
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.
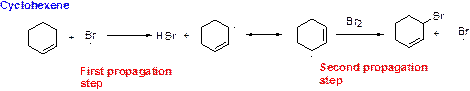
Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid are used, it leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reacts with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions Manual, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
- If we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward
- + Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward+ Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset H3C H H C CH3 CH-CH3 1-3-methylpent ene trans- cis- 5-6-3-1-2-4- tert- tri sec- di cyclo iso but pent hex meth prop eth yl ane ene yne ☑arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





