
a)
Case summary:
Person X is graduated from large university. He desired to become an entrepreneur. After death of his grandfather he got a business worth of $1million. Then he decided to buy minimum one franchise in the area of fast foods.an issue behind is that he will sell off investment after 3 years and go on to something else.
Person X has two alternatives franchise L and franchise S. Franchise L providing breakfast and lunch while franchise S is providing only dinner. Person X made evaluation of each franchise and find out that both have characteristics of risk and needs
Here are the net cash flows (in thousand $)
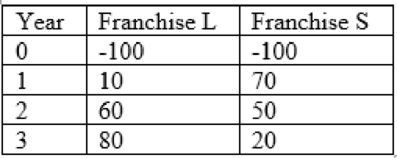
To determine: The definition of
b)
To determine: The relationship between IRR and YTM and IRR if equal
c)
To determine: The logic behind the IRR method and the franchises must be accepted if they are independent and equally exclusive.
d)
To determine: Whether IRR changes with respect to change in cost of capital.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 12 Solutions
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
- Which of the following would be expected to hold its value best during a time of inflation? A certificate of deposit. A corporate bond. A house.arrow_forwardWhat is a budget? A spending plan showing sources and uses of income. A limit on spending that cannot be exceeded. The amount of money that a credit card will let youarrow_forwardThe Pan American Bottling Co. is considering the purchase of a new machine that would increase the speed of bottling and save money. The net cost of this machine is $60,000. The annual cash flows have the following projections: Year 1 ........... 2 ........... 3 ........... 4 ........... 5 ........... Cash Flow $23,000 26,000 29,000 15,000 8,000 a. If the cost of capital is 13 percent, what is the net present value of selecting a new machine? I need to see the work. I can't use Excel to solve the problem. Excel doesn't help me solve Part a.arrow_forward
- Pat and Chris have identical interest-bearing bank accounts that pay them $15 interest per year. Pat leaves the $15 in the account each year, while Chris takes the $15 home to a jar and never spends any of it. After five years, who has more money? Pat. Chris. They both have the same amount. Don’t knowarrow_forwardAssume a firm has earnings before depreciation and taxes of $200,000 and no depreciation. It is in a 25 percent tax bracket. a. Compute its cash flow using the following format: Earnings before depreciation and taxes _____Depreciation _____Earnings before taxes _____Taxes @ 25% _____Earnings after taxes _____Depreciation _____Cash Flow _____ b. Compute the cash flow for the company if depreciation is $200,000. Earnings before depreciation and taxes _____Depreciation _____Earnings before taxes _____Taxes @ 25% _____Earnings after taxes _____Depreciation _____Cash Flow _____ c. How large a cash flow benefit did the depreciation provide?arrow_forwardAssume a $40,000 investment and the following cash flows for two alternatives. Year Investment X Investment Y 1 $6,000 $15,000 2 8,000 20,000 3 9,000 10,000 4 17,000 — 5 20,000 — Which of the alternatives would you select under the payback method?arrow_forward
- The Short-Line Railroad is considering a $140,000 investment in either of two companies. The cashflows are as follows:Year Electric Co. Water Works1.................. $85,000 $30,0002.................. 25,000 25,0003.................. 30,000 85,0004–10............ 10,000 10,000a. Using the payback method, what will the decision be?b. Using the Net Present Value method, which is the better project? The discount rate is 10%.arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance explain its important?arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? can you explain more?arrow_forward
- General accounting problem.arrow_forwardWhat do you know about corporate finance? tell me about thisarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the primary function of insurance? Making risk disappear. Pooling and sharing risk among the insured. Making someone else pay for an accident or loss. Don’t know.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning





