
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 12, Problem 46P
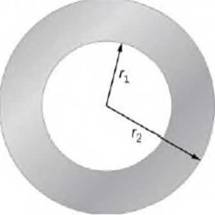
The accompanying figure shows a cross-section of a long, hollow, cylindrical conductor of inner radius r1= 3.0 cm and outer radius r2= 5.0 cm. A 50-A
current distributed uniformly over the cross-section flows into the page. Calculate the magnetic field at r = 2.0 cm. r = 4.0 cm. and r = 6.0 cm.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart law
Chapter 12 Solutions
University Physics Volume 2
Ch. 12 - Check Your Understanding Using Example 12.1, at...Ch. 12 - Check Your Understanding The wire loop forms a...Ch. 12 - 12.3 Check Your Understanding Using Example 12.3,...Ch. 12 - 12.4 Check Your Understanding Two wires, both...Ch. 12 - Check Your Understanding Using Example 12.5, at...Ch. 12 - Check Your Understanding Consider using Ampere’s...Ch. 12 - 12.7 Check Your Understanding What is the ratio of...Ch. 12 - Check your Understanding Repeat the calculations...Ch. 12 - For calculating magnetic fields, what are the...Ch. 12 - Describe the magnetic field due to the current in...
Ch. 12 - How can you decide if a wire is infinite?Ch. 12 - Identical currents are carried in two circular...Ch. 12 - How would you orient two long, straight, current...Ch. 12 - Compare and contrast the electric field of an...Ch. 12 - Is B constant in magnitude for points that lie on...Ch. 12 - Is the magnetic field of a current loop uniform?Ch. 12 - What happens to the length of a suspended spring...Ch. 12 - Two concentric circular wines with different...Ch. 12 - Is Ampere’s law valid for all closed paths? Why...Ch. 12 - Is the magnetic field inside a toroid completely...Ch. 12 - Explain why B=0 inside a long, hollow copper pipe...Ch. 12 - A diamagnetic material is brought dose to a...Ch. 12 - If you cut a bar magnet into two pieces, will you...Ch. 12 - A 10-A current flows through the wire shown. What...Ch. 12 - Ten amps flow through a square loop where each...Ch. 12 - What is the magnetic field at P due to the current...Ch. 12 - The accompanying figure shows a current loop...Ch. 12 - Find the magnetic field at the center C of the...Ch. 12 - Two long wires, one of which has a semicircular...Ch. 12 - A typical currant in a lightning bolt is 104 A....Ch. 12 - The magnitude of the magnetic field 50 cm from a...Ch. 12 - A transmission line strung 7.0 m above the ground...Ch. 12 - A long, straight, horizontal wire carries a...Ch. 12 - The two long, parallel wires shown in the...Ch. 12 - The accompanying figure shows two long, straight,...Ch. 12 - Repeat the calculations of the preceding problem...Ch. 12 - Consider the area between the wires of the...Ch. 12 - Two long, straight wires are parallel and 25 cm...Ch. 12 - Two long, straight wires are parallel and 10 cm...Ch. 12 - Two long, parallel wires are hung by cords of...Ch. 12 - A circuit with current I has two long parallel...Ch. 12 - The infinite, straight wire shown in the...Ch. 12 - When the current through a circular loop is 6.0 A,...Ch. 12 - How many turns must be wound on a flat, circular...Ch. 12 - A flat, circular loop has 20 turns. The radius of...Ch. 12 - A circular loop of radius R carries a current I....Ch. 12 - Two flat, circular coils, each with a radius R and...Ch. 12 - For the coils in the preceding problem, what is...Ch. 12 - A current 1 flows around the rectangular loop...Ch. 12 - Evaluate BdI for each of the cases shown in the...Ch. 12 - The coil whose lengthwise cross section is shown...Ch. 12 - A superconducting wire of diameter 0.25 cm carries...Ch. 12 - A long, straight wire of radius R caries a current...Ch. 12 - The accompanying figure shows a cross-section of a...Ch. 12 - A long, solid, cylindrical conductor of radius 3.0...Ch. 12 - A portion of a long, cylindrical coaxial cable is...Ch. 12 - A solenoid is wound with 2000 turns pet meter....Ch. 12 - A solenoid has 12 turns per centimeter. What...Ch. 12 - If a current is 2.0 A, bow many turns per...Ch. 12 - A solenoid is 40 cm long, has a diameter of 3.0...Ch. 12 - Determine the magnetic field on the central axis...Ch. 12 - By how much is the approximation B=0nI in error at...Ch. 12 - A solenoid with 25 turns per centimeter carries a...Ch. 12 - A toroid has 250 trims of wire and carries a...Ch. 12 - A toroid with a square cross section 3.0cm3.0cm...Ch. 12 - The magnetic field in the core of an air-filled...Ch. 12 - A solenoid has a ferromagnetic core, n = 1000...Ch. 12 - A 20-A current flows through a solenoid with 2000...Ch. 12 - The magnetic dipole moment of the iron atom is...Ch. 12 - Suppose you wish to produce 1.2-T magnetic field...Ch. 12 - A current of 1.5 A flows through the windings of a...Ch. 12 - A solenoid with an iron core is 25 cm long and is...Ch. 12 - Three long, straight, parallel wires, all carrying...Ch. 12 - A current I flows around a wire bent into the...Ch. 12 - The accompanying figure shows a long, straight...Ch. 12 - Current flows along a thin, infinite sheet as...Ch. 12 - (a) Use the result of the previous problem to...Ch. 12 - We often assume that the magnetic field is uniform...Ch. 12 - How is the percentage change in the strength of...Ch. 12 - Show that the expression for the magnetic field of...Ch. 12 - A toroid with an inner radius of 20 cm and an...Ch. 12 - A wire element has dI,IdI=JAdl=Jdv , where A and...Ch. 12 - A reasonably uniform magnetic field over a limited...Ch. 12 - A charge of 4.0C .s distributed uniformly around a...Ch. 12 - A thin, nonconducting disk of radius R is free to...Ch. 12 - Consider the disk in the previous problem....Ch. 12 - Consider the axial magnetic field...Ch. 12 - The current density in the long, cylindrical wire...Ch. 12 - A long, straight, cylindrical conductor contains a...Ch. 12 - Between the two ends of a horseshoe magnet the...Ch. 12 - Show that the magnetic field of a thin wire and...Ch. 12 - An Ampere loop is chosen as shown by dashed lines...Ch. 12 - , A ray long, thick, cylindrical wire of radius R...Ch. 12 - A very long, cylindrical wire of radius a has a...Ch. 12 - Magnetic field inside a torus. Consider a torus of...Ch. 12 - Two long coaxial copper tubes, each of length L,...Ch. 12 - The accompanying figure shows a flat, infinitely...Ch. 12 - A hypothetical current flowing in the z-direction...Ch. 12 - A nonconducting hard rubber circular disk of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is meant by high-throughput in culturing microorganisms? How has it benefited microbiology?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Two stars that are in the same constel...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
In the light reactions, what is the initial electron donor? Where do the electrons finally end up?
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
[14.110] The following mechanism has been proposed for the gas-phase reaction of chloroform (CHCI3) and chlorin...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Write an equation that uses the products of photosynthesis as reactants and the reactants of photosynthesis as ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forward
- Describe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward
- 3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forward
- When violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY