prob. 39PPCh. 12 - Prob. 40PPCh. 12 - Prob. 41PPCh. 12 - Prob. 42PPCh. 12 - Prob. 43PPCh. 12 - Prob. 44PPCh. 12 - Prob. 45PPCh. 12 - Prob. 46PPCh. 12 - Prob. 47PPCh. 12 - Prob. 48PPCh. 12 - Prob. 49PPCh. 12 - Prob. 50PPCh. 12 - Prob. 51PPCh. 12 - Prob. 52PPCh. 12 - Prob. 53ASPCh. 12 - Prob. 54ASPCh. 12 - Prob. 55ASPCh. 12 - Prob. 62IPCh. 12 - Prob. 64IPCh. 12 - Prob. 65IPCh. 12 - Prob. 66IPCh. 12 - Prob. 67IPCh. 12 - Prob. 68IPCh. 12 - Prob. 69IPCh. 12 - Prob. 74IP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. O ✓ No additional Hs to color in top molecule ง No additional Hs to color in bottom…arrow_forwardin the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstantarrow_forwardtrue or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forward
- in the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forwardtrue or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forward
- I2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward
- 2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Coenzymes and cofactors; Author: CH15 SWAYAM Prabha IIT Madras;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bubY2Nm7hVM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Aromaticity and Huckel's Rule; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-BguH4_WBQ;License: Standard Youtube License