
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.5, Problem 1.3PP
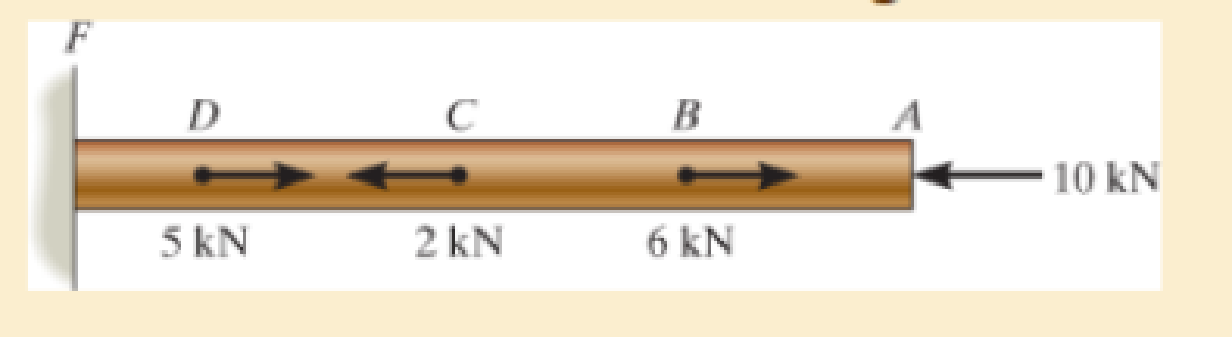
Determine the largest internal normal force in the bar.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A viscoelastic column is made of a material with a creep compliance of
D(t)= 0.75+0.5log10t+0.18(log10t)^2 GPA^-1
for t in s. If a constant compressive stress of σ0 = –100 MPa is applied at t = 0, how long will it take (= t1/2) for the height of the column to decrease to ½ its original value? Note: You will obtain multiple answers for this problem! One makes sense physically and one does not.
A group of 23 power transistors, dissipating 2 W each, are to be cooled by attaching them to a black-anodized square aluminum plate and mounting the plate on the wall of a room at 30°C. The emissivity of the transistor and the plate surfaces is 0.9. Assuming the heat transfer from the back side of the plate to be negligible and the temperature of the surrounding surfaces to be the same as the air temperature of the room, determine the length of the square plate if the average surface temperature of the plate is not to exceed 50°C. Start the iteration process with an initial guess of the size of the plate as 43 cm.
The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts + T)/2 = (50 + 30)/2 = 40°C are k = 0.02662 W/m·°C, ν = 1.702 × 10–5 m2 /s, Pr = 0.7255, and β = 0.003195 K–1.
Multiple Choice
0.473 m
0.284 m
0.513 m
0.671 m
A 40-cm-diameter, 127-cm-high cylindrical hot water tank is located in the bathroom of a house maintained at 20°C. The surface
temperature of the tank is measured to be 44°C and its emissivity is 0.4. Taking the surrounding surface temperature to be also 20°C,
determine the rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection and radiation.
The properties of air at 32°C are k=0.02603 W/m-K, v=1.627 x 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7276, and ẞ = 0.003279 K-1
The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection is
The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by radiation is
W.
W.
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 1.2 - In each case, explain how to find the resultant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The boom DF of the jib crane and the column DE...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The hand crank that is used in a press has the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - In each case, determine the largest internal shear...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest internal normal force in the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the internal normal force at section A...Ch. 1.5 - The lever is held to the fixed shaft using the pin...Ch. 1.5 - The single-V butt joint transmits the force of 5...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - The supporting wheel on a scaffold is held in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A and is...Ch. 1.5 - The small block has a thickness of 0.5 in. If the...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The board is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - If P=5 kN, determine the average shear stress in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads the...Ch. 1.5 - The column is made of concrete having a density of...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - If P = 15 kN, determine the average shear stress...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - The two steel members are joined together using a...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The two members used in the construction of an...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Rods AB and BC have diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm,...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the greatest constant angular velocity ...Ch. 1.5 - The radius of the pedestal is defined by r =...Ch. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - The tension member is fastened together using two...Ch. 1.7 - The steel swivel bushing in the elevator control...Ch. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the size of square bearing plates A and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - The steel pipe is supported on the circular base...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods support the vertical force...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and AC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required minimum thickness t of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 1.7 - The compound wooden beam is connected together by...Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The rods AB and CD are made of steel. Determine...Ch. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 2.5-m-long thin vertical plate is subjected to uniform heat flux on one side, while the other side is exposed to cool air at 5°C. The plate surface has an emissivity of 0.73, and its midpoint temperature is 55°C. Determine the heat flux subjected on the plate surface. Uniform heat flux -Plate, € = 0.73 Cool air 5°C 7 TSUIT Given: The properties of water at Tf,c= 30°C. k=0.02588 W/m.K, v=1.608 x 10-5 m²/s Pr = 0.7282 The heat flux subjected on the plate surface is W/m²arrow_forwardHot water is flowing at an average velocity of 5.82 ft/s through a cast iron pipe (k=30 Btu/h-ft-°F) whose inner and outer diameters are 1.0 in and 1.2 in, respectively. The pipe passes through a 50-ft-long section of a basement whose temperature is 60°F. The emissivity of the outer surface of the pipe is 0.5, and the walls of the basement are also at about 60°F. If the inlet temperature of the water is 150°F and the heat transfer coefficient on the inner surface of the pipe is 30 Btu/h-ft².°F, determine the temperature drop of water as it passes through the basement. Evaluate air properties at a film temperature of 105°C and 1 atm pressure. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts+ T∞)/2 = (150+60)/2 = 105°F are k=0.01541 Btu/h-ft-°F. v=0.1838 × 10-3 ft2/s, Pr = 0.7253, and ẞ = 0.00177R-1arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forward
- hand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forward! Required information Consider a flat-plate solar collector placed horizontally on the flat roof of a house. The collector is 1.3 m wide and 2.8 m long, and the average temperature of the exposed surface of the collector is 42°C. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature are k=0.02551 W/m-°C, v = 1.562 × 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7286, and ẞ= 0.003356 K-1 Determine the rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection during a calm day when the ambient air temperature is 8°C. The rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection is W.arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY