
Concept explainers
Joe Henry’s machine shop uses 2,500 brackets during the course of a year. These brackets are purchased from a supplier 90 miles away. The following information a known about the brackets:
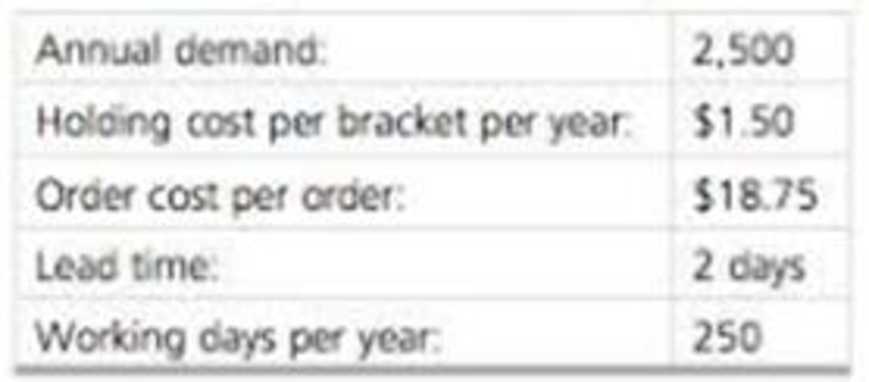
a) Given the above information, what would be the economic order quantity (EOQ)?
b) Given the EOQ, what would be the average inventory? What would be the annual inventory holding cost?
c) Given the EOQ, how many orders would be made each year? What would be the annual order cost?
d) Given the EOQ, what is the total annual cost of managing the inventory?
e) What is the time between orders?
f) What is the reorder point (ROP)?
a)
To calculate: The economic order quantity (EOQ).
Introduction:
Economic order quantity (EOQ):
EOQ is the quantity of units a company must add to its inventory so as to minimize the total inventory costs. It will determine the ideal order quantity which will decrease the inventory management costs.
Answer to Problem 15P
The economic order quantity (EOQ) is 250 brackets.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate EOQ:
Calculation of EOQ:
Hence, the economic order quantity (EOQ) is 250 brackets.
b)
To calculate: The average inventory and annual holding cost at EOQ.
Answer to Problem 15P
The average inventory is 125 units and the annual holding cost is $187.50.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate average inventory:
Formula to calculate annual holding cost:
Calculation of average inventory:
Hence, the average inventory is 125 units.
Calculation of annual holding cost:
Hence, the annual holding cost is $187.50.
c)
To determine: The optimal number of orders per year and annual ordering cost.
Answer to Problem 15P
The optimal number of orders per year is 10 orders and annual ordering cost is $187.50.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate optimal number of orders:
Formula to calculate annual order cost:
Calculation of optimal number of orders:
Hence, the optimal number of orders per year is 10 orders.
Calculation of annual ordering cost:
Hence, the annual ordering cost is $187.50 and annual ordering cost is $187.50.
d)
To determine: The total annual cost of managing the inventory.
Introduction:
Total cost of inventory:
The total cost involved in ordering and carrying an inventory and the costs associated with the management and handling of associated activities.
Answer to Problem 15P
The total annual cost of managing the inventory is $375 per year.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the total cost of inventory:
Calculation of total cost:
Hence, the total annual cost of managing the inventory is $375 per year
e)
To determine: The time between any two orders.
Introduction:
Optimal number of orders:
The optimal number of orders is the number of orders a firm has to make such that the overall inventory cost is minimized.
Answer to Problem 15P
The time between any two orders is 25days.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate time between any two orders:
Calculation of optimal number of orders:
Hence, the time between any two orders is 25 days.
f)
To calculate: The reorder point.
Introduction:
Reorder point (ROP):
The reorder point is the level of the firm’s inventory which triggers the firm to act and replenish the stock of the particular item. It will be the minimum quantity of the item; the firm must hold in its stock.
Answer to Problem 15P
The reorder point is 20 units.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate reorder point (ROP):
Calculation of reorder point (ROP):
Hence, the reorder point is 20 units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- The deaths are included in the discharges; this includes deaths occurring in less than 48 hours and postoperative deaths. Rehabilitation had 362 discharges, 22 deaths, 1<48 hours, 0 Postoperative. what is the gross death rate for the rehabilitation service?arrow_forwardA copy machine is available 24 hours a day. On a typical day, the machine produces 100 jobs. Each job takes about 3 minutes on the machine, 2 minutes of which is processing time and 1 minute is setup time (logging in, defining the job). About 20 percent of the jobs need to be reworked, in which case the setup time and the processing time have to be repeated. The remainder of the time, the equipment is idle. What is the OEE of the equipment?arrow_forwardHow do you think we can keep updating Toyota's ideas as new technologies come out and what customers want keeps changing?arrow_forward
- Given how TPS has helped change things in so many fields, do you think there are parts of it that might be hard to use in areas that aren’t about making things, like in healthcare or services? If so, why do you think that might be?arrow_forwardDo you feel there is anything positive about rework?arrow_forwardDo you think technology can achieve faster setup times? How would it be implemented in the hospital workforce?arrow_forward
- In your experience or opinion, do you think process changes like organizing workspaces make a bigger difference, or is investing in technology usually the better solution for faster setups?arrow_forwardHave you seen rework done in your business, and what was done to prevent that from occurring again?arrow_forwardResearch a company different than case studies examined and search the internet and find an example of a business that had to rework a process. How was the organization affected to rework a process in order to restore a good flow unit? Did rework hurt a process or improve the organization's operational efficiency? • Note: Include a reference with supportive citations in the discussion reply in your post.arrow_forward
- Setup time is very important in affecting a process and the capacity of a process. How do you reduce setup time? Give examples of reducing setup time. Please Provide a referenecearrow_forwardDo you think TPS was successful? If so, how? Are there other companies that have used TPS? If so, give examples. Please provide a referencearrow_forwardGiven the significant impact on finances, production timelines, and even equipment functionality, as you pointed out, what do you believe is the most effective single strategy a company can implement to significantly reduce the occurrence of rework within their operations?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing




