
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
For the below compound the chirality centers has to be labeled and number of chiral centers should be determined
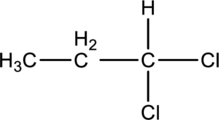
Concept introduction:
Chirality center:
When a carbon atom is bonded to four different groups, then that carbon is named as chiral carbon and it is called as chirality center. Generally, the carbon atom contains tetrahedral valency, therefore it bonded to four atoms or molecules. The chiral center is bonded with four different elements or groups. If the single carbon atom is bonded to two or more identical group or atom, then it is also not considered as chiral carbon. In addition to this, if the carbon atom contains multiple bond then it does not able to bond with four different groups then it is not considered to be as a chirality center.
b.
Interpretation:
For the below compound the chirality centers has to be labeled and number of chiral centers should be determined
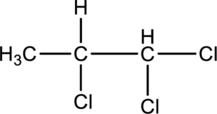
Concept introduction:
Refer to part “a.”.
c.
Interpretation:
For the below compound the chirality centers has to be labeled and number of chiral centers should be determined
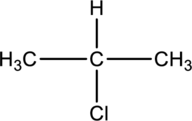
Concept introduction:
Refer to part “a.”.
d.
Interpretation:
For the below compound the chirality centers has to be labeled and number of chiral centers should be determined
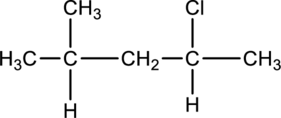
Concept introduction:
Refer to part “a.”.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Principles of General Organic & Biological Chemistry
- Polylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forwardPoly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forward
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- One of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forward
- curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forwardIdentify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forwardH- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


