
Concept explainers
In the 1920s, Barbara McClintock, later a Nobel laureate for her discovery of transposable elements, examined the behavior of chromosomes in wheat cells that had been subjected to X-rays. She noticed that the X-rays produced chromosomal breaks during G1 phase, and that after subsequent chromosome replication in S phase, the broken ends of the two sister chromatids could join together to make a fusion chromosome larger than the original. Even later, during mitotic metaphase and early in mitotic anaphase, the joined sister chromatids would form an unusual bridge structure in which chromatin was stretched between the two spindle poles and could then eventually break. She called this phenomenon the breakage-fusion-bridge cycle. Each of photographs (a) and (b) that follow shows a cell in early mitotic anaphase that has two such chromatin bridges.
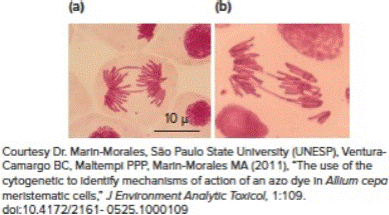
| a. | What ensures that the ends of normal chromosomes do not fuse together as do the ends of the sister chromatids after breakage? |
| b. | The following figure shows a chromosome with genes A–G; the arrow indicates the location of X-ray induced breakage. Draw the resulting bridge (that is, the large fused chromosome) as it would be seen in mitotic anaphase, and label all the genes and important chromosomal structures the bridge contains. Use arrows to show the forces exerted by the spindle apparatus on this bridge. 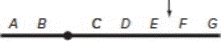 |
| c. | If the sister chromatids fuse, why must the fusion chromosome behave as a bridge during mitosis? [Think about the forces pulling on the bridge described in your answer to part (b).] |
| d. | What is likely to happen to the bridge during mitotic anaphase? What then is likely to happen in the two daughter cells produced by the mitosis just described, and why? (Hint: McClintock’s name for this phenomenon implies it is a cycle.) |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
GENETICS(LL)-W/CONNECT >CUSTOM<
- Please answer the following chart so I can understand how to do it.arrow_forwardDigoxin: Intravenous Bolus - Two Compartment Model Drug Digoxin Route: IV Bolus Dose: 0.750 mg Plasma Concentration Time Profile Beta Alpha Time (hrs) Conc (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN 0.00 #NUM! #NUM! #NUM! 0.10 12.290 2.509 #NUM! #NUMI 0.60 6.975 1.942 #NUM! #NUMI 1.00 4.649 1.537 #NUM! #NUMI 2.00 2.201 0.789 #NUM! #NUM! 3.00 1.536 0.429 #NUM! #NUM! 4.00 1.342 0.294 #NUM! #NUM! 5.00 1.273 0.241 #NUM! #NUMI 6.00 1.238 0.213 #NUM! #NUM! 7.00 1.212 0.192 #NUM! #NUM! 8.00 1.188 0.172 #NUMI #NUM! 9.00 1.165 0.153 #NUM! #NUMI 10.00 1.143 0.134 #NUMI #NUM! 11.00 1.122 0.115 #NUM! 12.00 1.101 0.096 #NUMI 13.00 1.080 0.077 #NUMI 16.00 1.020 0.020 #NUMI 24.00 0.876 -0.132 #NUMI Pharmacokinetic Parameters Parameter Value Alpha B Beta Units ng/ml hr-1 ng/ml hr-1 CO ng/ml H.C AUC ng x hr/ml Vc Vbeta Vss C L/hr TK (alpha) hr TX (beta) days 5+ F3 F4 F5 0+ F6 F7 % 6 95 14 #3 29 & t F8 F9 FW EWarrow_forwardLinuron, a derivative of urea, is used as an herbicide. Linuron serum levels were measured in 4Kg rabbits following a bolus IV injection of 10mg/kg. Time (minutes) Serum Linuron Levels (ug/ml) following IV dose 10 15.48 20 8.60 30 5.90 45 3.78 60 2.42 90 1.49 120 0.93 180 0.60 240 0.41 300 0.29 360 0.22 Analyze this data and perform the necessary calculations to determine the following pharmacokinetic parameters from the IV data: (5 points per parameter, 24 parameters/variables ■ 120 points possible). You do NOT need to submit graphs or data tables. Give the terminal regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the residual regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line:arrow_forward
- 3. In the tomato, red fruit (O+) is dominant over orange fruit (0), and yellow flowers (W+) are dominant over white flowers (w). A cross was made between true-breeding plants with red fruit and yellow flowers, and plants with orange fruit and white flowers. The F₁ plants were then crossed to plants with orange fruit and white flowers, which produced the following results: a. b. 333 red fruit, yellow flowers 64 red fruit, white flowers 58 orange fruit, yellow flowers 350 orange fruit, white flowers Conduct a chi-square analysis to demonstrate that these two genes DO NOT assort independently. Make sure to interpret the P value obtained from your chi-square test. Calculate and provide the map distance (in map units) between the two genes.arrow_forwardName: Date: Investigation: Is a dog more closely related to a coyote or a wolf? Gray Wolf Species Name: Canis lupus Color: Light gray to black Size: 80-120 pounds, 2.5 feet tall Appearance: broad snout, round ears, long tail Coyote Species Name: Canis latrans Color: Light gray to brown Size: 20-50 pounds, 1.5 feet tall Appearance: narrow snout, pointed ears, long tail Dog, Alaskan Malamute Species Name: Canis lupus familiaris Color: Gray and white or brown and white Size: 70-80 pounds, 2 feet tall Appearance: broad snout, round ears, long tail 1. Examine the images and descriptions above. Underline any similarities between the dog and the wolf. Place a star next to any coyote traits that are similar to the dog. 2. Based on appearance alone, which do you think is the most closely related to a dog? www.biologycorner.comarrow_forwardyu yeuwyuyuierydtgcygucygzycghjcygyugfyudguygcywgduycgyudgs ygarrow_forward
- According to a recent study, 1 out of 50,000 people will be diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis can be caused by a mutant form of the CFTR gene (dominant gene symbol is F and mutant is f). A. Using the rate of incidence above, what is the frequency of carriers of the cystic fibrosis allele for CFTR in the US? (3 pts) B. In a clinical study, 400 people from the population mentioned in (A.) were genotyped for BRCA1 Listed below are the results. Are these results in Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium? Use Chi Square to show whether or not they are. (3 pts) # of women BRCA1 genotype BB 390 Bb bb 12pt v 10 0 V Paragraph B IUA BIUA > V T² v <arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich? _______ kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich exactl ______kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forward
- In humans, red-green color blindness is recessive and X-linked, whereas albinism is recessive and autosomal. What types of children can be produced as the result of marriage between two homozygous parents, a normal-vision albino woman and a color-blind, normal male?arrow_forwardIn Drosophila, an X linked recessive mutation, scalloped (sd), causes irregular wing margins. Diagram the F1 and F2 results if a (a) scalloped female is crossed with a normal male; (b) a scalloped male is crossed with a normal female (assume the female is homozygous). Compare these results to what you would find if the trait was not sex linked.arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich exactl ______kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





