
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.2, Problem 1.3P
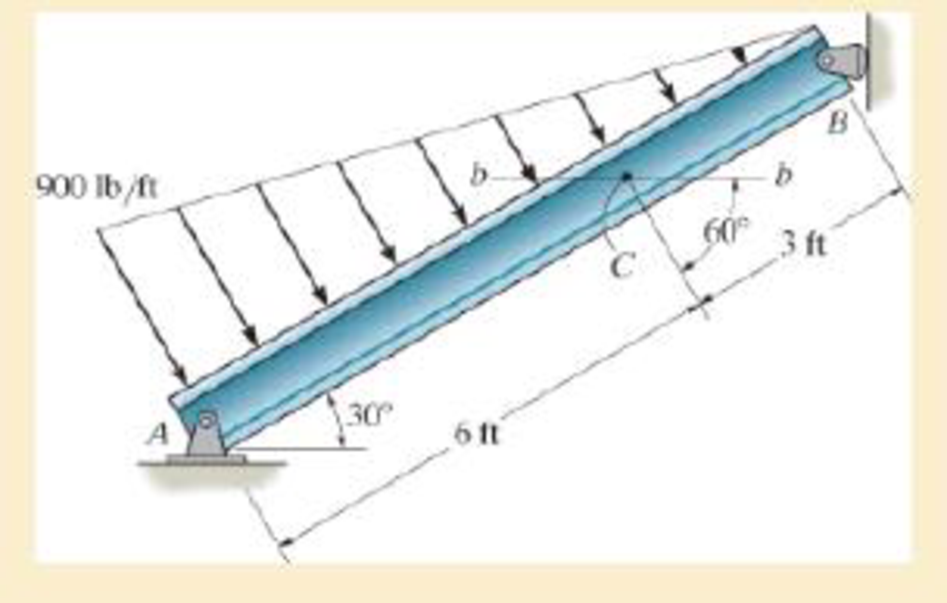
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on section b–b through the centroid C on the beam.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
From thermodynamics
please fill in the table show all work step by step
The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s.
(Figure 1)
Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction.
Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point.
25 ft
B
= 4x
A
20 ft
x
A virtual experiment is designed to determine the effect of friction on the timing and speed
of packages being delivered to a conveyor belt and the normal force applied to the tube.
A package is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped tube of radius R = 5m.
The particle at the bottom will transfer to the conveyor belt, as shown below.
Run the simulations for μ = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and determine the time and speed at
which the package is delivered to the conveyor belt. In addition, determine the maximum
normal force and its location along the path as measured by angle 0.
Submit in hardcopy form:
(0) Free Body Diagram, equations underneath, derivations
(a) Your MATLAB mfile
(b) A table listing the values in 5 columns:
μ, T (time of transfer), V (speed of transfer), 0 (angle of max N), Nmax (max N)
(c) Based on your results, explain in one sentence what you think will happen to the
package if the friction is increased even further, e.g. μ = 0.8.
NOTE: The ODE is…
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 1.2 - In each case, explain how to find the resultant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The boom DF of the jib crane and the column DE...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The hand crank that is used in a press has the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - In each case, determine the largest internal shear...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest internal normal force in the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the internal normal force at section A...Ch. 1.5 - The lever is held to the fixed shaft using the pin...Ch. 1.5 - The single-V butt joint transmits the force of 5...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - The supporting wheel on a scaffold is held in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A and is...Ch. 1.5 - The small block has a thickness of 0.5 in. If the...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The board is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - If P=5 kN, determine the average shear stress in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads the...Ch. 1.5 - The column is made of concrete having a density of...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - If P = 15 kN, determine the average shear stress...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - The two steel members are joined together using a...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The two members used in the construction of an...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Rods AB and BC have diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm,...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the greatest constant angular velocity ...Ch. 1.5 - The radius of the pedestal is defined by r =...Ch. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - The tension member is fastened together using two...Ch. 1.7 - The steel swivel bushing in the elevator control...Ch. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the size of square bearing plates A and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - The steel pipe is supported on the circular base...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods support the vertical force...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and AC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required minimum thickness t of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 1.7 - The compound wooden beam is connected together by...Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The rods AB and CD are made of steel. Determine...Ch. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Using your text editor, enter (that is, type in) the C++ program shown in Display 1.8. Be certain to type the f...
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
The ____________ is always transparent.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Patm = 1 bar Piston m = 50 kg 5 g of Air T₁ = 600 K P₁ = 3 bar Stops A 9.75 x 10-3 m² FIGURE P3.88arrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Harrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forward
- Assume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forwardPlease solve 13 * √(2675.16)² + (63.72 + 2255,03)² = 175x106 can you explain the process for getting d seperate thank youarrow_forwardIf the 300-kg drum has a center of mass at point G, determine the horizontal and vertical components of force acting at pin A and the reactions on the smooth pads C and D. The grip at B on member DAB resists both horizontal and vertical components of force at the rim of the drum. P 60 mm; 60 mm: 600 mm A E 30° B C 390 mm 100 mm D Garrow_forward
- The design of the gear-and-shaft system shown requires that steel shafts of the same diameter be used for both AB and CD. It is further required that the angle D through which end D of shaft CD rotates not exceed 1.5°. Knowing that G = 77.2 GPa, determine the required diameter of the shafts. 40 mm 400 mm 100 mm 600 mm T-1000 N-m Darrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hzarrow_forward13.44 The end of a cylindrical liquid cryogenic propellant tank in free space is to be protected from external (solar) radiation by placing a thin metallic shield in front of the tank. Assume the view factor Fts between the tank and the shield is unity; all surfaces are diffuse and gray, and the surroundings are at 0 K. Tank T₁ Shield, T T₁ = 100 K E1 Solar irradiation Gs ε₁ = ε₂ = 0.05 ε₁ = 0.10 Gs = 1250 W/m² E2 Find the temperature of the shield T, and the heat flux (W/m²) to the end of the tank.arrow_forward
- question 664 thank youarrow_forward13.38 Consider the attic of a home located in a hot climate. The floor of the attic is characterized by a width of L₁ = 8 m while the roof makes an angle of 0 = 30° from the horizontal direction, as shown in the schematic. The homeowner wishes to reduce the heat load to the home by adhering bright aluminum foil (ε = 0.07) onto the surfaces of the attic space. Prior to installation of the foil, the surfaces are of emissivity & = 0.90. Attic A2, 82, T2 0 = 30° A1, E1, T₁ 土 L₁ = 8 m (a) Consider installation on the bottom of the attic roof only. Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer after to before the installation of the foil. (b) Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer after to before installation if the foil is installed only on the top of the attic floor. (c) Determine the ratio of the radiation heat transfer if the foil is installed on both the roof bottom and the floor top.arrow_forward13.1 Determine F2 and F2 for the following configura- tions using the reciprocity theorem and other basic shape factor relations. Do not use tables or charts. (a) Small sphere of area A, under a concentric hemi- sphere of area A₂ = 3A₁ A₂ A1 (a) (b) Long duct. Also, what is F₁₂? A₂ Αν (b) (c) Long inclined plates (point B is directly above the center of A₁) B 100 mm A₂ - 220 mm (c) (d) Long cylinder lying on infinite plane + A₁ Az (d) (e) Hemisphere-disk arrangement -A₂, hemisphere, diameter D A₂ A₁, disk, diameter D/2 (e) (f) Long, open channel 1 m AA₂ 2 m (f) (g) Long cylinders with A₁ = 4A₁. Also, what is F₁₂? -D₁ A1 -A₂ -D2 (e) (h) Long, square rod in a long cylinder. Also, what is F22? w=D/5 18 A₁ -A2 (h) -Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY